Buildroot 2023.08 has been published and we're excited to share new images! This release includes our latest 6.1 kernel, as well as support for our new Nitrogen8M Plus SMARC platform!
For the impatient
You can download pre-built Buildroot 2023.08 images from here:
- 20231228-br2023.08-nitrogen8m_qt5_gst1.img.gz for Nitrogen8M SBC & SOM
- 20231228-br2023.08-nitrogen8mm_qt5_gst1.img.gz for Nitrogen8M Mini SBC & SOM
- 20231228-br2023.08-nitrogen8mn_qt5_gst1.img.gz for Nitrogen8M Nano SBC & SOM
- 20231228-br2023.08-nitrogen8mp_qt5_gst1.img.gz for Nitrogen8M Plus SBC & SOM
- 20231228-br2023.08-nitrogen6x_qt5_gst1.img.gz for Nitrogen6X/MAX/SOM/SOMv2/VM/Lite, BD-SL
Update 20231228 changelog:
- Support for Nitrogen8M Mini SMARC.
In order to flash those images you can follow our video on this topic:
Or for those fluent in command lines, you can simply use zcat:
~$ zcat 2023*br2023.08-nitrogen*.img.gz | sudo dd of=/dev/sdX bs=1MWhat's new?
Buildroot 2023.08 release
It would be too long of a list to enumerate all the changes Buildroot went through since the last release. For recent changes, we invite you to check the last release announcement:
We'll focus on the i.MX changes for this release in the next sections.
Ezurio (formerly Boundary Devices) layer
As usual, we provide our own Ezurio (formerly Boundary Devices) external layer:
This includes the following custom configurations
nitrogen8m_qt5_gst1_defconfig:- For i.MX 8MQ based Nitrogen8M, Nitrogen8M SOM
- Qt5 modules
- GStreamer1.0 with all its plugins
- NXP proprietary packages (VPU, GPU, SDMA)
- NXP-based kernel (6.1.y)
- BD-SDMAC WiFi/BT modules support
- LWB5+ Wifi/BT modules support
- Miscellaneous tools (adbd, CAN, I2C, IIO, etc...)
nitrogen8mm_qt5_gst1_defconfig:- For i.MX 8M Mini based Nitrogen8M Mini, Nitrogen8M Mini SOM
- Same set of packages as
nitrogen8m_qt5_gst1_defconfig
nitrogen8mn_qt5_gst1_defconfig:- For i.MX 8M Nano based Nitrogen8M Nano, Nitrogen8M Nano SOM
- Same set of packages as
nitrogen8m_qt5_gst1_defconfig
nitrogen8mp_qt5_gst1_defconfig:- For i.MX 8M Plus based Nitrogen8M Plus SOM
- Same set of packages as
nitrogen8m_qt5_gst1_defconfig
nitrogen6x_qt5_gst1_defconfig:- For BD-SL-i.MX6 (SABRE Lite), Nitrogen6X, Nitrogen6X SOM v2, Nitrogen6 Lite, Nitrogen6 MAX, Nitrogen6 VM
- TiWi-BLE and Murata WiFi/BT modules support
- Same set of packages as
nitrogen8m_qt5_gst1_defconfig
nitrogen6sx_qt5_gst1_defconfig:- For Nitrogen6_SoloX
- Same set of packages as
nitrogen6x_qt5_gst1_defconfig
nitrogen7_gst1_defconfig:- For Nitrogen7
- Same set of packages as
nitrogen6x_qt5_gst1_defconfigminus Qt5
nitrogen6x_qt5_gst1_mainline_defconfig:- For BD-SL-i.MX6 (SABRE Lite), Nitrogen6X, Nitrogen6X SOM v2, Nitrogen6 Lite, Nitrogen6 MAX
- Same set of packages as
nitrogen6x_qt5_gst1_defconfig - Mainline kernel
New features
Buildroot 2022.08 includes the following versions of packages:
- BlueZ5 5.68
- GStreamer 1.22.2
- GStreamer-imx v0.13.1 for i.MX6
- GStreamer-imx v2.2.0 for i.MX8M
- imx-codec 4.3.5
- imx-gpu-viv 6.4.11.p1.2
- imx-vpu-hantro 1.29.0 for i.MX8M
- imx-vpu-hantro-vc 1.9.0 for i.MX8MP
- imx-vpu 5.4.39.3 for i.MX6
- Linux kernel 6.1.y
- qcacld-2.0 LEA-3.1 Wi-Fi driver
- Qt5 5.15.10
- Support for Nitrogen8MP SMARC added
- Wayland 1.22.0
- Weston 12.0.1
There are a few differences between Yocto and Buildroot releases at this stage:
- Buildroot images use standard packages without NXP modifications
- This applies to GStreamer, Weston, libdrm, wayland etc...
- The main drawback is that Weston can't be used with G2D
- The (big) advantage is that it makes the codebase much easier to maintain, being able to use all the latest packages without having to be stuck at an earlier version chosen by NXP
- Open-source gstreamer-imx plugin is used instead of NXP forks
- This allows us to have imx-related changes for GStreamer in 1 package only
Build procedure
Just like our Yocto image, we now use a Docker file to build our images on our Jenkins server so that everyone can use the exact same environment. This ensures reproducible builds without having to think about missing dependencies. If interested in using this approach, we invite you to read the following blog post using the following docker file:
Otherwise you can follow Buildroot documentation to know the host requirements:
Once your development environment is setup properly, you can
- Download the source code. To ease the repo cloning process, we decided to create a manifest to match what is done for Yocto/Android:
~$ sudo apt-get install repo
~$ mkdir ~/br2023.08 && cd br2023.08
~/br2023.08$ repo init -u https://github.com/boundarydevices/buildroot-manifest -b 2023.08.x
~/br2023.08$ repo sync- Create an output folder for your configuration:
~/br2023.08$ make BR2_EXTERNAL=$PWD/buildroot-external-boundary/
-C $PWD/buildroot/ O=$PWD/output nitrogen8mm_qt5_gst1_defconfig
~/br2023.08$ cd output- Build the image
~/br2023.08/output$ make- Your image is now ready!
~/br2023.08/output$ ls -l images/sdcard.img
~/br2023.08/output$ sudo dd if=images/sdcard.img of=/dev/sdX bs=1MTesting the image
As usual, the login for this image is root with no password. The external repository README details many commands that can be tested on the image.
- Once booted up, the Weston desktop should appear automatically, from there you can start a 3D test to ensure GPU acceleration
# cd /usr/share/examples/viv_samples/vdk/
# ./tutorial7 -h 720- You can also check the GStreamer VPU acceleration by decoding the well known Big Buck Bunny video
# wget http://linode.boundarydevices.com/videos/trailer_1080p_h264_mp3.avi -P /root/
# gst-launch-1.0 filesrc location=/root/trailer_1080p_h264_mp3.avi !
decodebin ! waylandsink- If you have our OV5640 5MP MIPI camera, you can check the GStreamer video capture
# gst-launch-1.0 v4l2src device=/dev/video0 ! video/x-raw,width=1280,height=720 !
waylandsink- This build fully supports the Basler daA3840 8MP camera from Basler when using our Nitrogen 8M Plus
# gst-launch-1.0 -v v4l2src device=/dev/video2 ! waylandsink
...
[ 352.348796] wdr3 res: 1920 1080
[ 352.352471] enter isp_mi_start
[ 357.581179] ###### 62.42 fps ######
[ 362.771924] ###### 62.42 fps ######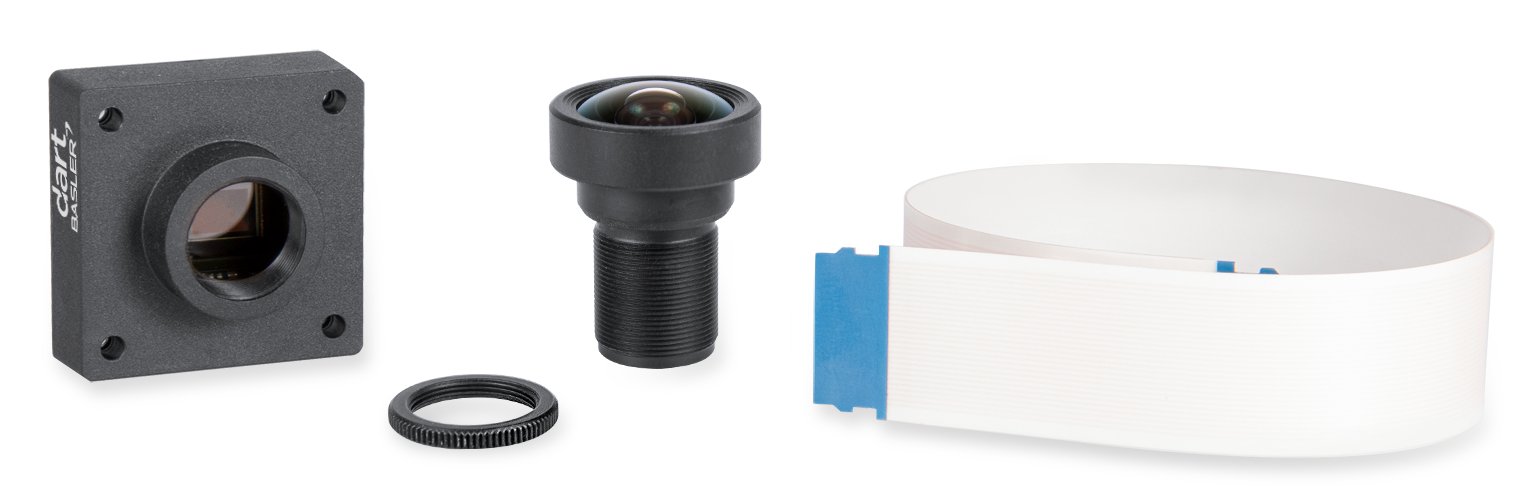
- We now have support for the IMX219 camera using our Nitrogen8M Plus SMARC. We tested using the Arducam imx219
# gst-launch-1.0 -v v4l2src device=/dev/video2 ! waylandsink
- This build also includes qt5 and examples can be run from "/usr/lib/qt/examples"
# cd /usr/lib/qt/examples/
# ls
README network qtestlib svg
bluetooth nfc quick virtualkeyboard
corelib opengl quickcontrols vulkan
dbus positioning quickcontrols2 wayland
examples.pro qml script widgets
gui qmltest sensors xml
location qpa serialbus
multimedia qt3d serialport
multimediawidgets qtconcurrent sql- As for Wi-Fi connectivity, the image embeds the minimum to get you started
# wpa_passphrase MYSSID MYPASSWORD >> /etc/wpa_supplicant.conf
# /etc/init.d/S50wpa-supplicant stop
# sleep 1
# /etc/init.d/S50wpa-supplicant start
# iw wlan0 link
Connected to a4:3e:51:08:54:f6 (on wlan0)
SSID: MYSSID
freq: 5660
RX: 47685 bytes (747 packets)
TX: 2054 bytes (0 packets)
signal: -58 dBm
tx bitrate: 150.0 MBit/s MCS 7 40MHz short GI
# udhcpc -i wlan0
udhcpc: started, v1.31.1
udhcpc: sending discover
udhcpc: sending select for 192.168.1.46
udhcpc: lease of 192.168.1.46 obtained, lease time 86400
deleting routers
adding dns 192.168.1.1
# ping google.com -I wlan0
PING google.com (216.58.198.206): 56 data bytes
64 bytes from 216.58.198.206: seq=0 ttl=116 time=6.971 ms
64 bytes from 216.58.198.206: seq=1 ttl=116 time=13.145 ms
...- Finally, if you want to use Bluetooth connectivity, the procedure goes as follows
# echo 1 > /sys/class/rfkill/rfkill0/state
# hcitool scan
Scanning ...
48:C1:AC:00:D7:DCVoyager PRO+/filters:background_color(white)/2023-01/Nitrogen6-SOM-Transparent.png)
/filters:background_color(white)/2024-10/Nitrogen8M_Mini_SBC-e1550333331743.png)
/filters:background_color(white)/2024-10/Nitrogen 8M Mini SMARC1.267 without wireless.png)
/filters:background_color(white)/2024-10/Nit8M_Mini_SOM_Front.png)
/filters:background_color(white)/2024-09/8MP_SMARC-RENDER-IF573.front.png)
/filters:background_color(white)/2024-12/nitrogen8m-plus-som.png)
/filters:background_color(white)/2024-10/Nitrogen8M_SBC-e1550277453741.png)
/filters:background_color(white)/2023-01/Nitrogen8M_SOM-e1550334029145.png.png)


