Introduction
The Lyra 24S is a secure, high-performance wireless module optimized for the needs of battery and line-powered IoT devices running on Bluetooth networks.
Based on the Series 2 EFR32BG24 SoC, it enables Bluetooth® Low Energy connectivity, delivering exceptional RF performance and energy efficiency, industry-leading Se- cure Vault® technology, and future-proofing capabilities.
The Lyra 24S is a complete System in Package solution offered with robust and fully upgradeable software stacks, global regulatory certifications, advanced development and debugging tools, and documentation that simplifies and minimizes the development cycle of your end-product, helping to accelerate its time-to-market.
Overview
This document describes key hardware aspects of the Lyra 24S. This document is intended to assist device manufacturers and related parties with the integration of this radio into their host devices. Data in this document is drawn from several sources. For full documentation on the Lyra 24S, visit:
https://www.ezurio.com/lyra24-series
This datasheet is subject to change. Please contact Ezurio for further information.
Application Areas
- Smart Home Devices
- Lighting
- Gateways and Digital Assistants
- Building Automation and Security
Features & Benefits
The Lyra 24 device features and benefits are described below.
- Bluetooth Low Energy 5.4
- Bluetooth Mesh connectivity
- Built-in antenna or RF pin
- Up to 10 dBm TX output power (see Maximum Regulatory Certified RF TX Power per Country)
- -97 dBm BLE 1M RX sensitivity
- 32-bit ARM® Cortex®-M33 core running up to 78 MHz
- 1536/256 kB of Flash/RAM memory
- Vault High or Vault Mid security
- Rich set of analog and digital peripherals
- 32 GPIO pins
- -40 to 105 °C
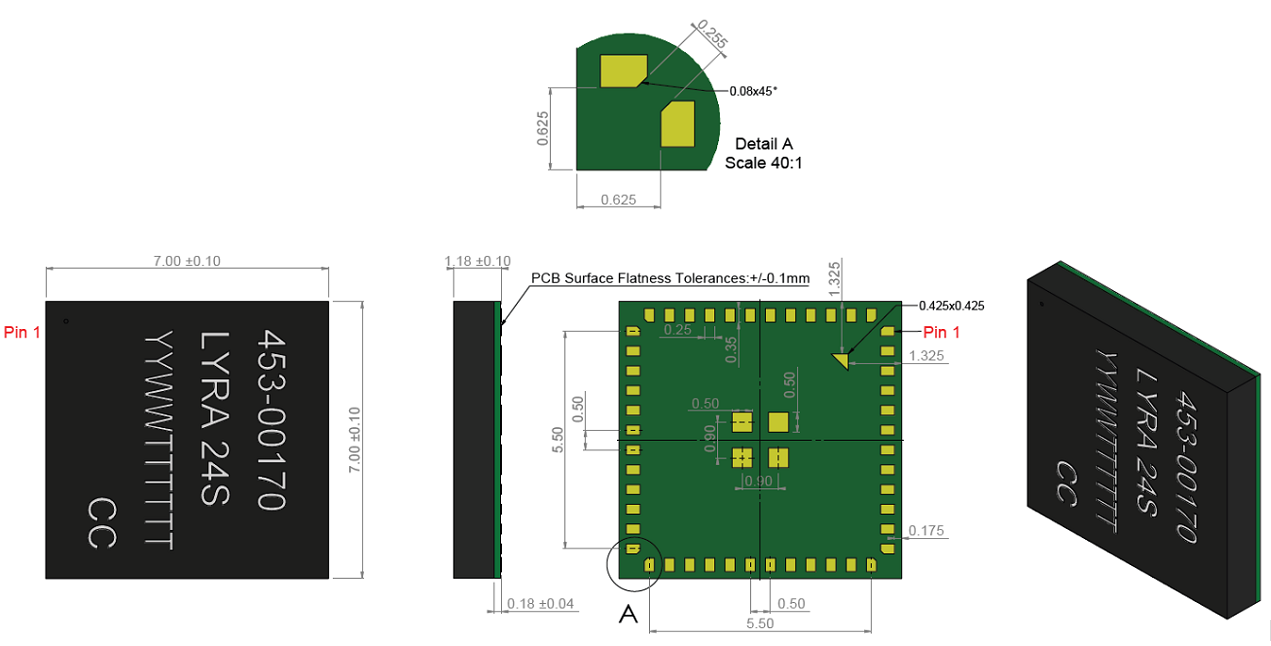
- 7mm x 7mm x 1.18mm
Specification Summary
Processor / SoC / Chipset
| Wireless |
|
Bluetooth
| Standards | Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) 5.4 Bluetooth Mesh |
| Receive Sensitivity |
|
| Peripheral Interface | 32x Multifunction I/O lines |
|---|---|
| UART | 1 × Universal Synchronous/Asynchronous Receiver/Transmitter (USART), supporting UART/SPI/SmartCard (ISO 7816)/IrDA/I2S 2 × Enhanced Universal Synchronous/Asynchronous Receiver/Transmitter (EUSART) supporting UART/SPI/DALI/ IrDA |
| GPIO | Up to 32 General Purpose I/O pins with output state retention and asynchronous interrupts |
| ADC |
|
| ACMP` | 2 × Analog Comparator (ACMP) |
| VDAC | 2 × Digital to Analog Converter (VDAC) |
| DMA | 8 Channel DMA Controller |
| PRS | 16 Channel Peripheral Reflex System (PRS) |
| Timers |
|
| I2C | 2 × I2C interface with SMBus support |
| TEMP | Die temperature sensor with +/- 1.5 °C accuracy after single-point calibration |
| Keypad Scanner | Keypad scanner supporting up to 6x8 matrix (KEYSCAN) |
| RF Oscillator | Low-Frequency RC Oscillator with precision mode to replace 32 kHz sleep crystal (LFRCO) |
Power
| Input Voltage | 1.8 to 3.8 V |
| Current Consumption |
|
Mechanical
| Dimensions | 7 mm x 7 mm x 1.18 mm |
Software
| Security |
|
| Firmware | AT Command Set – fully featured and extensible to suit any developer’s needs.
C Code – Full software development with Silicon Labs SDK and Toolchain
|
Environmental
| Operating Temperature | -40 to +105 °C |
| Lead Free | Lead-free and RoHS Compliant |
Certifications
| Regulatory Compliance |
|
Development
| Development Kit |
|
Warranty
| Warranty Terms | One Year Warranty |
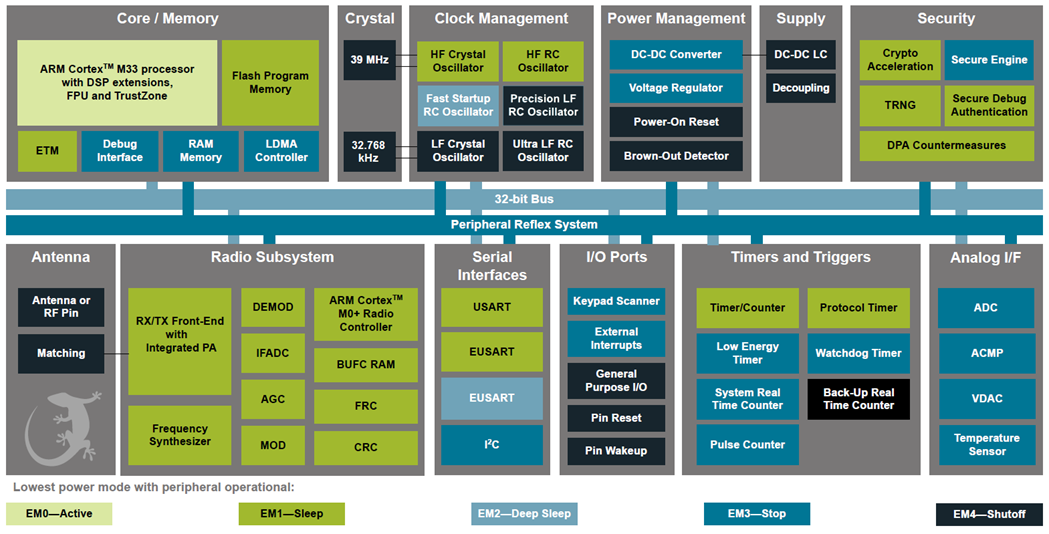
Architecture
Block Diagrams
The Lyra 24S module is a highly integrated, high-performance system in package with all the hardware components needed to enable 2.4 GHz wireless connectivity and support robust networking capabilities via multiple wireless protocols.
Built around the EFR32BG24 Wireless SoC, the Lyra 24S includes a built-in antenna, an RF matching network (optimized for transmit power efficiency), supply decoupling and filtering components, an LC tank for DC-DC conversion, a 39 MHz reference crystal, and an RF shield. Also, it supports the use of an external 32 kHz crystal as a low frequency reference signal via GPIO pins for use cases demanding maximum energy efficiency.
For designs where an external antenna solution may be beneficial, a module variant with a 50 Ω-matched RF pin instead of the built-in antenna is available.
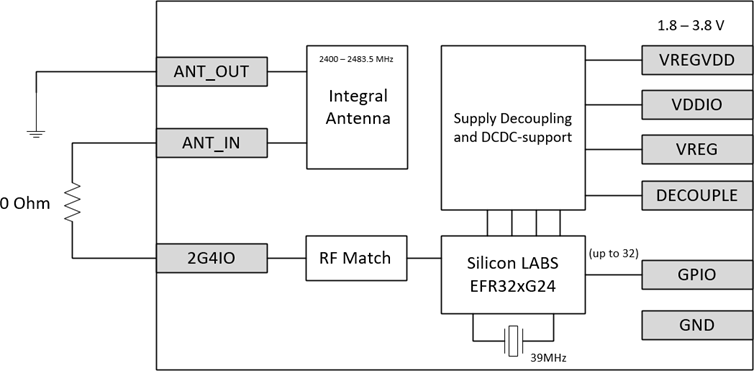
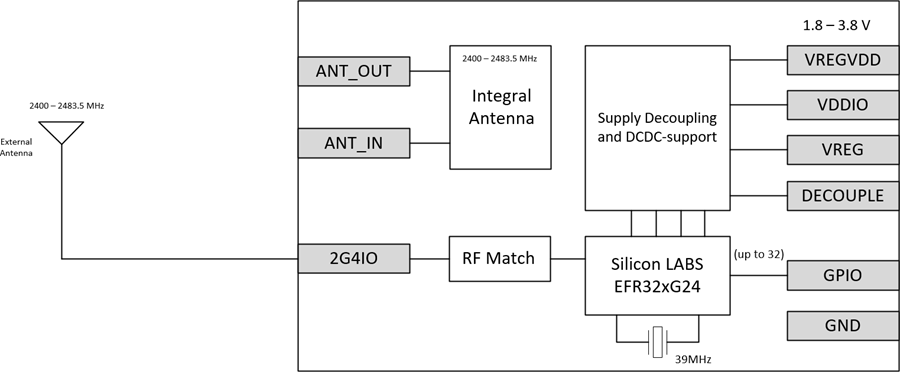
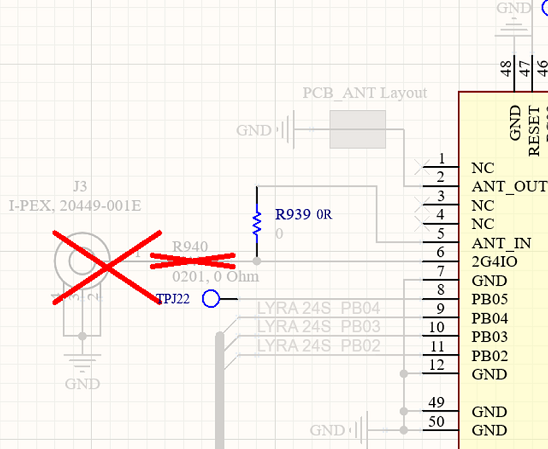
Note: There is only one Module, SIP, LYRA 24S, Integrated Antenna (Silicon Labs EFR32BG24) 453-00170, to create the External Antenna connection requires removal of 0R resistor (as shown in the first diagram above) on customer’s board to allow the external antenna to be connected Lyra 24S pin 3 2G4IO (as shown in the second diagram above). See section Lyra 24S Module 50 Ohms RF Track Design for Connecting External Antenna with the Lyra 24S.
A simplified internal schematic for the Lyra 24S module is shown below.
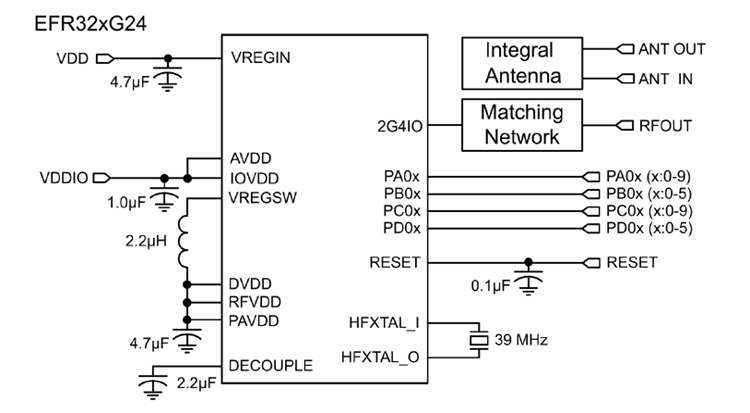
EFR32BG24 SoC
The EFR32BG24 SoC features a 32-bit ARM Cortex M33 core, a 2.4 GHz high-performance radio, 1536 kB of Flash memory, 256 kB of RAM, a dedicated core for security, a rich set of MCU peripherals, and various clock management and serial interfacing options. See the EFR32xG24 Reference Manual for details.
Integrated Antenna
Lyra 24S modules come with two antenna solution variants: a built-in integral ground loop type antenna realized by a PCB trace design, or a 50Ω-matched RF pin to support an external antenna. Typical performance characteristics for the built-in antenna are detailed in the table below. See Antenna Characteristics and External Antenna Integration with the Lyra 24S Module 453-00170 for other relevant details.
| Parameter | Symbol | Test Condition | Min | Typ | Max | Unit |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Antenna frequency range | FRANGE | 2400 | — | 2483.5 | MHz | |
| Antenna Gain | GMAX | Maximum relative to isotropic | — | — | 1.48 | dBi |
| Antenna Efficiency | Efficiency | -2.5 | — | -1.36 | dB | |
| Reference impedance | Z | — | 50 | — | Ω | |
| Dielectric Constant Host Board | DICONST | — | 4.3 | — | ||
| Trace Thickness | TTHICKNESS | — | 47 | — | um | |
| VSWR | VSWR | Maximum | — | — | 2:1 |
Antenna efficiency, gain, and radiation pattern are dependent on the application PCB layout and mechanical design. Antenna specification is based on the assumption that the host board design guidelines in section are followed.
External Antenna
Lyra 24S module can be used with external antennas (certified by Ezurio) and requires a RF 50 Ohm track (Ground Coplanar Waveguide) to be designed to run from Lyra 24S module 2G4IO (pin 6) to an RF antenna connector (IPEX MHF 4) on the host PCB. The 50Ohm RF track design and length MUST be copied as defined in section Lyra 24S Module 50 Ohms RF Track Design for Connecting External Antenna with the Lyra 24S.
The list of supported external antennas (certified by Ezurio) are listed in section External Antenna Integration with the Lyra 24S Module
Power Supply
The Lyra 24S requires a primary supply (VDD) and IO supply (VDDIO) voltage to operate. All necessary decoupling, filtering and DC-DC-related components are included in the module.
General Purpose Input/Output (GPIO)
The Lyra 24S has up to 32 General Purpose Input/Output pins. Each GPIO pin can be individually configured as either an output or input. More advanced configurations including open-drain, open-source, and glitch-filtering can be configured for each individual GPIO pin. The GPIO pins can be overridden by peripheral connections, like SPI communication. Each peripheral connection can be routed to several GPIO pins on the device. The input value of a GPIO pin can be routed through the Peripheral Reflex System to other peripherals. The GPIO subsystem supports asynchronous external pin interrupts.
All of the pins on ports A and port B are EM2 capable. These pins may be used by Low-Energy peripherals in EM2/3 and may also be used as EM2/3 pin wake-ups. Pins on ports C and D are latched/retained in their current state when entering EM2 until EM2 exit upon which internal peripherals could once again drive those pads.
A few GPIOs also have EM4 wake functionality. These pins are listed in Alternate Pin Functions.
Security
Lyra 24S modules support one of two levels in the Security Portfolio offered by Silicon Labs: Secure Vault Mid or Secure Vault High. Lyra 24S modules support Secure Vault High.
Secure Vault is a collection of technologies that deliver state-of-the-art security and upgradability features to protect and future proof IoT devices against costly threats, attacks, and tampering. A dedicated security CPU enables the Secure Vault functions and isolates cryptographic functions and data from the Cortex-M33 core. Lyra 24S support Secure Vault High.
Secure Vault Features
| Feature | Secure Vault Mid | Secure Vault High |
|---|---|---|
| True Random Number Generator (TRNG) | Yes | Yes |
| Secure Boot with Root of Trust and Secure Loader (RTSL) | Yes | Yes |
| Secure Debug with Lock/Unlock | Yes | Yes |
| DPA Countermeasures | Yes | Yes |
| Anti-Tamper | Yes | |
| Secure Attestation | Yes | |
| Secure Key Management | Yes | |
| Symmetric Encryption |
|
|
| Public Key Encryption - ECDSA / ECDH / EdDSA |
|
|
| Key Derivation |
|
|
| Hashes |
|
|
Secure Boot with Root of Trust and Secure Loader (RTSL)
The Secure Boot with RTSL authenticates a chain of trusted firmware that begins from an immutable memory (ROM).
It prevents malware injection, prevents rollback, ensures that only authentic firmware is executed, and protects Over The Air updates. For more information about this feature, see Silicon Labs’ AN1218: Series 2 Secure Boot with RTSL.
Cryptographic Accelerator
The Cryptographic Accelerator is an autonomous hardware accelerator with Differential Power Analysis (DPA) countermeasures to protect keys.
It supports AES encryption and decryption with 128/192/256-bit keys, ChaCha20 encryption, and Elliptic Curve Cryptography (ECC) to support public key operations, and hashes.
Supported block cipher modes of operation for AES include:
- ECB (Electronic Code Book)
- CTR (Counter Mode)
- CBC (Cipher Block Chaining)
- CFB (Cipher Feedback)
- GCM (Galois Counter Mode)
- CCM (Counter with CBC-MAC)
- CBC-MAC (Cipher Block Chaining Message Authentication Code)
- GMAC (Galois Message Authentication Code)
The Cryptographic Accelerator accelerates Elliptical Curve Cryptography and supports the NIST (National Institute of Standards and Technology) recommended curves including P-192, P-256, P-384, and P-521 for ECDH (Elliptic Curve Diffie-Hellman) key derivation, and ECDSA (Elliptic Curve Digital Signature Algorithm) sign and verify operations. Also supported is the non-NIST Curve25519 for ECDH and Ed25519 for EdDSA (Edwards-curve Digital Signature Algorithm) sign and verify operations.
Secure Vault also supports ECJ-PAKE (Elliptic Curve variant of Password Authenticated Key Exchange by Juggling) and PBKDF2 (Password-Based Key Derivation Function 2).
Supported hashes include SHA-1, SHA-2/256/384/512 and Poly1305.
This implementation provides a fast and energy efficient solution to state of the art cryptographic needs.
True Random Number Generator
The True Random Number Generator module is a non-deterministic random number generator that harvests entropy from a thermal energy source. It includes start-up health tests for the entropy source as required by NIST SP800-90B and AIS-31 as well as online health tests required for NIST SP800-90C.
The TRNG is suitable for periodically generating entropy to seed an approved pseudo random number generator.
Secure Debug with Lock/Unlock
For obvious security reasons, it is critical for a product to have its debug interface locked before being released in the field.
In addition, Secure Vault High also provides a secure debug unlock function that allows authenticated access based on public key cryptography. This functionality is particularly useful for supporting failure analysis while maintaining confidentiality of IP and sensitive end-user data.
For more information about this feature, see Silicon Labs’ AN1190: Series 2 Secure Debug.
DPA Countermeasures
The AES and ECC accelerators have Differential Power Analysis (DPA) countermeasures support. This makes it very expensive from a time and effort standpoint to use DPA to recover secret keys.
Secure Key Management with PUF
Key material in Secure Vault High products is protected by "key wrapping" with a standardized symmetric encryption mechanism. This method has the advantage of protecting a virtually unlimited number of keys, limited only by the storage that is accessible by the Cortex-M33, which includes off-chip storage as well. The symmetric key used for this wrapping and unwrapping must be highly secure because it can expose all other key materials in the system. The Secure Vault Key Management system uses a Physically Unclonable Function (PUF) to generate a persistent device-unique seed key on power up to dynamically generate this critical wrapping/unwrapping key which is only visible to the AES encryption engine and is not retained when the device loses power.
Anti-Tamper
Secure Vault High devices provide internal tamper protection which monitors parameters such as voltage, temperature, and electro- magnetic pulses as well as detecting tamper of the security sub-system itself. Additionally, 8 external configurable tamper pins support external tamper sources, such as enclosure tamper switches.
For each tamper event, the user is able to select the severity of the tamper response ranging from an interrupt, to a reset, to destroying the PUF reconstruction data which will make all protected key materials un-recoverable and effectively render the device inoperable. The tamper system also has an internal resettable event counter with programmable trigger threshold and refresh periods to mitigate false positive tamper events.
For more information about this feature, see Silicon Labs’ AN1247: Anti-Tamper Protection Configuration and Use.
Secure Attestation
Secure Vault High products support Secure Attestation, which begins with a secure identity that is created during the Silicon Labs manufacturing process. During device production, each device generates its own public/private keypair and securely stores the wrapped private key into immutable OTP memory and this key never leaves the device. The corresponding public key is extracted from the device and inserted into a binary DER-encoded X.509 device certificate, which is signed into a Silicon Labs CA chain and then programmed back into the chip into an immutable OTP memory.
The secure identity can be used to authenticate the chip at any time in the life of the product. The production certification chain can be requested remotely from the product. This certification chain can be used to verify that the device was authentically produced by Silicon Labs. The device unique public key is also bound to the device certificate in the certification chain. A challenge can be sent to the chip at any point in time to be signed by the device private key. The public key in the device certificate can then be used to verify the challenge response, proving that the device has access to the securely stored private key, which prevents counterfeit products or impersonation attacks.
For more information about this feature, see Silicon Labs’ AN1268: Authenticating Silicon Labs Devices Using Device Certificates.
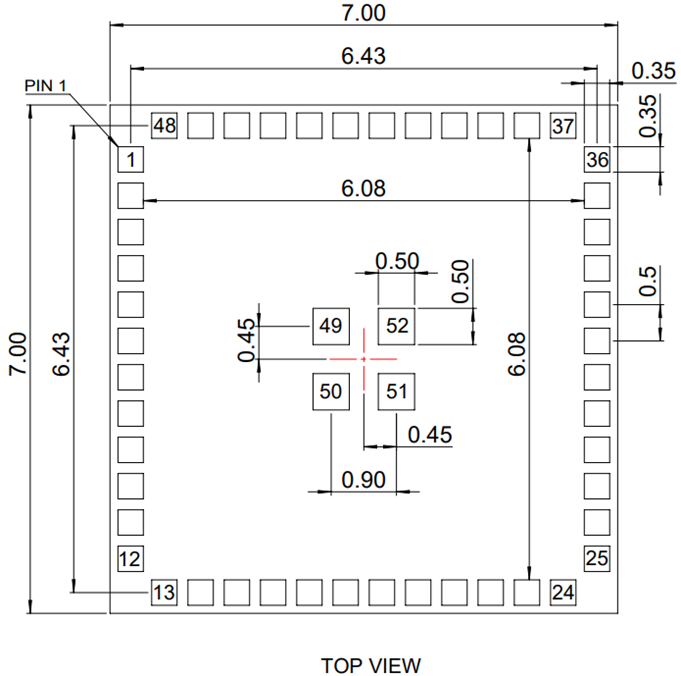
Pin-Out / Package Layout
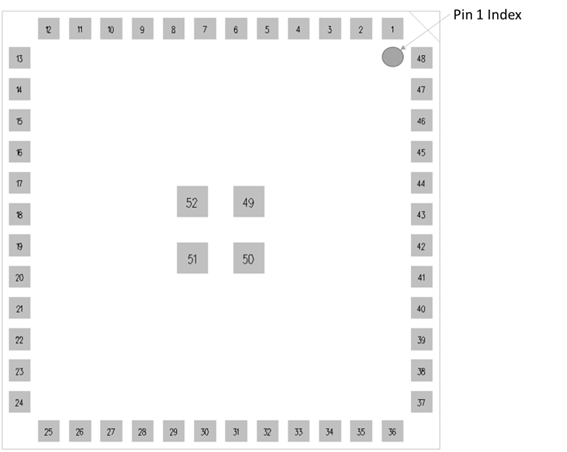
For GPIO pin to peripheral assignment in AT firmware, see User Guide – AT Interface Application – Lyra 24 Series.
The next table shows the Lyra 24S pinout and general descriptions for each pin. Refer to Alternate Pin Functions, Analog Peripheral Connectivity, and Digital Peripheral Connectivity for details on functions and peripherals supported by each GPIO pin.
| Pin Name | No. | Description | Pin Name | No. | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DNC | 1 | Do not connect | GND | 52 | GROUND |
| ANT OUT | 2 | Integral Ant Out | GND | 51 | GROUND |
| DNC | 3 | Do not connect | GND | 50 | GROUND |
| DNC | 4 | Do not connect | GND | 49 | GROUND |
| ANT IN | 5 | Integral Ant In | GND | 48 | GROUND |
| 2G4IO | 6 | RF IN/OUT | RESETn1 | 47 | RESET |
| GND | 7 | GROUND | PC09 | 46 | GPIO |
| PB05 | 8 | GPIO | PC08 | 45 | GPIO |
| PB04 | 9 | GPIO | PC07 | 44 | GPIO |
| PB03 | 10 | GPIO | PC06 | 43 | GPIO |
| PB02 | 11 | GPIO | PC05 | 42 | GPIO |
| GND | 12 | GROUND | PC04 | 41 | GPIO |
| PB01 | 13 | GPIO | PC03 | 40 | GPIO |
| PB00 | 14 | GPIO | PC02 | 39 | GPIO |
| PA00 | 15 | GPIO | PC01 | 38 | GPIO |
| PA01 | 16 | GPIO | PC00 | 37 | GPIO |
| PA02 | 17 | GPIO | PD00 | 36 | GPIO LF XTAL Output (Optional) |
| PA03 | 18 | GPIO | PD01 | 35 | GPIO LF XTAL Input (Optional) |
| PA04 | 19 | GPIO | PD02 | 34 | GPIO |
| PA05 | 20 | GPIO | PD03 | 33 | GPIO |
| PA06 | 21 | GPIO | PD04 | 32 | GPIO |
| PA07 | 22 | GPIO | PD05 | 31 | GPIO |
| PA08 | 23 | GPIO | VDDIO | 30 | I/O power supply |
| PA09 | 24 | GPIO | GND | 29 | GROUND |
| GND | 25 | GROUND | VDD | 28 | Power supply |
| VDCDC | 26 | Test pin (internal test usage) | DECOUPLE | 27 | Test pin (internal test usage) |
Alternate Pin Functions
Some GPIOs support alternate functions like debugging, wake-up from EM4, external low frequency crystal access, etc. The following table shows both which module pins have alternate capabilities and the functions they support. Refer to the SoCs reference manual for more details.
| GPIO | Alternate Functions | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| PA00 | IADC0.VREFP | ||
| PA01 | GPIO.SWCLK | ||
| PA02 | GPIO.SWDIO | ||
| PA03 | GPIO.SWV GPIO.TDO GPIO.TRACEDATA0 | ||
| PA04 | GPIO.TDI GPIO.TRACECLK | ||
| PA05 | GPIO.TRACEDATA1 GPIO.EM4WU0 | ||
| PA06 | GPIO.TRACEDATA2 | ||
| PA07 | GPIO.TRACEDATA3 | ||
| PB00 | VDAC0.VDAC_CH0_MAIN_OU TPUT | ||
| PB01 | GPIO.EM4WU3 | VDAC0.VDAC_CH1_MAIN_OU TPUT | |
| PB02 | VDAC1.VDAC_CH0_MAIN_OU TPUT | ||
| PB03 | GPIO.EM4WU4 | VDAC1.VDAC_CH1_MAIN_OU TPUT | |
| PC00 | GPIO.EM4WU6 | ||
| PC01 | GPIO.EFP_TX_SDA | ||
| PC02 | GPIO.EFP_TX_SCL | ||
| PC05 | GPIO.EFP_INT GPIO.EM4WU7 | ||
| PC07 | GPIO.EM4WU8 | GPIO.THMSW_EN | GPIO.THMSW_HALFSWITCH |
| PD00 | LFXO.LFXTAL_O | ||
| PD01 | LFXO.LFXTAL_I LFXO.LF_EXTCLK | ||
| PD02 | GPIO.EM4WU9 | ||
Analog Peripheral Connectivity
Many analog resources are routable and can be connected to numerous GPIO's. The table below indicates which peripherals are available on each GPIO port. When a differential connection is being used, positive inputs are restricted to the EVEN pins and negative inputs are restricted to the ODD pins. When a single ended connection is being used positive input is available on all pins. See the SoC's Reference Manual for more details on the ABUS and analog peripherals.
| Peripheral | Signal | PA | PB | PC | PD | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EVEN | ODD | EVEN | ODD | EVEN | ODD | EVEN | ODD | ||
| ACMP0 | ANA_NEG | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| ANA_POS | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | |
| ACMP1 | ANA_NEG | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| ANA_POS | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | |
| IADC0 | ANA_NEG | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| ANA_POS | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | |
| VDAC0 | VDAC_CH0_ABUS_OUT- PUT | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| VDAC_CH1_ABUS_OUT | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | |
| VDAC1 | VDAC_CH0_ABUS_OUT- PUT | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| VDAC_CH1_ABUS_OUT | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | |
Digital Peripheral Connectivity
Many digital resources are routable and can be connected to numerous GPIOs. The table below indicates which peripherals are available on each GPIO port.
| Peripheral.Resource | PORT | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PA | PB | PC | PD | |
| ACMP0.DIGOUT | Available | Available | Available | Available |
| ACMP1.DIGOUT | Available | Available | Available | Available |
| CMU.CLKIN0 | Available | Available | ||
| CMU.CLKOUT0 | Available | Available | ||
| CMU.CLKOUT1 | Available | Available | ||
| CMU.CLKOUT2 | Available | Available | ||
| EUSART0.CS | Available | Available | ||
| EUSART0.CTS | Available | Available | ||
| EUSART0.RTS | Available | Available | ||
| EUSART0.RX | Available | Available | ||
| EUSART0.SCLK | Available | Available | ||
| EUSART0.TX | Available | Available | ||
| EUSART1.CS | Available | Available | Available | Available |
| EUSART1.CTS | Available | Available | Available | Available |
| EUSART1.RTS | Available | Available | Available | Available |
| EUSART1.RX | Available | Available | Available | Available |
| EUSART1.SCLK | Available | Available | Available | Available |
| EUSART1.TX | Available | Available | Available | Available |
| FRC.DCLK | Available | Available | ||
| FRC.DFRAME | Available | Available | ||
| FRC.DOUT | Available | Available | ||
| HFXO0.BUFOUT_REQ_IN_ASYNC | Available | Available | ||
| I2C0.SCL | Available | Available | Available | Available |
| I2C0.SDA | Available | Available | Available | Available |
| I2C1.SCL | Available | Available | ||
| I2C1.SDA | Available | Available | ||
| KEYSCAN.COL_OUT_0 | Available | Available | Available | Available |
| KEYSCAN.COL_OUT_1 | Available | Available | Available | Available |
| KEYSCAN.COL_OUT_2 | Available | Available | Available | Available |
| KEYSCAN.COL_OUT_3 | Available | Available | Available | Available |
| KEYSCAN.COL_OUT_4 | Available | Available | Available | Available |
| KEYSCAN.COL_OUT_5 | Available | Available | Available | Available |
| KEYSCAN.COL_OUT_6 | Available | Available | Available | Available |
| KEYSCAN.COL_OUT_7 | Available | Available | Available | Available |
| KEYSCAN.ROW_SENSE_0 | Available | Available | ||
| KEYSCAN.ROW_SENSE_1 | Available | Available | ||
| KEYSCAN.ROW_SENSE_2 | Available | Available | ||
| KEYSCAN.ROW_SENSE_3 | Available | Available | ||
| KEYSCAN.ROW_SENSE_4 | Available | Available | ||
| KEYSCAN.ROW_SENSE_5 | Available | Available | ||
| LETIMER0.OUT0 | Available | Available | ||
| LETIMER0.OUT1 | Available | Available | ||
| MODEM.ANT0 | Available | Available | Available | Available |
| MODEM.ANT1 | Available | Available | Available | Available |
| MODEM.ANT_ROLL_OVER | Available | Available | ||
| MODEM.ANT_RR0 | Available | Available | ||
| MODEM.ANT_RR1 | Available | Available | ||
| MODEM.ANT_RR2 | Available | Available | ||
| MODEM.ANT_RR3 | Available | Available | ||
| MODEM.ANT_RR4 | Available | Available | ||
| MODEM.ANT_RR5 | Available | Available | ||
| MODEM.ANT_SW_EN | Available | Available | ||
| MODEM.ANT_SW_US | Available | Available | ||
| MODEM.ANT_TRIG | Available | Available | ||
| MODEM.ANT_TRIG_STOP | Available | Available | ||
| MODEM.DCLK | Available | Available | ||
| MODEM.DIN | Available | Available | ||
| MODEM.DOUT | Available | Available | ||
| PCNT0.S0IN | Available | Available | ||
| PCNT0.S1IN | Available | Available | ||
| PRS.ASYNCH0 | Available | Available | ||
| PRS.ASYNCH1 | Available | Available | ||
| PRS.ASYNCH2 | Available | Available | ||
| PRS.ASYNCH3 | Available | Available | ||
| PRS.ASYNCH4 | Available | Available | ||
| PRS.ASYNCH5 | Available | Available | ||
| PRS.ASYNCH6 | Available | Available | ||
| PRS.ASYNCH7 | Available | Available | ||
| PRS.ASYNCH8 | Available | Available | ||
| PRS.ASYNCH9 | Available | Available | ||
| PRS.ASYNCH10 | Available | Available | ||
| PRS.ASYNCH11 | Available | Available | ||
| PRS.ASYNCH12 | Available | Available | ||
| PRS.ASYNCH13 | Available | Available | ||
| PRS.ASYNCH14 | Available | Available | ||
| PRS.ASYNCH15 | Available | Available | ||
| PRS.SYNCH0 | Available | Available | Available | Available |
| PRS.SYNCH1 | Available | Available | Available | Available |
| PRS.SYNCH2 | Available | Available | Available | Available |
| PRS.SYNCH3 | Available | Available | Available | Available |
| RAC.LNAEN | Available | Available | Available | Available |
| RAC.PAEN | Available | Available | Available | Available |
| TIMER0.CC0 | Available | Available | Available | Available |
| TIMER0.CC1 | Available | Available | Available | Available |
| TIMER0.CC2 | Available | Available | Available | Available |
| TIMER0.CDTI0 | Available | Available | Available | Available |
| TIMER0.CDTI1 | Available | Available | Available | Available |
| TIMER0.CDTI2 | Available | Available | Available | Available |
| TIMER1.CC0 | Available | Available | Available | Available |
| TIMER1.CC1 | Available | Available | Available | Available |
| TIMER1.CC2 | Available | Available | Available | Available |
| TIMER1.CDTI0 | Available | Available | Available | Available |
| TIMER1.CDTI1 | Available | Available | Available | Available |
| TIMER1.CDTI2 | Available | Available | Available | Available |
| TIMER2.CC0 | Available | Available | ||
| TIMER2.CC1 | Available | Available | ||
| TIMER2.CC2 | Available | Available | ||
| TIMER2.CDTI0 | Available | Available | ||
| TIMER2.CDTI1 | Available | Available | ||
| TIMER2.CDTI2 | Available | Available | ||
| TIMER3.CC0 | Available | Available | ||
| TIMER3.CC1 | Available | Available | ||
| TIMER3.CC2 | Available | Available | ||
| TIMER3.CDTI0 | Available | Available | ||
| TIMER3.CDTI1 | Available | Available | ||
| TIMER3.CDTI2 | Available | Available | ||
| TIMER4.CC0 | Available | Available | ||
| TIMER4.CC1 | Available | Available | ||
| TIMER4.CC2 | Available | Available | ||
| TIMER4.CDTI0 | Available | Available | ||
| TIMER4.CDTI1 | Available | Available | ||
| TIMER4.CDTI2 | Available | Available | ||
| USART0.CLK | Available | Available | Available | Available |
| USART0.CS | Available | Available | Available | Available |
| USART0.CTS | Available | Available | Available | Available |
| USART0.RTS | Available | Available | Available | Available |
| USART0.RX | Available | Available | Available | Available |
| USART0.TX | Available | Available | Available | Available |
Electrical Characteristics
All electrical parameters in all tables are specified under the following conditions, unless stated otherwise:
- Typical values are based on TA=25 °C and VDD = VDDIO = 3.0 V, by production test and/or technology characterization.
- Radio performance numbers are measured in conducted mode, based on Silicon Laboratories reference designs using output power-specific external RF impedance-matching networks for interfacing to a 50 Ω antenna.
- Minimum and maximum values represent the worst conditions across supply voltage, process variation, and operating temperature, unless stated otherwise.
Absolute Maximum Ratings
| Parameter | Symbol | Test Condition | Min | Typ | Max | Unit |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Storage temperature range | TSTG | -40 | — | +105 | °C | |
| Voltage on any supply pin | VDDMAX | -0.3 | — | 3.8 | V | |
| Voltage ramp rate on any supply pin | VDDRAMPMAX | — | — | 1.0 | V/µs | |
| DC voltage on any GPIO pin | VDIGPIN | -0.3 | — | VVDDIO+0.3 | V | |
| DC voltage on RESETn pin1 | VRESETn | -0.3 | — | 3.8 | V | |
| Absolute voltage on RFOUT pin | VMAX2G4 | -0.3 | — | VVDD+0.3 | V | |
| Total current into VDD pin | IVDDMAX | Source | — | — | 200 | mA |
| Total current into GND pin | IVSSMAX | Sink | — | — | 200 | mA |
| Current per I/O pin | IIOMAX | Sink | — | — | 50 | mA |
| Source | — | — | 50 | mA | ||
| Current for all I/O pins | IIOALLMAX | Sink | — | — | 200 | mA |
| Source | — | — | 200 | mA |
Note 1: The RESETn pin has a pull-up device to the internal DVDD supply. For minimum leakage, RESETn should not exceed the voltage at DVDD, which is generated by theDC-DC converter.DVDD is equal to1.8 Vwhen DC-DC is active and bypassed toVDD when DC-DC is inactive.
Recommended Operating Conditions
| Parameter | Symbol | Test Condition | Min | Typ | Max | Unit |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Operating ambient temperature range | TA | -40 | — | +105 | °C | |
| VDD operating supply voltage | VVDD | DC-DC in regulation | 2.2 | 3.0 | 3.8 | V |
| DC-DC in bypass | 1.8 | 3.0 | 3.8 | V | ||
| VDDIO operating supply voltage | VVDDIO | AVDDBODEN=0, IOVDDxBODEN=01 | 1.71 | 3.0 | 3.8 | V |
| HCLK and SYSCLK frequency | fHCLK | VSCALE2, MODE = WS1 | — | — | 78 | MHz |
| VSCALE2, MODE = WS0 | — | — | 40 | MHz | ||
| VSCALE1, MODE = WS0 | — | — | 40 | MHz | ||
| EM01 Group A clock frequency | fEM01GRPACLK | VSCALE2 | — | — | 78 | MHz |
| VSCALE1 | — | — | 40 | MHz | ||
| EM01 Group C clock frequency | fEM01GRPCCLK | VSCALE2 | — | — | 78 | MHz |
| VSCALE1 | — | — | 40 | MHz | ||
| Radio HCLK frequency | fRHCLK | VSCALE2 or VSCALE1 | — | 39.0 | — | MHz |
Note:
- The AVDD and IOVDD BOD enable bits are intheEMU_BOD3SENSEregister. These BODs are disabled on reset.
DC Electrical Characteristics
RF Transmitter General Characteristics for the 2.4 GHz Band
Unless otherwise indicated, typical conditions are: VDD = VDDIO = 3.0 V, DC-DC in regulation. RF center frequency 2.45 GHz. TA = 25°C.
| Parameter | Symbol | Test Condition | Min | Typ | Max | Unit |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RF tuning frequency range | FRANGE | 2402 | — | 2480 | MHz | |
| Maximum TX power (see Maximum Regulatory Certified RF TX Power per Country) | POUTMAX | 10 dBm | — | 10.0 | — | dBm |
| 0 dBm | — | -1.4 | — | dBm | ||
| Minimum active TX power | POUTMIN | 10 dBm | — | -29.1 | — | dBm |
| 0 dBm | — | -24.9 | — | dBm | ||
| Output power step size | POUTSTEP | 0 dBm | 0.1 | 0.6 | 10 | dB |
| 10 dBm, -5 dBm < Output power < 0 dBm | 0.2 | 0.7 | 1.7 | dB | ||
| 10 dBm, 0 dBm < Output power < 10 dBm | 0.04 | 0.2 | 0.8 | dB | ||
| Output power variation vs supply voltage variation, frequency = 2450 MHz | POUTVAR_V | 10 dBm output power with VDD voltage swept from 1.8 V to 3.8 V | — | 0.02 | — | dB |
| 0 dBm output power with VDD voltage swept from 1.8 V to 3.8 V | — | 0.06 | — | dB | ||
| Output power variation vs temperature, Frequency = 2450 MHz | POUTVAR_T | 0 dBm, (-40 to +105 °C) | — | 1.1 | — | dB |
| Output power variation over the RF tuning frequency range | POUTVAR_F | 10 dBm | — | 0.6 | — | dB |
| 0 dBm | — | 0.07 | — | dB |
RF Receiver General Characteristics for the 2.4 GHz Band
Unless otherwise indicated, typical conditions are: VDD = VDDIO = 3.0 V, DC-DC in regulation. RF center frequency 2.45 GHz. TA = 25°C.
| Parameter | Symbol | Test Condition | Min | Typ | Max | Unit |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RF tuning frequency range | FRANGE | 2402 | — | 2480 | MHz |
RF Receiver Characteristics for Bluetooth Low Energy in the 2.4 GHz Band 1 Mbps Data Rate
Unless otherwise indicated, typical conditions are: VDD = VDDIO = 3.0 V, DC-DC in regulation. RF center frequency 2.45 GHz. TA = 25°C.
| Parameter | Symbol | Test Condition | Min | Typ | Max | Unit |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rx Max Strong Signal Input Level for 0.1% BER | RXSAT | Signal is reference signal1 | — | 10 | — | dBm |
| Sensitivity | SENS | Signal is reference signal, 37 byte payload1 | — | -97 | — | dBm |
| Signal is reference signal, 255 byte payload1 | — | -95.4 | — | dBm | ||
| With non-ideal signals2 1 | — | -95.0 | — | dBm | ||
| Signal to co-channel interferer | C/ICC | (see notes)1 3 | — | 8.7 | — | dB |
| N ± 1 Adjacent channel selectivity | C/I1 | Interferer is reference signal at +1 MHz offset1 4 3 5 | — | -5.4 | — | dB |
| Interferer is reference signal at -1 MHz offset1 4 3 5 | — | -5.3 | — | dB | ||
| N ± 2 Alternate channel selectivity | C/I2 | Interferer is reference signal at +2 MHz offset1 4 3 5 | — | -40.9 | — | dB |
| Interferer is reference signal at -2 MHz offset1 4 3 5 | — | -39.7 | — | dB | ||
| N ± 3 Alternate channel selectivity | C/I3 | Interferer is reference signal at +3 MHz offset1 4 3 5 | — | -45.5 | — | dB |
| Interferer is reference signal at -3 MHz offset1 4 3 5 | — | -45.7 | — | dB | ||
| Selectivity to image frequency | C/IIM | Interferer is reference signal at image frequency with 1 MHz precision1 5 | — | -23.3 | — | dB |
| Selectivity to image frequency ± 1 MHz | C/IIM_1 | Interferer is reference signal at image frequency +1 MHz with 1 MHz precision1 5 | — | -40.9 | — | dB |
| Interferer is reference signal at image frequency -1 MHz with 1 MHz precision1 5 | — | -5.4 | — | dB | ||
| Intermodulation performance | IM | n = 3 (see note6) | — | -17.3 | — | dBm |
Notes:
- 0.017% Bit Error Rate.
- With non-ideal signals as specified in Bluetooth Test Specification RF-PHY.TS.5.0.1 section 4.7.1
- Desired signal -67 dBm.
- Desired frequency 2402 MHz ≤ Fc ≤ 2480 MHz.
- With allowed exceptions.
- As specified in Bluetooth Core specification version 5.1, Vol 6, Part A ,Section 4.4
RF Receiver Characteristics for Bluetooth Low Energy in the 2.4 GHz Band 2 Mbps Data Rate
Unless otherwise indicated, typical conditions are: VDD = VDDIO = 3.0 V, DC-DC in regulation. RF center frequency 2.45 GHz. TA = 25°C.
| Parameter | Symbol | Test Condition | Min | Typ | Max | Unit |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rx Max Strong Signal Input Level for 0.1% BER | RXSAT | Signal is reference signal1 | — | 10 | — | dBm |
| Sensitivity | SENS | Signal is reference signal, 37 byte payload1 | — | -94.3 | — | dBm |
| Signal is reference signal, 255 byte payload1 | — | -92.7 | — | dBm | ||
| With non-ideal signals2 1 | — | -92.5 | — | dBm | ||
| Signal to co-channel interferer | C/ICC | (see notes)1 3 | — | 8.6 | — | dB |
| N ± 1 Adjacent channel selectivity | C/I1 | Interferer is reference signal at +2 MHz offset1 4 3 5 | — | -5.3 | — | dB |
| Interferer is reference signal at -2 MHz offset1 4 3 5 | — | -5.8 | — | dB | ||
| N ± 2 Alternate channel selectivity | C/I2 | Interferer is reference signal at +4 MHz offset1 4 3 5 | — | -42.2 | — | dB |
| Interferer is reference signal at -4 MHz offset1 4 3 5 | — | -44.2 | — | dB | ||
| N ± 3 Alternate channel selectivity | C/I3 | Interferer is reference signal at +6 MHz offset1 4 3 5 | — | -48.1 | — | dB |
| Interferer is reference signal at -6 MHz offset1 4 3 5 | — | -50.2 | — | dB | ||
| Selectivity to image frequency | C/IIM | Interferer is reference signal at image frequency with 1 MHz precision1 5 | — | -22.8 | — | dB |
| Selectivity to image frequency ± 2 MHz | C/IIM_1 | Interferer is reference signal at image frequency +2 MHz with 1 | — | -42.2 | — | dB |
| Interferer is reference signal at image frequency -2 MHz with 1 MHz precision1 5 | — | -5.3 | — | dB | ||
| Intermodulation performance | IM | n = 3 (see note6) | — | -18.3 | — | dBm |
Notes:
- 0.017% Bit Error Rate.
- With non-ideal signals as specified in Bluetooth Test Specification RF-PHY.TS.5.0.1 section 4.7.1
- Desired signal -64 dBm.
- Desired frequency 2402 MHz ≤ Fc ≤ 2480 MHz.
- With allowed exceptions.
- As specified in Bluetooth Core specification version 5.1, Vol 6, Part A, Section 4.4
RF Receiver Characteristics for Bluetooth Low Energy in the 2.4 GHz Band 500 kbps Data Rate
Unless otherwise indicated, typical conditions are: VDD = VDDIO = 3.0 V, DC-DC in regulation. RF center frequency 2.45 GHz. TA = 25°C.
| Parameter | Symbol | Test Condition | Min | Typ | Max | Unit |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rx Max Strong Signal Input Level for 0.1% BER | RXSAT | Signal is reference signal1 | — | 10 | — | dBm |
| Sensitivity | SENS | Signal is reference signal, 37-byte payload1 | — | -100.7 | — | dBm |
| Signal is reference signal, 255-byte payload1 | — | -99.4 | — | dBm | ||
| With non-ideal signals2 1 | — | -98.4 | — | dBm | ||
| Signal to co-channel interferer | C/ICC | (see notes)1 3 | — | 2.7 | — | dB |
| N ± 1 Adjacent channel selectivity | C/I1 | Interferer is reference signal at +1 MHz offset1 4 3 5 | — | -7.1 | — | dB |
| Interferer is reference signal at -1 MHz offset1 4 3 5 | — | -7.4 | — | dB | ||
| N ± 2 Alternate channel selectivity | C/I2 | Interferer is reference signal at +2 MHz offset1 4 3 5 | — | -46.8 | — | dB |
| Interferer is reference signal at -2 MHz offset1 4 3 5 | — | -49.7 | — | dB | ||
| N ± 3 Alternate channel selectivity | C/I3 | Interferer is reference signal at +3 MHz offset1 4 3 5 | — | -49.4 | — | dB |
| Interferer is reference signal at -3 MHz offset1 4 3 5 | — | -54.5 | — | dB | ||
| Selectivity to image frequency | C/IIM | Interferer is reference signal at image frequency with 1 MHz precision1 5 | — | -49 | — | dB |
| Selectivity to image frequency ± 1 MHz | C/IIM_1 | Interferer is reference signal at image frequency +1 MHz with 1 | — | -49.4 | — | dB |
| Interferer is reference signal at image frequency -1 MHz with 1 MHz precision1 5 | — | -46.8 | — | dB |
Notes:
- 0.017% Bit Error Rate.
- With non-ideal signals as specified in Bluetooth Test Specification RF-PHY.TS.5.0.1 section 4.7.1
- Desired signal -72 dBm.
- Desired frequency 2402 MHz ≤ Fc ≤ 2480 MHz.
- With allowed exceptions.
RF Receiver Characteristics for Bluetooth Low Energy in the 2.4 GHz Band 125 kbps Data Rate
Unless otherwise indicated, typical conditions are: VDD = VDDIO = 3.0 V, DC-DC in regulation. RF center frequency 2.45 GHz. TA = 25°C.
| Parameter | Symbol | Test Condition | Min | Typ | Max | Unit |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rx Max Strong Signal Input Level for 0.1% BER | RXSAT | Signal is reference signal1 | — | 10 | — | dBm |
| Sensitivity | SENS | Signal is reference signal, 37-byte payload1 | — | -105.1 | — | dBm |
| Signal is reference signal, 255-byte payload1 | — | -104.7 | — | dBm | ||
| With non-ideal signals2 1 | — | -104.3 | — | dBm | ||
| Signal to co-channel interferer | C/ICC | (see notes)1 3 | — | 0.9 | — | dB |
| N ± 1 Adjacent channel selectivity | C/I1 | Interferer is reference signal at +1 MHz offset1 4 3 5 | — | -12.4 | — | dB |
| Interferer is reference signal at -1 MHz offset1 4 3 5 | — | -12.8 | — | dB | ||
| N ± 2 Alternate channel selectivity | C/I2 | Interferer is reference signal at +2 MHz offset1 4 3 5 | — | -52.6 | — | dB |
| Interferer is reference signal at -2 MHz offset1 4 3 5 | — | -55.5 | — | dB | ||
| N ± 3 Alternate channel selectivity | C/I3 | Interferer is reference signal at +3 MHz offset1 4 3 5 | — | -53.8 | — | dB |
| Interferer is reference signal at -3 MHz offset1 4 3 5 | — | -60 | — | dB | ||
| Selectivity to image frequency | C/IIM | Interferer is reference signal at image frequency with 1 MHz precision1 5 | — | -53 | — | dB |
| Selectivity to image frequency ± 1 MHz | C/IIM_1 | Interferer is reference signal at image frequency +1 MHz with 1 MHz precision1 5 | — | -53.8 | — | dB |
| Interferer is reference signal at image frequency -1 MHz with 1 MHz precision1 5 | — | -52.6 | — | dB |
Notes:
- 0.017% Bit Error Rate.
- With non-ideal signals as specified in Bluetooth Test Specification RF-PHY.TS.5.0.1 section 4.7.1
- Desired signal -79 dBm.
- Desired frequency 2402 MHz ≤ Fc ≤ 2480 MHz.
- With allowed exceptions.
High-Frequency Crystal
| Parameter | Symbol | Test Condition | Min | Typ | Max | Unit |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Crystal frequency | fHFXTAL | — | 39 | — | MHz | |
| Initial calibrated accuracy | ACCHFXTAL | -5 | — | +5 | ppm | |
| Temperature drift | DRIFTHFXTAL | Across specified temperature range | -30 | — | 30 | ppm |
Low-Frequency Crystal Oscillator
| Parameter | Symbol | Test Condition | Min | Typ | Max | Unit |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Crystal Frequency | FLFXO | — | 32.768 | — | kHz | |
| Supported Crystal equivalent series resistance (ESR) | ESRLFXO | GAIN = 0 | — | — | 80 | kΩ |
| GAIN = 1 to 3 | — | — | 100 | kΩ | ||
| Supported range of crystal load capacitance 1 | CL_LFXO | GAIN = 0 | 4 | — | 6 | pF |
| GAIN = 1 | 6 | — | 10 | pF | ||
| GAIN = 2 (see note2) | 10 | — | 12.5 | pF | ||
| GAIN = 3 (see note2) | 12.5 | — | 18 | pF | ||
| Current consumption | ICL12p5 | ESR=70 kΩ, CL=12.5pF, GAIN3 = 2, AGC4 = 1 | — | 294 | — | nA |
| Startup Time | TSTARTUP | ESR=70 kΩ, CL=7pF, GAIN3 = 1, AGC4 = 1 | — | 52 | — | ms |
| On-chip tuning cap step size | SSLFXO | — | 0.26 | — | pF | |
| On-chip tuning capacitor value at minimum setting5 | CLFXO_MIN | CAPTUNE = 0 | — | 5.2 | — | pF |
| On-chip tuning capacitor value at maximum setting5 | CLFXO_MAX | CAPTUNE = 0x4F | — | 26.2 | — | pF |
Notes:
- Total load capacitance seen by the crystal
- Crystals with a load capacitance of greater than 12 pF require external load capacitors.
- In LFXO_CAL Register
- In LFXO_CFG Register
- The effective load capacitance seen by the crystal will be CLFXO/2. This is because each
- XTAL pin has a tuning cap and the two caps will be seen in series by the crystal
Precision Low Frequency RC Oscillator (LFRCO)
| Parameter | Symbol | Test Condition | Min | Typ | Max | Unit |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nominal oscillation frequency | FLFRCO | — | 32.768 | — | kHz | |
| Frequency accuracy | FLFRCO_ACC | Normal mode | -3 | — | 3 | % |
| Precision mode1, across operating temperature range2 | -500 | — | 500 | ppm | ||
| Startup time | tSTARTUP | Normal mode | — | 204 | — | µs |
| Precision mode1 | — | 11.7 | — | ms | ||
| Current consumption | ILFRCO | Normal mode | — | 189.9 | — | nA |
| Precision mode1, T = stable at 25 °C 3 | — | 649.8 | — | nA |
Notes:
- The LFRCO operates in high-precision mode when CFG_HIGHPRECEN is set to 1. High-precision mode is not available in EM4.
- Includes ± 40 ppm frequency tolerance of the HFXO crystal.
- Includes periodic re-calibration against HFXO crystal oscillator.
GPIO Pins
| Parameter | Symbol | Test Condition | Min | Typ | Max | Unit |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Leakage current | ILEAK_IO | MODEx = DISABLED, VDD = VDDIO = 3.0 V | — | 2.5 | — | nA |
| Input low voltage1 | VIL | Any GPIO pin | — | — | 0.3*VDDIO | V |
| RESETn | — | — | 0.3*DVDD | V | ||
| Input high voltage1 | VIH | Any GPIO pin | 0.7*VDDIO | — | — | V |
| RESETn | 0.7*DVDD | — | — | V | ||
| Hysteresis of input voltage | VHYS | Any GPIO pin | 0.05*VDDIO | — | — | V |
| RESETn | 0.05*DVDD | — | — | V | ||
| Output high voltage | VOH | Sourcing 20 mA, VDDIO = 3.0 V | 0.8*VDDIO | — | — | V |
| Output low voltage | VOL | Sinking 20 mA, VDDIO = 3.0 V | — | — | 0.2*VDDIO | V |
| GPIO rise time | TGPIO_RISE | VDDIO = 3.0 V, Cload = 50pF, SLEWRATE = 4, 10% to 90% | — | 8.4 | — | ns |
| GPIO fall time | TGPIO_FALL | VDDIO = 3.0 V, Cload = 50pF, SLEWRATE = 4, 90% to 10% | — | 7.1 | — | ns |
| Pull up/down resistance2 | RPULL | Any GPIO pin. Pull-up to VDDIO: MODEn = DISABLE DOUT=1. Pull-down to GND: MODEn = WIREDORPULLDOWN DOUT = 0. | 35 | 44 | 55 | kΩ |
| RESETn pin. Pull-up to DVDD | 35 | 44 | 55 | kΩ | ||
| Maximum filtered glitch width | TGF | MODE = INPUT, DOUT = 1 | — | 27 | — | ns |
Notes:
- GPIO input thresholds are proportional to the VDDIO pin. RESETn input thresholds are proportional to the internal DVDD supply, which is generated by the DC-DC converter. DVDD is equal to 1.8 V when DC-DC is active and bypassed to VDD when DC-DC is inactive.
- GPIO pull-ups connect to VDDIO supply, pull-downs connect to GND. RESETn pull-up connects to internal DVDD supply, which is generated by the DC-DC converter. DVDD is equal to 1.8 V when DC-DC is active and bypassed to VDD when DC-DC is inactive.
Microcontroller Peripherals
The set of peripherals available in Lyra 24S modules includes:
- 12-bit 1 Msps ADC
- Analog Comparators
- 16-bit and 32-bit Timers/Counters
- 24-bit Low Energy Timer for waveform generation
- 32-bit Real Time Counter
- USART (UART/SPI/SmartCards/IrDA/I2S)
- I2C peripheral interfaces
- 12 Channel Peripheral Reflex System
Details on their electrical performance can be found in the relevant portions of Section 4 of the EFR32BG24 SoC datasheet.
To learn which GPIO ports provide access to every peripheral, consult Analog Peripheral Connectivity and Digital Peripheral Connectivity.
Current Consumption
MCU Current Consumption at 3.0V
Unless otherwise indicated, typical conditions are: VDD = VDDIO = 3.0 V, DC-DC in regulation. Voltage scaling level = VSCALE1. TA = 25 °C. Minimum and maximum values in this table represent the worst conditions across process variation at TA = 25 °C.
| Parameter | Symbol | Test Condition | Min | Typ | Max | Unit |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Current consumption in EM0 mode with all peripherals disabled | IACTIVE | 78 MHz HFRCO w/ DPLL referenced to 39 MHz crystal, CPU running Prime from flash, VSCALE2 | — | 33.3 | — | µA/MHz |
| 78 MHz HFRCO w/ DPLL referenced to 39 MHz crystal, CPU running while loop from flash, VSCALE2 | — | 32.8 | — | µA/MHz | ||
| 78 MHz HFRCO w/ DPLL referenced to 39 MHz crystal, CPU running CoreMark loop from flash, VSCALE2 | — | 49.1 | — | µA/MHz | ||
| 39 MHz crystal, CPU running Prime from flash | — | 33.9 | — | µA/MHz | ||
| 39 MHz crystal, CPU running while loop from flash | — | 33.4 | — | µA/MHz | ||
| 39 MHz crystal, CPU running CoreMark loop from flash | — | 49.4 | — | µA/MHz | ||
| 38 MHz HFRCO, CPU running while loop from flash | — | 28.1 | — | µA/MHz | ||
| Current consumption in EM1 mode with all peripherals disabled | IEM1 | 78 MHz HFRCO w/ DPLL referenced to 39 MHz crystal, VSCALE2 | — | 22.6 | — | µA/MHz |
| 39 MHz crystal | — | 24.4 | — | µA/MHz | ||
| 38 MHz HFRCO | — | 19.0 | — | µA/MHz | ||
| Current consumption in EM2 mode, VSCALE0 | IEM2_VS | 256 kB RAM and full Radio RAM retention, RTC running from LFXO1 | — | 3.1 | — | µA |
| 256 kB RAM and full Radio RAM retention, RTC running from LFRCO1 | — | 3.1 | — | µA | ||
| 16 kB RAM and full Radio RAM retention, RTC running from LFXO1 | — | 1.3 | — | µA | ||
| 16 kB RAM and full Radio RAM retention, RTC running from LFRCO1 | — | 1.3 | — | µA | ||
| 16 kB RAM and full Radio RAM retention, RTC running from LFRCO in precision mode1 | — | 1.9 | — | µA | ||
| Current consumption in EM3 mode, VSCALE0 | IEM3_VS | 256 kB RAM and full Radio RAM retention, RTC running from ULFRCO1 | — | 2.9 | — | µA |
| 16 kB RAM and full Radio RAM retention, RTC running from ULFRCO1 | — | 1.1 | — | µA | ||
| Current consumption in EM4 mode | IEM4 | No BURTC, no LF oscillator | — | 0.31 | — | µA |
| BURTC with LFXO | — | 0.64 | — | µA | ||
| Current consumption during reset | IRST | Hard pin reset held | — | 467 | — | µA |
Note:
- CPU cache retained, EM0/1 peripheral states retained
Radio Current Consumption with 3.0 V Supply
RF current consumption measured with MCU in EM1 and all MCU peripherals disabled. Unless otherwise indicated, typical conditions are: VDD = VDDIO = 3.0 V, DC-DC in regulation. TA = 25 °C.
| Parameter | Symbol | Test Condition | Min | Typ | Max | Unit |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Current consumption in receive mode, active packet reception, VSCALE1, EM1P | IRX_ACTIVE | 125 kbit/s, 2GFSK, f = 2.4 GHz | — | 5.4 | — | mA |
| 500 kbit/s, 2GFSK, f = 2.4 GHz | — | 5.5 | — | mA | ||
| 1 Mbit/s, 2GFSK, f = 2.4 GHz | — | 5.1 | — | mA | ||
| 2 Mbit/s, 2GFSK, f = 2.4 GHz | — | 5.8 | — | mA | ||
| Current consumption in receive mode, listening for packet, VSCALE1, EM1P | IRX_LISTEN | 125 kbit/s, 2GFSK, f = 2.4 GHz | — | 5.4 | — | mA |
| 500 kbit/s, 2GFSK, f = 2.4 GHz | — | 5.4 | — | mA | ||
| 1 Mbit/s, 2GFSK, f = 2.4 GHz | — | 5.0 | — | mA | ||
| 2 Mbit/s, 2GFSK, f = 2.4 GHz | — | 5.8 | — | mA | ||
| Current consumption in transmit mode | ITX | f = 2.4 GHz, CW, 10 dBm output power | — | 23.4 | — | mA |
Integration Guidelines
Antenna Characteristics
Typical Lyra 24S radiation patterns for the built-in antenna under optimal operating conditions are plotted in the figures that follow. Antenna gain and radiation patterns have a strong dependence on the size and shape of the application PCB the module is mounted on, as well as on the proximity of any mechanical design to the antenna.
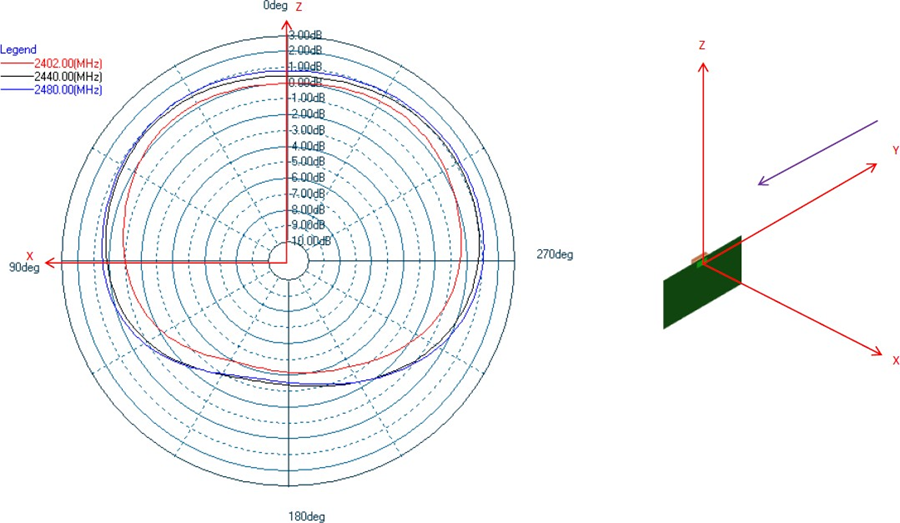
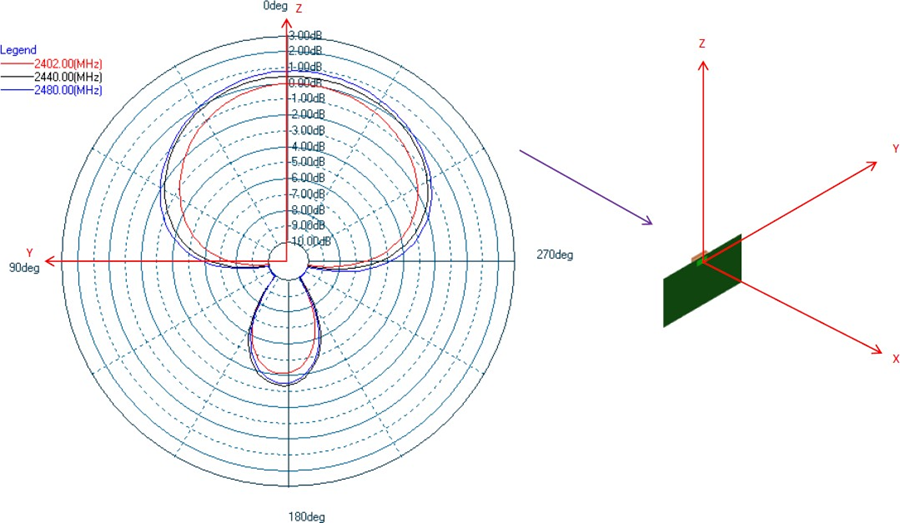
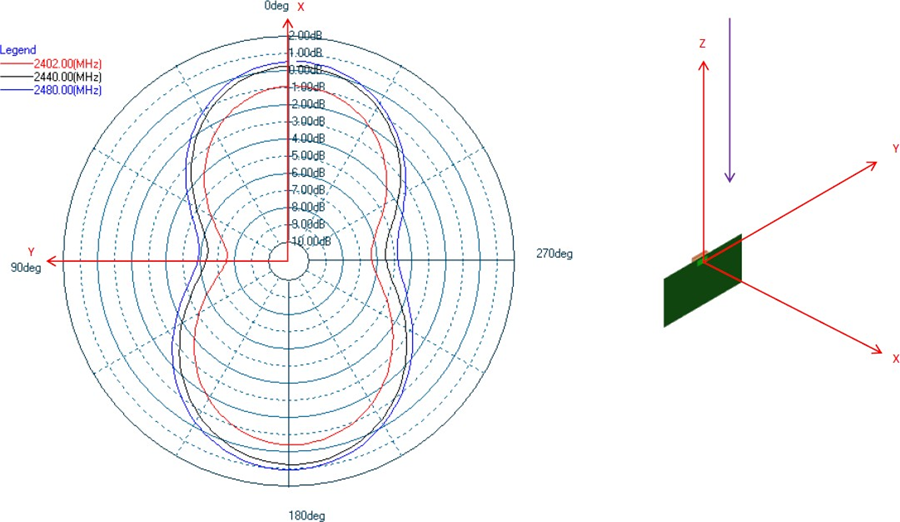
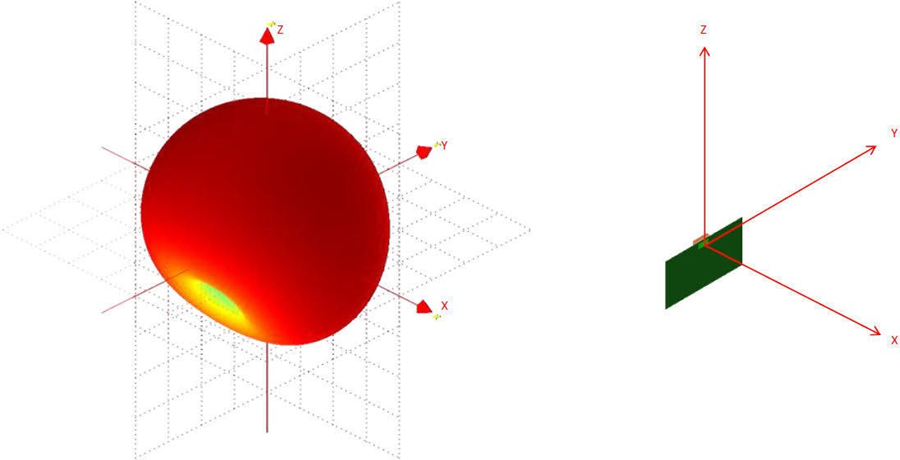
Impact of Human Body and Other Materials in Close Proximity
Placing the module in contact with or very close to the human body will negatively impact antenna efficiency and reduce range.
Avoid placing plastic or any other dielectric material near the antenna. Conformal coating and other thin dielectric layers are acceptable directly on top of the antenna region, but this will also negatively impact antenna efficiency and reduce range.
Any metallic objects near the antenna will prevent the antenna from radiating freely. The minimum recommended distance of metallic and/or conductive objects is 10 mm in any direction from the antenna except in the directions of the application PCB ground planes.
Circuit (Overview and Checklist)
PCB Layout
PCB Layout on Host PCB - General
For optimal performance of the Lyra 24S the following guidelines are recommended:
- Place the module 1.50 mm from the edge of the copper “keep-in” area at the middle of the long edge of the application PCB, as illustrated in Recommended Layout for Lyra 24S (Integrated Antenna) below.
- Copy the exact design from TOP Layer Antenna Layout with Coordinates below with the values for coordinates A to L given in Antenna Polygon Coordinates table below, Referenced to Center of Lyra 24S.
- Make a cutout in all lower layers aligned with the right edge and the bottom edge of the integral loop antenna as indicated by the red box in Antenna Clearance in Inner and Bottom Layers below.
- Connect all ground pads directly to a solid ground plane in the top layer.
- Connect 2G4IO to ANT_IN through a 0-ohm resistor.
- The 0-ohm gives the ability to test conducted and to evaluate the antenna impedance in the design.
- Place ground vias as close to the ground pads of the Lyra 24S as possible.
- Place ground vias along the antenna loop right and bottom side.
- Place ground vias along the edges of the application board.
- Do not place plastic or any other dielectric material in contact with the antenna.
- A minimum clearance of 0.5 mm is advised.
- Solder mask, conformal coating and other thin dielectric layers are acceptable directly on top of the antenna region.
- Proper module placement and electrical connection should be ensured by measuring radiated output power from antenna.
- Impedance of the antenna can be verified by measuring S11 at ANT_IN pin that is corresponding antenna specification.
- With an external antenna, use a 50Ω trace to connect RF signal to the antenna, as it is illustrated in section Lyra 24S Module 50 Ohms RF Track Design for Connecting External Antenna with the Lyra 24S.
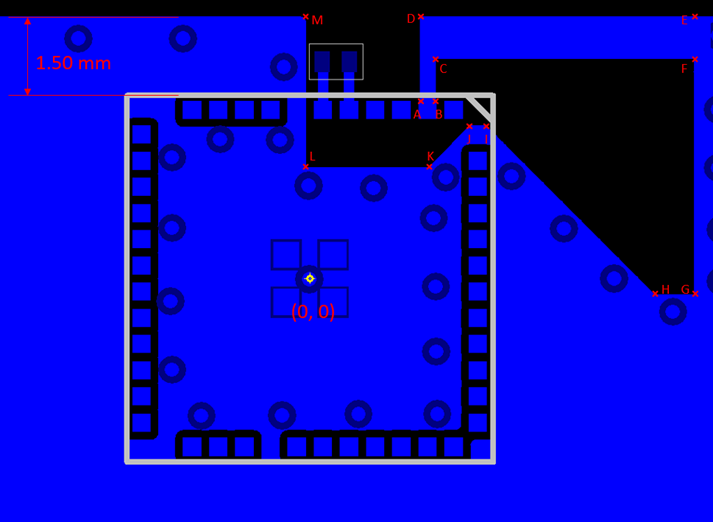
Antenna Polygon Coordinates, Referenced to Center of Lyra 24S
| Point | Coordinate |
|---|---|
| A | (2.10, 3.30) |
| B | (2.40, 3.30 |
| C | (2.40, 4.20) |
| D | (2.10, 5.00) |
| E | (7.35, 5.00) |
| F | (7.35, 4.20) |
| G | (7.35, -0.03) |
| H | (6.59, -0.30) |
| I | (3.39, 2.90) |
| J | (3.05, 2.90) |
| K | (2.27, 2.13) |
| L | (-0.08, 2.13) |
| M | (-0.08, 5.00) |
Tolerance for the coordinates is +/- 0.05 mm.
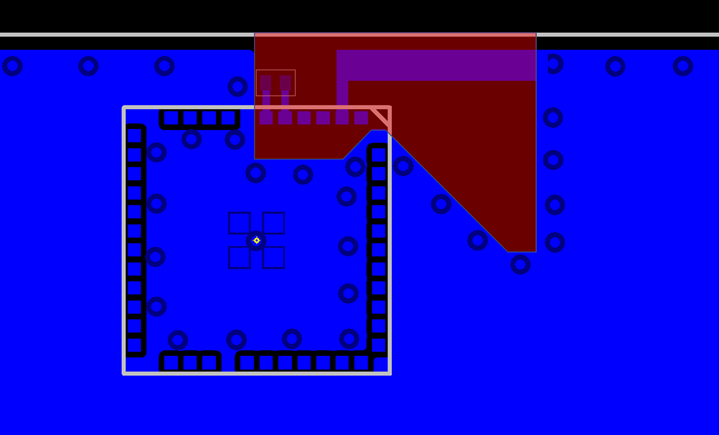
Best Design Practices
- The design of a good RF system relies on thoughtful placement and routing of the RF signals. The following guidelines are recommended:
- Place the Lyra 24S and antenna close to the center of the longest edge of the application board.
- Do not place any circuitry between the board edge and the antenna.
- Make sure to tie all GND planes in the application board together with as many vias as can be fitted.
- Generally, ground planes are recommended in all areas of the application board except in the antenna keep-out area shown in the previous diagram.
- Open-ended stubs of copper in the outer layer ground planes must be removed if they are more than 5 mm long to avoid radiation of spurious emissions.
- The width of the GND plane to the sides of the Lyra 24S will impact the efficiency of the on-board integral loop antenna.
- To achieve optimal performance, a GND plane width of 55 mm is recommended as seen below.
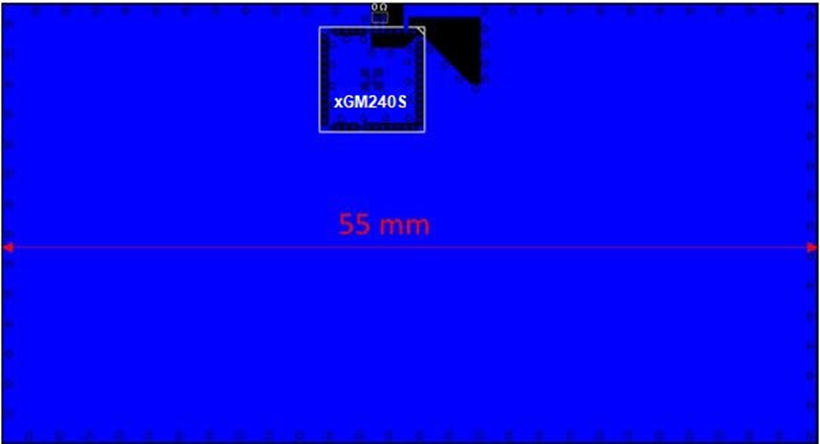
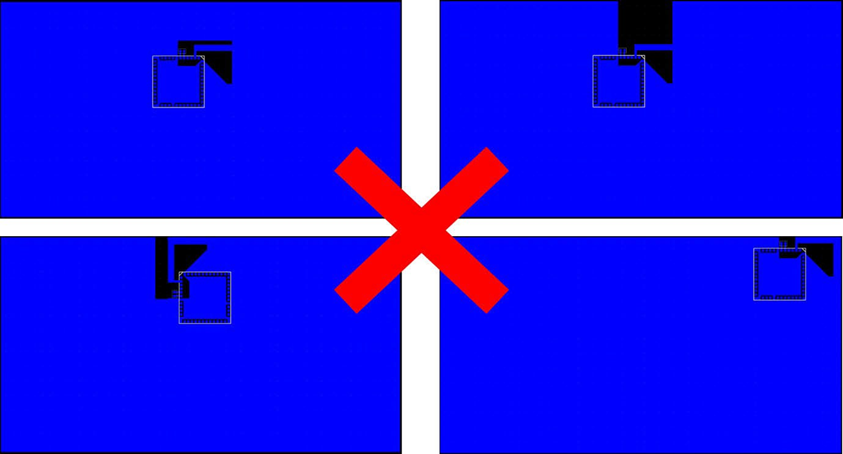
- See Antenna Radiation and Efficiency for Lyra 24S Integrated Antenna for reference. The below illustrates layout scenarios that will lead to severely degraded RF performance for the application board. Antenna Keep-Out on Host PCB.
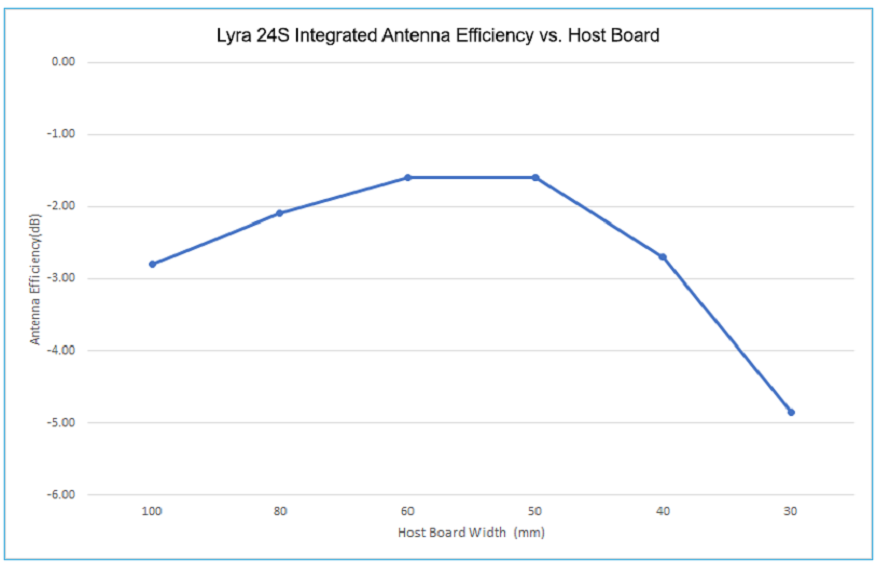
Radio Performance vs. Carrier Board Size
As with most applications, the carrier board size is determined by the overall form factor or size of the additional circuitry. The recommended carrier board width of 55 mm is thus not always possible in the end-application. If another form factor is required, the antenna performance of the integrated antenna will likely be compromised, but it may still be sufficiently good for providing the required link quality and range of the end-application. As can be seen below, the best performance is achieved for a carrier board size of 55 mm x 30 mm, with relatively constant performance for larger boards and rapidly declining performance for smaller boards.
WARNING: Any antenna tuning, and/or change of the loop dimensions, is likely to invalidate a modular certification, unless it is done to compensate for the degradation caused by a host board deviating in size from the manufacturer's best-case reference. Separate guidance might be provided by the manufacturer to address this particular kind of degradation, in which case a Permissive Change to the modular approval might not even become necessary: however, since this is evaluated on a case-by-case basis, please consult your certification house on the best approach.
External Antenna Integration
Lyra 24S Module 50 Ohms RF Track Design for Connecting External Antenna with the Lyra 24
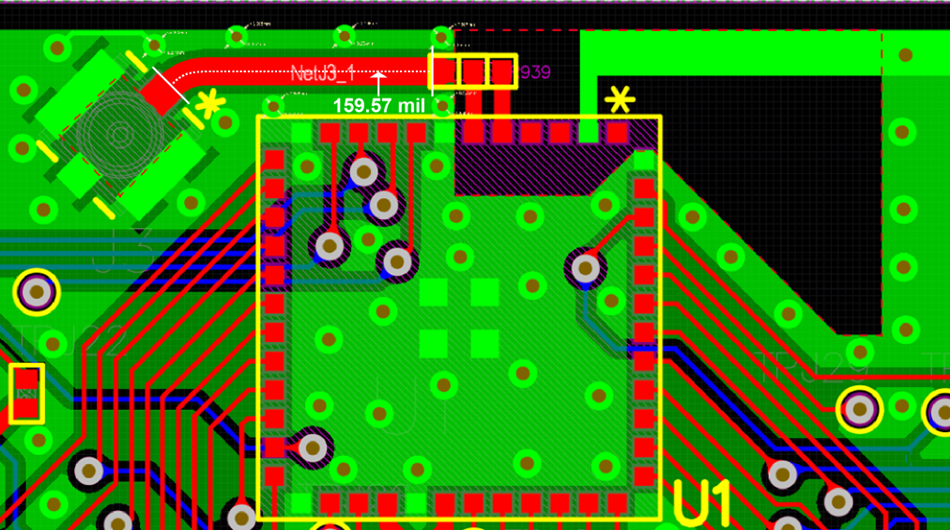
Lyra 24S module can be used with external antennas (certified by Ezurio), and requires a 50 Ohm RF trace (GCPW, that Grounded Coplanar Waveguide) to be designed to run from Lyra 24S module 2G4IO (pin6) to a RF antenna connector (IPEX MHF4) on host PCB. The 50 Ohms RF track design and length MUST be copied (as specified in this section). Lyra 24SP module GND pin7 used to support GCPW 50Ohm RF trace.
Lyra 24S for External antenna connection host PCB 50-Ohm RF trace schematic with MHF4 RF connector
| Lyra 24S External antenna connection | Lyra 24S Internal antenna connection |
|---|---|
|
|
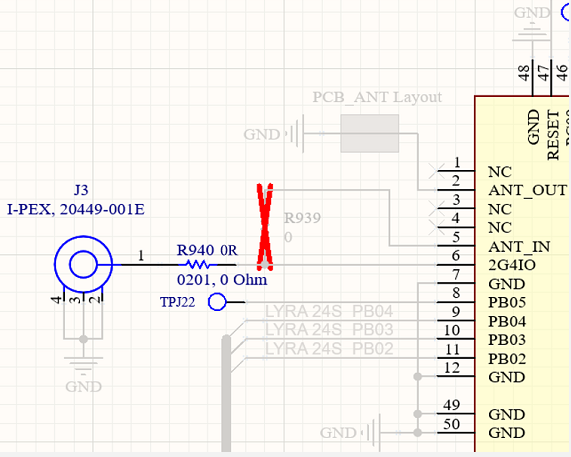  |   |
Layer1 (RF Track and RF GND)
Layer2 (RF GND)
Checklist for PCB:
- MUST use a 50-Ohm RF trace (GCPW, that is Grounded Coplanar Waveguide) from 2F4IO (pin6) of the Lyra 24S module (453-00170) to RF antenna connector (IPEX MHF4 Receptable (MPN: 20449-001E)) on host PCB.
- To ensure regulatory compliance, MUST follow exactly the following considerations for 50-Ohms RF trace design and test verification:
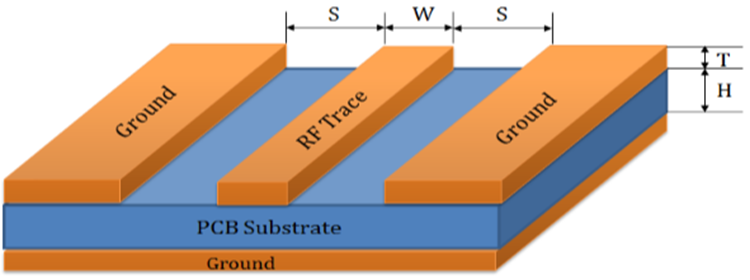
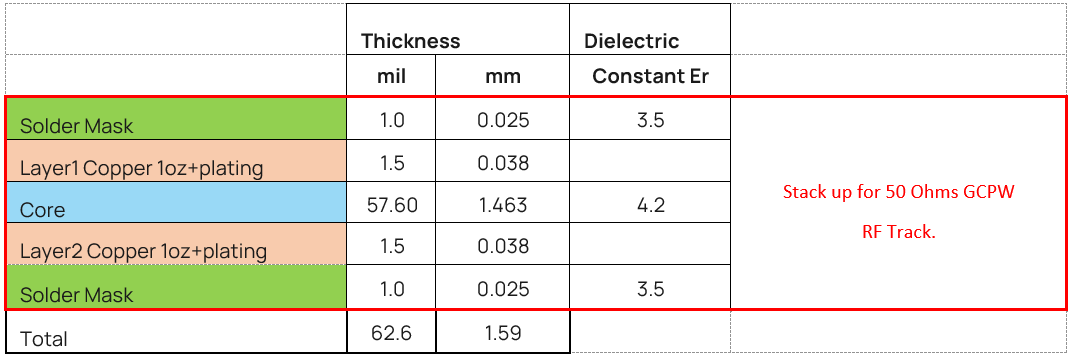
Note:
- The plating (ENIG) above base 1ounce copper is not listed, but plating expected to be ENIG.
The 50-Ohms RF trace design MUST be Grounded Coplanar Waveguide (GCPW) with
- Layer1 RF track width (W) of 20 mil and
- Layer1 gap (S) to GND of 5 mil and where the
- Layer1 to Layer 2 dielectric thickness (H) MUST be 57.6 mil (dielectric constant Er 4.2).
- Further the Layer1 base copper must be 1-ounce base copper (that is 1.5 mil) plus the plating and
- Layer1 MUST be covered by solder mask of 1.0 mil thickness (dielectric constant Er 3.5).
- The 50-Ohms RF trace design MUST follow the PCB stack-up shown above. (Layer1 to Layer2 thickness MUST be identical to the Lyra 24S development board).
- The 50-Ohms RF track should be a controlled-impedance trace e.g., ±10%.
- The 50-Ohms RF trace length MUST be identical (as seen in Layer 2 diagram above) (159.57 mil) to that on the Lyra 24S development board from Lyra 24S module 2G4IO RF pad (pin6) to the RF connector IPEX MHF4 Receptable (MPN: 20449-001E).
- Place GND vias regularly spaced either side of 50-Ohms RF trace to form GCPW (Grounded coplanar waveguide) transmission line as shown in Layer 2 diagram above and use Lyra 24S module GND pin7.
- Use spectrum analyzer to confirm the radiated (and conducted) signal is within the certification limit.
External Antenna Integration with the Lyra 24S Module 453-00170
Please refer to the Lyra 24S Regulatory Information Guide for details on using Lyra 24S module with external antennas in each regulatory region. The Lyra 24S has been designed to operate with the below external antennas (with a maximum gain of 2.0dBi). The required antenna impedance is 50 ohms. See below. External antennas improve radiation efficiency.
| Manufacturer | Model | Ezurio Connectivity Part Number | Weight (g) | Dimensions (mm) | Type | Connector | Peak Gain 2400-2500 MHz | Peak Gain 2400-2480 MHz |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ezurio (Laird Connectivity) | NanoBlue | EBL2400A1-10MH4L | 2 | 44.45 x 12.7 x 0.81 | PCB Dipole | IPEX MHF4 | 2 dBi | - |
| Ezurio (Laird Connectivity) | FlexPIFA | 001-0022 | 1.13 | 40.1 x 11.0 x 2.5 | PIFA | IPEX MHF4 | - | 2 dBi |
| Mag Layers | EDA-8709-2G4C1-B27-CY | 0600-00057 | NA | NA | Dipole | IPEX MHF4 | 2 dBi | - |
| Ezurio (Laird Connectivity) | mFlexPIFA | EFA2400A3S-10MH4L | 1.8 | 25.4 × 23.4 × 2.5 | PIFA | IPEX MHF4 | - | 2 dBi |
Host Platform Implementation Details
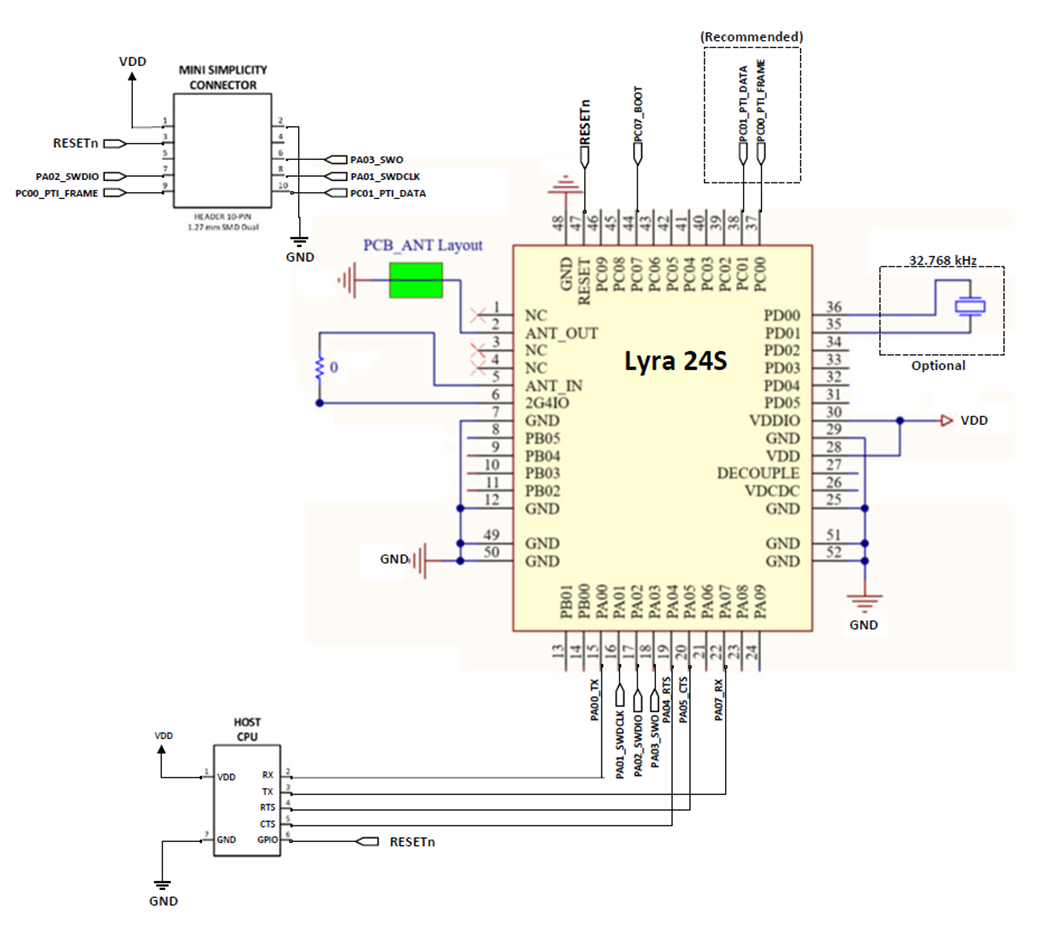
Network Co-Processor (NCP) Application with UART Host
The Lyra 24S can be controlled via the UART interface as a peripheral to an external host processor. Typical power supply, programming/debug interface, and host interface connections are shown in the figure below. For more details, see AN958: Debugging and Programming Interfaces for Custom Designs.
Note: For boot pin, see Boot section.
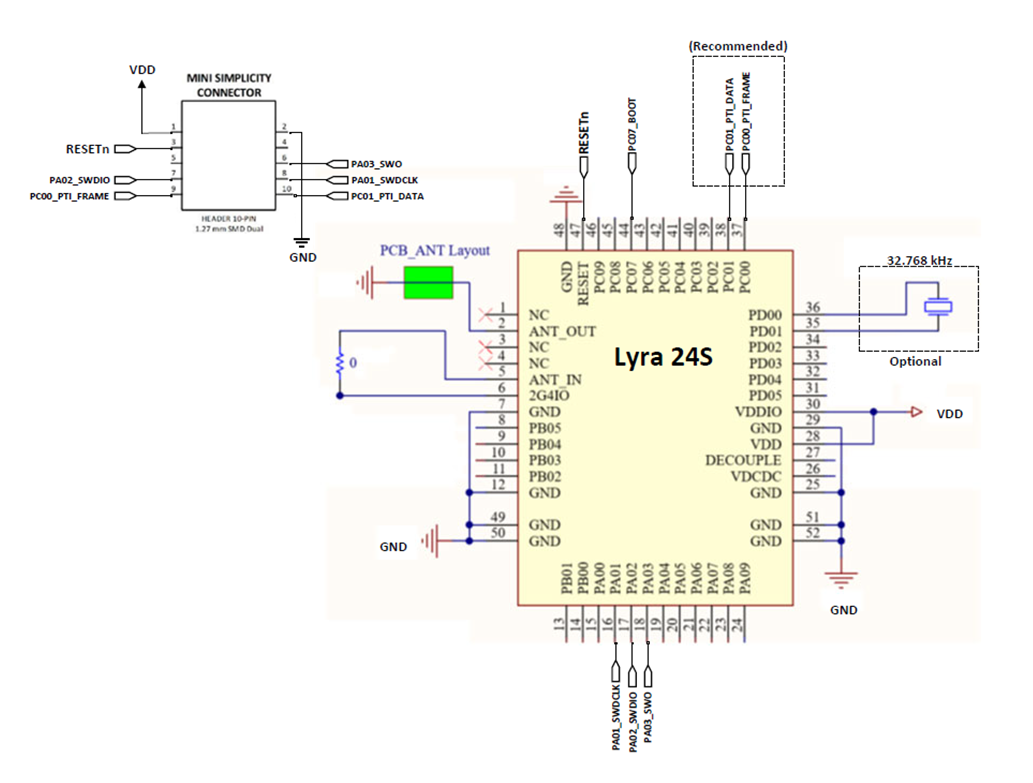
SoC Application
The Lyra 24S can be used in a stand-alone SoC configuration without an external host processor. Typical power supply and programming/debug interface connections are shown in the figure below. For more details, see AN958: Debugging and Programming Interfaces for Custom Designs.
Boot
The BOOT pin is used to determine when execution of the bootloader is required. Upon reset, execution of the bootloader begins. The state of the BOOT pin is read immediately upon start-up of the bootloader. If LOW, execution of the bootloader continues, facilitating firmware update via the UART. If the BOOT pin is HIGH, the bootloader will stop execution and pass control to the main application firmware.
Reset
The Lyra 24S can be reset by pulling the RESET line low, by the internal watchdog timer, or by software command. The reset state does not provide power saving functionality and it is not recommended as a means to conserve power.
Debug
See Silicon Labs’ AN958: Debugging and Programming Interfaces for Custom Designs.
The Lyra 24S supports hardware debugging via 4-pin JTAG or 2-pin serial-wire debug (SWD) interfaces. It is recommended to expose the debug pins in your own hardware design for firmware update and debug purposes. The table below lists the required pins for JTAG and SWD debug interfacing, which are also presented in Alternate Pin Functions.
If JTAG interfacing is enabled, the module must be power cycled to return to a SWD debug configuration if necessary.
| Pin Name | JTAG Signal | SWD Signal | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|
| PA04 | TDI | N/A | This pin is disabled after reset. Once enabled the pin has a built-in pull-up. |
| PA03 | TDO | N/A | This pin is disabled after reset. |
| PA02 | TMS | SWDIO | Pin is enabled after reset and has a built-in pull-up. |
| PA01 | TCK | SWCLK | Pin is enabled after reset and has a built-in pull-down. |
Packet Trace Interface (PTI)
The Lyra 24S integrates a true PHY-level packet trace interface (PTI) peripheral that can capture packets non-intrusively to monitor and log device and network traffic without burdening processing resources in the module's SoC. The PTI generates two output signals that can serve as a powerful debugging tool, especially in conjunction with other hardware and software development tools available from Silicon Labs. The PTI_DATA and PTI_FRAME signals can be accessed through any GPIO on ports C and D (see FRC.DOUT and FRC.DFRAME peripheral resources in Pin Out / Package Layout).
WL_DEV_WAKE Mapping
Application Note for Surface Mount Modules
Shipping and Labeling
PCB Land Pattern
Notes:
- All dimensions shown are in millimeters (mm) unless otherwise noted.
- Dimensioning and Tolerancing is per the ANSI Y14.5M-1994 specification.
- This Land Pattern Design is based on IPC-SM-782 guidelines.
- All dimensions shown are at Maximum Material Condition (MMC). Least Material Condition (LMC) is calculated based on a Fabrication Allowance of 0.05mm.
- All pads are to be non-solder mask defined (NSMD). Clearance between the solder mask and the metal pad is to be 60um minimum, all the way around the pad.
- A stainless steel, laser-cut and electro-polished stencil with trapezoidal walls should be used to assure good solder paste release.
- The stencil thickness should be 0.125mm (5 mils).
10. The ratio of stencil aperture to land pad size should be 1:1 for all perimeter pads.
11. A No-Clean, Type-3 solder paste is recommended.
12. The recommended card reflow profile is per the JEDEC/IPC J-STD-020 specification for Small Body Components.
Above notes and stencil design are shared as recommendations only. A customer or user may find it necessary to use different parameters and fine tune their SMT process as required for their application and tooling.
Package Marking

| Part Number | Line 1 Marking | Line 2 Marking | Line 3 Marking | Line 4 Marking |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 453-00170 | 453-00170 | LYRA 24S | YYWWTTTTTT See Note 1 | CC See Note 2 |
Notes:
- YY = Year. WW = Work Week, TTTTTTT = Trace Code
- Country of Origin ISO Code Abbreviation.
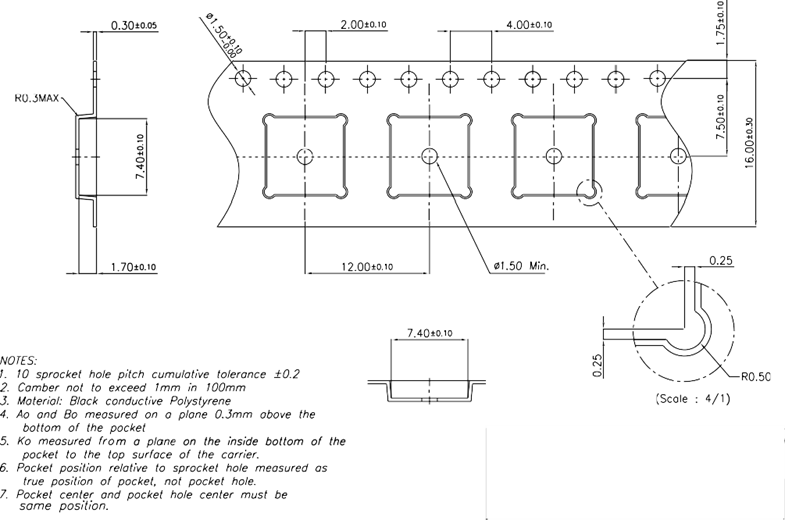
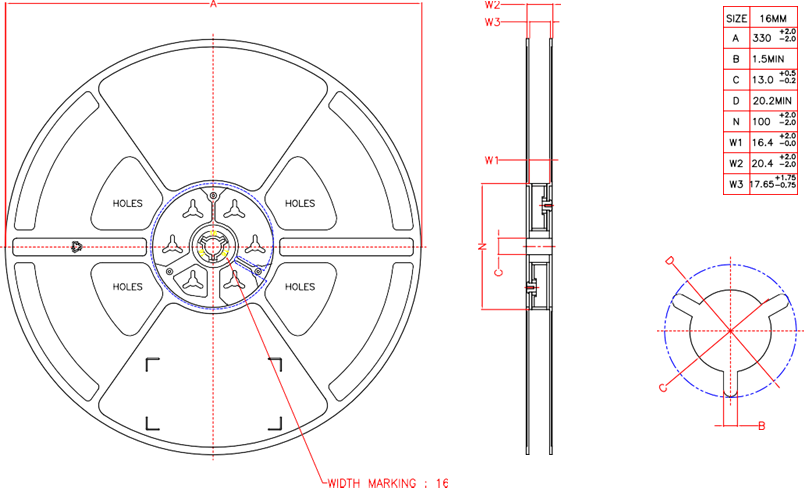
Tray and Reel
Lyra 24S modules are delivered to the customer in Tray or reel. Find the packaging dimensions below. All dimensions are given in mm unless otherwise indicated.
Recommended Stencil Aperture
Reflow Parameters/ Soldering
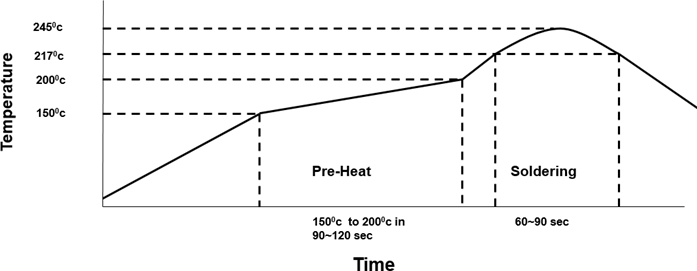
Reflow for lead Free Solder Paste
Optimal solder reflow profile depends on solder paste properties and should be optimized as part of an overall process development.
- It is important to provide a solder reflow profile that matches the solder paste supplier's recommendations.
- Temperature ranges beyond that of the solder paste supplier's recommendation could result in poor solderability.
- All solder paste suppliers recommend an ideal reflow profile to give the best solderability.
Recommended Reflow Profile for lead Free Solder Paste
Miscellaneous
Cleaning
In general, cleaning the populated modules is strongly discouraged. Residuals under the module cannot be easily removed with any cleaning process.
- Cleaning with water can lead to capillary effects where water is absorbed into the gap between the host board and the module. The combination of soldering flux residuals and encapsulated water could lead to short circuits between neighboring pads. Water could also damage any stickers or labels.
- Cleaning with alcohol or a similar organic solvent will likely flood soldering flux residuals into the RF shield, which is not accessible for post-washing inspection. The solvent could also damage any stickers or labels.
- Ultrasonic cleaning could damage the module permanently.
Rework
The Lyra 24P module can be unsoldered from the host board if the Moisture Sensitivity Level (MSL) requirements are met as described in this datasheet.
Never attempt a rework on the module itself, i.e. replacing individual components. Such actions terminate warranty coverage.
Environmental and Reliability
Environmental Requirements
Handling Requirements
The Lyra 24P module contain a highly sensitive electronic circuitry. Handling without proper ESD protection may damage the module permanently.
Moisture Sensitivity Level (MSL)
Per J-STD-020, devices rated as MSL 4 and not stored in a sealed bag with desiccant pack should be baked prior to use.
Devices are packaged in a Moisture Barrier Bag with a desiccant pack and Humidity Indicator Card (HIC). Devices that will be subjected to reflow should reference the HIC and J-STD-033 to determine if baking is required.
If baking is required, refer to J-STD-033 for bake procedure.
Required Storage Conditions
Per J-STD-033, the shelf life of devices in a Moisture Barrier Bag is 12 months at <40C and <90% room humidity (RH).
Do not store in salty air or in an environment with a high concentration of corrosive gas, such as Cl2, H2S, NH3, SO2, or NOX. Do not store in direct sunlight.
The product should not be subject to excessive mechanical shock.
Repeated Reflow Soldering
Only a single reflow soldering process is encouraged for host boards.
Reliability Tests
Climatic and Dynamic
| Test Name | Test Condition | Qualification | LoT ID or Start | Fail/Pass or End | Notes | Summary | Status |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Test Group A – Accelerated Environment Stress Tests | |||||||
| THB | JA101 85°C, 85%RH Vcc=3.8V, 1000 hours | 3 lots, N=>25 | Q048531 Q048715 Q048533 | 0/25 0/33 0/25 | 1 1 1 | 3 lots 0/83 | Pass |
| Temp Cycle | JA104 Cond C: -65°C to 150°C 500 cycles | 3 lots, N=>25 | Q048534 Q048535 Q048526 | 0/25 0/25 0/25 | 1 1 1 | 3 lots 0/75 | Pass |
| HTSL | JA103 150°C, 1000hr | 3 lots, N=>25 | Q048444 Q048529 Q048530 | 0/25 0/25 0/25 | 1 1 1 | 3 lots 0/75 | Pass |
| Test Group B – Accelerated Lifetime Simulation Tests | |||||||
| HTOL | JA108 TJ ≥ 125°C, Dynamic Vcc=3.8V, 1000 hours | 3 lots, N=>77 | Q048618 Q049010 Q048287 Q049006 Q048200 Q049005 | 0/55 0/32 0/58 0/20 0/49 0/55 | 2 2 2 2 2 2 | 6 lots 0/269 | Pass |
| LTOL | JA108 TA = -10°C, Dynamic Vcc=3.8V, 1000 hours | 1 lot, N=>32 | Q042871 | 0/59 | 2 | 1 lot 0/59 | Pass |
| ELFR | JA108 TJ ≥ 125°C, Dynamic Vcc=3.8V, 48 hours | 3 lots, N=>500 | Q048286 Q049476 Q048085 Q049007 | 0/494 0/6 0/504 0/534 | 2 2 2 2 | 4 lots 0/1538 | Pass |
| NVM Endurance, Retention and Operating Life | JESD22-A117 25°C 500 hours | 3 lots, N=>39 | Q048257 Q048332 Q048620 | 0/44 0/44 0/44 | 2 2 2 | 3 lots 0/132 | Pass |
| NVM Endurance, Retention and Operating Life | JESD22-A117 + JESD22-A103 150°C, 1000 hours | 3 lots, N=>39 | Q048331 Q048262 Q048621 | 0/44 0/44 0/44 | 2 2 2 | 3 lots 0/132 | Pass |
| Test Group E – Electrical Verification | |||||||
| ESD-HMB | JS-001 | 1 lot, N=>3 | Q048512 | 2.5 kV | Class 2 | ||
| ESD-CDM | JS-002 | 1 lot, N=>3 | Q049478 | 3 | TC 250 | Class C1 | |
| Latch Up | JESD78 ±100mA; Overvoltage=3.8V | 1 lot, N=>3 | Q048513 Q048509 | 25 °C 105 °C | Pass | ||
Reliability Prediction
Reliability Prediction Approach
- Apply Telcordia SR-232 Issue 3 Parts Count calculation
- Confidence Level 90%
- Quality Level II
| Lyra 24S | 40C | 105C |
|---|---|---|
| FIT (10-9) | 58 | 1092 |
| MTBF (Mhours) | 17 | 0.9 |
Regulatory, Qualification & Certifications
Regulatory Approvals
Note: For complete regulatory information, refer to the Lyra 24S Regulatory Information document which is also available from the product page https://www.ezurio.com/wireless-modules/bluetooth-modules/bluetooth-5-modules/lyra-24-series-bluetooth-5-modules
The Lyra 24S holds current certifications in the following countries:
| Country/Region | Regulatory ID |
|---|---|
| USA (FCC) | SQG-LYRA24S |
| Canada (ISED) | 3147A-LYRA24S |
| UK (UKCA) | N/A |
| EU | N/A |
| Japan (MIC) | 201-230070 |
| Korea (KC) | R-C-L8C-LYRA24S |
| Australia (AS) | N/A |
| New Zealand (NZS) | N/A |
Certified Antennas
| Manufacturer | Model | Ezurio Connectivity Part Number | Weight (g) | Dimensions (mm) | Type | Connector | Peak Gain 2400-2500 MHz | Peak Gain 2400-2480 MHz |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ezurio (Laird Connectivity) | NanoBlue | EBL2400A1-10MH4L | 2 | 44.45 x 12.7 x 0.81 | PCB Dipole | IPEX MHF4 | 2 dBi | - |
| Ezurio (Laird Connectivity) | FlexPIFA | 001-0022 | 1.13 | 40.1 x 11.0 x 2.5 | PIFA | IPEX MHF4 | - | 2 dBi |
| Mag Layers | EDA-8709-2G4C1-B27-CY | 0600-00057 | NA | NA | Dipole | IPEX MHF4 | 2 dBi | - |
| Ezurio (Laird Connectivity) | mFlexPIFA | EFA2400A3S-10MH4L | 1.8 | 25.4 × 23.4 × 2.5 | PIFA | IPEX MHF4 | - | 2 dBi |
Maximum Regulatory Certified RF TX Power per Country
For shipped AT Firmware
Ezurio AT firmware implements maximum RF TX power settings per country highlighted below.
| Country and implementation | Global | EU | UK | USA | Canada | Australia | New Zealand | Japan | South Korea | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AT FW | Region code | GL | EU | UK | US | CA | AU | NZ | JP | SK |
| AFH | Turned on or off? | on | on | on | on | on | on | on | on | on |
| 10dBm mode | Target TX power conducted | 7dBm | 7dBm | 7dBm | 10dBm | 10dBm | 7dBm | 7dBm | 9dBm | 10dBm |
| Antenna Gain setting | 0dBi | 0dBi | 0dBi | 0dBi | 0dBi | 0dBi | 0dBi | 0dBi | 0dBi | |
| TX power setting | 7dBm | 7dBm | 7dBm | 10dBm | 10dBm | 7dBm | 7dBm | 9dBm | 10dBm |
453-00170 Lyra 24P – Bluetooth v5.4 PCB Module (10dBm) with Integrated Antenna is shipped AT firmware where the radio regulatory region “global” is set which is lowest common settings across RF TX power across certified countries. To switch to the specific radio regulatory region country of USA, Canada, Europe, UK, Australia, New Zealand, Japan and South Korea, customer can use appropriate AT command for setting the radio regulatory region per country.
For Customers C Code Development -
Customers developing with C Code – Full software development with Silicon Labs SDK and Toolchain, MUST implement the maximum RF TX power settings per country and other parameters mentioned in this section.
AFH Firmware Module Description
See Silabs AFH firmware module (in Silabs BLE stack) operation description https://docs.silabs.com/bluetooth/5.0/general/system-and-performance/adaptive-frequency-hopping
This was enabled for CE Adaptivity requirements (since Lyra 24S declared as Adaptive for CE), so left enabled for all certified countries.
Europe (CE), UK (UKCA), Australia (RCM, New Zealand (RCM) Radio RF TX power Table
| Module Ezurio Part number | 453-000170 | ||||||||
| Description | Module, SIP, Lyra 24S, Integrated Antenna (Silicon Labs EFR32BG24) | ||||||||
| Antenna Gain (dBi) | 1.48dBi peak for Integrated antenna. 2.0dBi peak external antenna. | ||||||||
| Radio Regulatory country: | Europe (CE), CANADA (ISED), Australia (RCM), New Zealand (RCM) | ||||||||
| Declared as FHSS or DTS? | DTS | ||||||||
| AFH FW module? | AFH firmware module turned ON (so CE Adaptivity met). | ||||||||
Silabs BLE SDK: Silabs Gecko SDK Suite: | 5.0.0.0 GA (December 14, 2022). 4.2 (December 14, 2022). | ||||||||
| 10dBm mode | CERTIFIED maximum conducted RF TX power per BLE PHY
(below is for when Lyra 24S is connected to an external antenna of 2dBi peak gain, use this RF TX power setting for Integrated antenna (1.48dBi) as well). | CERTIFIED LOWEST COMMON RF TX power setting across BLE PHY’s, other restrict… | IMPLEMENTED in Ezurio AT FW or customer MUST implement in customers own developed C-code. AFH firmware module turned ON. | ||||||
| NOTE 1 | NOTE 2 | NOTE 3 | NOTE 4A | NOTE 4B | |||||
| BLE PHY | Physical channel (channel Index) | Frequency (MHz) channel centre. | Certified conducted Maximum TX Power setting dBm | Measured Conducted Peak POWER (dBm) | Certified Lowest common conducted certified RF TX power setting across all 4 BLE data rates. | Target RF TX power conducted to implement in FW. Other restrictions (if any). | Antenna Gain setting in FW | TX power setting in FW | |
| BLE 1Mbps | CH0 (CH37) | 2402 MHz | 7dBm | 7.45dBm | 7dBm | 7dBm | 0dBi | 7dBm | |
| CH39 (CH39) | 2480 MHz | 7dBm | 7.16dBm | 7dBm | 7dBm | 0dBi | 7dBm | ||
| BLE 2Mbps | CH1 (CH0) | 2404 MHz | 7dBm | 7.46dBm | 7dBm | 7dBm | 0dBi | 7dBm | |
| CH38 (CH36) | 2478 MHz | 7dBm | 7.16dBm | 7dBm | 7dBm | 0dBi | 7dBm | ||
| BLE 125kbps | CH0 (CH37) | 2402 MHz | 7dBm | 7.45dBm | 7dBm | 7dBm | 0dBi | 7dBm | |
| CH39 (CH39) | 2480 MHz | 7dBm | 7.17dBm | 7dBm | 7dBm | 0dBi | 7dBm | ||
| BLE 500kbps | CH0 (CH37) | 2402 MHz | 7dBm | 7.45dBm | 7dBm | 7dBm | 0dBi | 7dBm | |
| CH39 (CH39) | 2480 MHz | 7dBm | 7.17dBm | 7dBm | 7dBm | 0dBi | 7dBm | ||
Notes:
NOTE 1: CERTIFIED maximum conducted RF TX power per BLE PHY. This is not what is implemented in AT firmware, this is what was certified only.
NOTE 2: Certified Lowest common TX power setting across BLE PHY’s. This lowest common TX power setting is stated since we do not use per BLE RF TX power setting in AT firmware, but same TX power setting across all 4 BLE PHY’s.
NOTE 3: IMPLEMENT in AT firmware target RF TX power conducted. This target actual implemented in AT firmware. So for CE, UKCA, RCM (Australia and New Zealand), this is actual target 7dBm conducted). To implement that, NOTE 4A defines what Antenna Gain setting MUST be used and NOTE 4B defines what TX power setting MUST be used.
NOTE 4: IMPLEMENTED in AT firmware (or MUST implement in customers own developed C-code) the Actual target RF TX power conducted:
NOTE 4A: the Antenna Gain setting of 0dBi and
NOTE 4B: the TX power setting to 7dBm which results in:
Target Actual RF TX power (dBm) = TX power setting (dBm) - Antenna Gain setting(dBi)
7dBm = 7dBm – 0dBi
USA (FCC), Canada (ISED) Radio RF TX power Table
| Module Ezurio Part number | 453-000170 | |||||||
| Description | Module, SIP, Lyra 24S, Integrated Antenna (Silicon Labs EFR32BG24) | |||||||
| Antenna Gain (dBi) | 1.48dBi peak for Integrated antenna. 2.0dBi peak external antenna. | |||||||
| Radio Regulatory country: | USA (FCC) and CANADA (ISED) | |||||||
| Declared as FHSS or DTS? | DTS | |||||||
| AFH FW module? | AFH firmware module turned ON. | |||||||
Silabs BLE SDK: Silabs Gecko SDK Suite: | 5.0.0.0 GA (December 14, 2022). 4.2 (December 14, 2022). | |||||||
| 10dBm mode | CERTIFIED maximum conducted RF TX power per BLE PHY | CERTIFIED LOWEST COMMON RF TX power setting across BLE PHY’s, other restrict… | Implemented in Ezurio AT FW or customer MUST implement in customers own developed C-code. AFH firmware module turned ON. | |||||
| NOTE 1 | NOTE 2 | NOTE 3 | NOTE 4A | NOTE 4B | ||||
| BLE PHY | Physical channel (channel Index) | Frequency (MHz) channel centre. | Certified conducted Maximum TX Power setting dBm | Measured Conducted Peak POWER (dBm) | Certified Lowest common conducted certified RF TX power setting across all 4 BLE data rates. | Target RF TX power conducted to implement in FW. Other restrictions (if any). | Antenna Gain setting in FW | TX power setting in FW |
| BLE 1Mbps | CH0 (CH37) | 2402 MHz | 10dBm | 10.27dBm | 10dBm | 10dBm | 0dBi | 10dBm |
| CH39 (CH39) | 2480 MHz | 10dBm | 9.72dBm | 10dBm | 10dBm | 0dBi | 10dBm | |
| BLE 2Mbps | CH1 (CH0) | 2404 MHz | 10dBm | 10.26dBm | 10dBm | 10dBm | 0dBi | 10dBm |
| CH38 (CH36) | 2478 MHz | 10dBm | 9.71dBm | 10dBm | 10dBm | 0dBi | 10dBm | |
| BLE 125kbps | CH0 (CH37) | 2402 MHz | 10dBm | 10.25dBm | 10dBm | 10dBm | 0dBi | 10dBm |
| CH39 (CH39) | 2480 MHz | 10dBm | 9.70dBm | 10dBm | 10dBm | 0dBi | 10dBm | |
| BLE 500kbps | CH0 (CH37) | 2402 MHz | 10dBm | 10.24dBm | 10dBm | 10dBm | 0dBi | 10dBm |
| CH39 (CH39) | 2480 MHz | 10dBm | 9.69dBm | 10dBm | 10dBm | 0dBi | 10dBm | |
Notes:
NOTE 1: CERTIFIED maximum conducted RF TX power per BLE PHY. This is not what is implemented in AT firmware, this is what was certified only.
NOTE 2: Certified Lowest common TX power setting across BLE PHY’s. This lowest common TX power setting is stated since we do not use per BLE RF TX power setting in AT firmware, but same TX power setting across all 4 BLE PHY’s.
NOTE 3: IMPLEMENT in AT firmware target RF TX power conducted. This target actual implemented in AT firmware. So for Usa(FCC), Canada (ISED) this is actual target 10dBm conducted). To implement that, NOTE 4A defines what Antenna Gain setting MUST be used and NOTE 4B defines what TX power setting MUST be used.
NOTE 4:IMPLEMENTED in AT firmware (or MUST implement in customers own developed C-code) the Actual target RF TX power conducted:-
NOTE 4A: the Antenna Gain setting of 0dBi and
NOTE 4B: the TX power setting to 10dBm which results in:
Target Actual RF TX power (dBm) = TX power setting (dBm) - Antenna Gain setting(dBi)
10dBm = 10dBm – 0dBi
Japan (MIC) Radio RF TX Power Table
| Module Ezurio Part number | 453-000170 | |||||||
| Description | Module, SIP, Lyra 24S, Integrated Antenna (Silicon Labs EFR32BG24) | |||||||
| Antenna Gain (dBi) | 1.48dBi peak for Integrated antenna. 2.0dBi peak external antenna. | |||||||
| Radio Regulatory country: | Japan (MIC) | |||||||
| Declared as FHSS or DTS? | DTS | |||||||
| AFH FW module? | AFH firmware module turned ON. | |||||||
| Silabs BLE SDK: | 5.0.0.0 GA (December 14, 2022). | |||||||
| Silabs Gecko SDK Suite: | 4.2 (December 14, 2022). | |||||||
| 10dBm mode | CERTIFIED maximum conducted RF TX power per BLE PHY | CERTIFIED LOWEST COMMON RF TX power setting across BLE PHY’s, other restrict… | IMPLEMENTED in Ezurio AT FW or customer MUST implement in customers own developed C-code. AFH firmware module turned ON. | |||||
| NOTE 1 | NOTE 2 | NOTE 3 | NOTE 4A | NOTE 4B | ||||
| BLE PHY | Physical channel (channel Index) | Frequency (MHz) channel centre. | Certified conducted Maximum TX Power setting dBm | Measured Conducted Peak POWER (dBm) | Certified Lowest common conducted certified RF TX power setting across all 4 BLE data rates. | Target RF TX power conducted to implement in FW. Other restrictions (if any). | Antenna Gain setting in FW | TX power setting in FW |
| BLE 1Mbps | CH0 (CH37) | 2402 MHz | 9dBm | 9.01dBm | 9dBm | 9dBm | 0dBi | 9dBm |
| CH39 (CH39) | 2480 MHz | 9dBm | 8.67dBm | 9dBm | 9dBm | 0dBi | 9dBm | |
| BLE 2Mbps | CH1 (CH0) | 2404 MHz | 9dBm | 8.99dBm | 9dBm | 9dBm | 0dBi | 9dBm |
| CH38 (CH36) | 2478 MHz | 9dBm | 8.67dBm | 9dBm | 9dBm | 0dBi | 9dBm | |
| BLE 125kbps | CH0 (CH37) | 2402 MHz | 9dBm | 8.97dBm | 9dBm | 9dBm | 0dBi | 9dBm |
| CH39 (CH39) | 2480 MHz | 9dBm | 8.64dBm | 9dBm | 9dBm | 0dBi | 9dBm | |
| BLE 500kbps | CH0 (CH37) | 2402 MHz | 9dBm | 8.99dBm | 9dBm | 9dBm | 0dBi | 9dBm |
| CH39 (CH39) | 2480 MHz | 9dBm | 8.65dBm | 9dBm | 9dBm | 0dBi | 9dBm | |
Notes:
NOTE 1: CERTIFIED maximum conducted RF TX power per BLE PHY. This is not what is implemented in AT firmware, this is what was certified only.
NOTE 2: Certified Lowest common TX power setting across BLE PHY’s. This lowest common TX power setting is stated since we do not use per BLE RF TX power setting in AT firmware, but same TX power setting across all 4 BLE PHY’s.
NOTE 3: IMPLEMENT in AT firmware target RF TX power conducted. This target actual implemented in AT firmware. So for Japan (MIC), this is actual target 9dBm conducted). To implement that, NOTE 4A defines what Antenna Gain setting MUST be used and NOTE 4B defines what TX power setting MUST be used.
NOTE 4: IMPLEMENTED in AT firmware (or MUST implement in customers own developed C-code) the Actual target RF TX power conducted:-
NOTE 4A: the Antenna Gain setting of 0dBi and
NOTE 4B: the TX power setting to 9dBm which results in:
Target Actual RF TX power (dBm) = TX power setting (dBm) - Antenna Gain setting(dBi)
9dBm = 9dBm – 0dBi
South Korea Radio RF TX Power Table
| Module Ezurio Part number | 453-000170 | ||||||||
| Description | Module, SIP, Lyra 24S, Integrated Antenna (Silicon Labs EFR32BG24) | ||||||||
| Antenna Gain (dBi) | 1.48dBi peak for Integrated antenna. 2.0dBi peak external antenna. | ||||||||
| Radio Regulatory country: | South Korea | ||||||||
| Declared as FHSS or DTS? | FHSS (uses Silabs AFH FW module ON) | ||||||||
| AFH FW module? | AFH firmware module turned ON. | ||||||||
Silabs BLE SDK: Silabs Gecko SDK Suite: | 5.0.0.0 GA (December 14, 2022) 4.2 (December 14, 2022). | ||||||||
| 10dBm mode | CERTIFIED maximum conducted RF TX power per BLE PHY | CERTIFIED LOWEST COMMON RF TX power setting across BLE PHY’s, other restrict… | IMPLEMENTED in Ezurio AT FW or customer MUST implement in customers own developed C-code. AFH firmware module turned ON. | ||||||
| NOTE 1 | NOTE 2 | NOTE 3 | NOTE 4A | NOTE 4B | |||||
| BLE PHY | Physical channel (channel Index) | Frequency (MHz) channel centre. | Certified conducted Maximum TX Power setting dBm | Certified Measured Conducted Peak POWER (dBm) | Certified Lowest common conducted certified RF TX power setting across all 4 BLE data rates. | Target RF TX power conducted to implement in FW. Other restrictions (if any). | Antenna Gain setting in FW | TX power setting in FW | |
| BLE 1Mbps | CH0 (CH37) | 2402 | 10dBm | 10dBm | 10dBm | 0dBi | 10dBm | ||
| CH39 (CH39) | 2480 | 10dBm | 10dBm | 10dBm | 0dBi | 10dBm | |||
| BLE 2Mbps | CH1 (CH0) | 2404 | 10dBm | 10dBm | 10dBm | 0dBi | 10dBm | ||
| CH38 (CH36) | 2478 | 10dBm | 10dBm | 10dBm | 0dBi | 10dBm | |||
| BLE 125kbps | CH0 (CH37) | 2402 | 10dBm | 10dBm | 10dBm | 0dBi | 10dBm | ||
| CH39 (CH39) | 2480 | 10dBm | 10dBm | 10dBm | 0dBi | 10dBm | |||
| BLE 500kbps | CH0 (CH37) | 2402 | 10dBm | 10dBm | 10dBm | 0dBi | 10dBm | ||
| CH39 (CH39) | 2480 | 10dBm | 10dBm | 10dBm | 0dBi | 10dBm | |||
Notes:
NOTE 1: CERTIFIED maximum conducted RF TX power per BLE PHY in 20dBm mode or 10dBm mode tables. This is not what is implemented in AT firmware, this is what was certified only.
NOTE 2: Certified Lowest common TX power setting across BLE PHY’s. This lowest common TX power setting is stated since we do not use per BLE RF TX power setting in AT firmware, but same TX power setting across all 4 BLE PHY’s.
NOTE 3: IMPLEMENT in AT firmware target RF TX power conducted. This target actual implemented in AT firmware. So for South Korea, this is actual target 10dBm conducted).
To implement that, NOTE 4A defines what Antenna Gain setting MUST be used and NOTE 4B defines what TX power setting MUST be used.
NOTE 4: IMPLEMENTED in AT firmware (or MUST implement in customers own developed C-code) the Actual target RF TX power conducted:-
NOTE 4A: the Antenna Gain setting of 0dBi and
NOTE 4B: the TX power setting to 10dBm which results in:
Target Actual RF TX power (dBm) = TX power setting (dBm) - Antenna Gain setting(dBi)
10dBm = 10dBm – 0dBi
Global (Lowest Common Across Certified Countries) Radio RF TX Power Table
| Module Ezurio Part number | 453-000170 | ||||||||
| Description | Module, SIP, Lyra 24S, Integrated Antenna (Silicon Labs EFR32BG24) | ||||||||
| Antenna Gain (dBi) | 1.48dBi peak for Integrated antenna. 2.0dBi peak external antenna. | ||||||||
| Radio Regulatory country: | Global (lowest common across certified countries) | ||||||||
| Declared as FHSS or DTS? | FHSS | ||||||||
| AFH FW module? | AFH firmware module turned ON. | ||||||||
| Silabs BLE SDK: | 5.0.0.0 GA (December 14, 2022). | ||||||||
| Silabs Gecko SDK Suite: | 4.2 (December 14, 2022). | ||||||||
| 10dBm mode | CERTIFIED maximum conducted RF TX power per BLE PHY | CERTIFIED LOWEST COMMON RF TX power setting across BLE PHY’s, other restrict… | IMPLEMENTED in Ezurio AT FW or customer MUST implement in customers own developed C-code. AFH firmware module turned ON. | ||||||
| NOTE 1 | NOTE 2 | NOTE 3 | NOTE 4A | NOTE 4B | |||||
| BLE PHY | Physical channel (channel Index) | Frequency (MHz) channel centre. | Certified conducted Maximum TX Power setting dBm | Certified Measured Conducted Peak POWER (dBm) | Certified Lowest common conducted certified RF TX power setting across all 4 BLE data rates. | Target RF TX power conducted to implement in FW. Other restrictions (if any). | Antenna Gain setting in FW | TX power setting in FW | |
| BLE 1Mbps | CH0 (CH37) | 2402 | 7dBm | 7.45dBm | 7dBm | 7dBm | 0dBi | 7dBm | |
| CH39 (CH39) | 2480 | 7dBm | 7.16dBm | 7dBm | 7dBm | 0dBi | 7dBm | ||
| BLE 2Mbps | CH1 (CH0) | 2404 | 7dBm | 7.46dBm | 7dBm | 7dBm | 0dBi | 7dBm | |
| CH38 (CH36) | 2478 | 7dBm | 7.16dBm | 7dBm | 7dBm | 0dBi | 7dBm | ||
| BLE 125kbps | CH0 (CH37) | 2402 | 7dBm | 7.45dBm | 7dBm | 7dBm | 0dBi | 7dBm | |
| CH39 (CH39) | 2480 | 7dBm | 7.17dBm | 7dBm | 7dBm | 0dBi | 7dBm | ||
| BLE 500kbps | CH0 (CH37) | 2402 | 7dBm | 7.45dBm | 7dBm | 7dBm | 0dBi | 7dBm | |
| CH39 (CH39) | 2480 | 7dBm | 7.17dBm | 7dBm | 7dBm | 0dBi | 7dBm | ||
NOTE 1: CERTIFIED maximum conducted RF TX power per BLE PHY in 20dBm mode or 10dBm mode tables. This is not what is implemented in AT firmware, this is what was certified only.
NOTE 2: Certified Lowest common TX power setting across BLE PHY’s. This lowest common TX power setting is stated since we do not use per BLE RF TX power setting in AT firmware, but same TX power setting across all 4 BLE PHY’s.
NOTE 3: IMPLEMENT in AT firmware target RF TX power conducted. This target actual implemented in AT firmware. So for Global (lowest common across certified countries), this is actual target 7dBm conducted).
To implement that, NOTE 4A defines what Antenna Gain setting MUST be used and NOTE 4B defines what TX power setting MUST be used.
NOTE 4: IMPLEMENTED in AT firmware (or MUST implement in customers own developed C-code) the Actual target RF TX power conducted:-
NOTE 4A: the Antenna Gain setting of 0dBi and
NOTE 4B: the TX power setting to 7dBm which results in:
Target Actual RF TX power (dBm) = TX power setting (dBm) - Antenna Gain setting(dBi)
7dBm = 7dBm – 0dBi
Bluetooth SIG Qualification
The Bluetooth Qualification Process promotes global product interoperability and reinforces the strength of the Bluetooth® brand and ecosystem to the benefit of all Bluetooth SIG members. The Bluetooth Qualification Process helps member companies ensure their products that incorporate Bluetooth technology comply with the Bluetooth Patent & Copyright License Agreement and the Bluetooth Trademark License Agreement (collectively, the Bluetooth License Agreement) and Bluetooth Specifications.
The Bluetooth Qualification Process is defined by the Qualification Program Reference Document (QPRD) v3.
To demonstrate that a product complies with the Bluetooth Specification(s), each member must for each of its products:
- Identify the product, the design included in the product, the Bluetooth Specifications that the design implements, and the features of each implemented specification
- Complete the Bluetooth Qualification Process by submitting the required documentation for the product under a user account belonging to your company
The Bluetooth Qualification Process consists of the phases shown below:
To complete the Qualification Process the company developing a Bluetooth End Product shall be a member of the Bluetooth SIG. To start the application please use the following link: Apply for Adopter Membership
Scope
This guide is intended to provide guidance on the Bluetooth Qualification Process for End Products that reference multiple existing designs, that have not been modified, (refer to Section 3.2.2.1 of the Qualification Program Reference Document v3).
For a Product that includes a new Design created by combining two or more unmodified designs that have DNs or QDIDs into one of the permitted combinations in Table 3.1 of the QPRDv3, a Member must also provide the following information:
- DNs or QDIDs for Designs included in the new Design
- The desired Core Configuration of the new Design (if applicable, see Table 3.1 below)
- The active TCRL Package version used for checking the applicable Core Configuration (including transport compatibility) and evaluating test requirements
Any included Design must not implement any Layers using withdrawn specification(s).
When creating a new Design using Option 2a, the Inter-Layer Dependency (ILD) between Layers included in the Design will be checked based on the latest TCRL Package version used among the included Designs.
For the purposes of this document, it is assumed that the member is combining unmodified Core-Controller Configuration and Core-Host Configuration designs, to complete a Core-Complete Configuration.
Qualification Steps When Referencing a single existing design, (unmodified) – Option 1 in the QPRDv3
For this qualification, follow these steps:
- To start a listing, go to: https://qualification.bluetooth.com/
- Select Start the Bluetooth Qualification Process.
- Product Details to be entered:
- Project Name (this can be the product name or the Bluetooth Design name).
- Product Description
- Model Number
- Product Publication Date (the product publication date may not be later than 90 days after submission)
- Product Website (optional)
- Internal Visibility (this will define if the product will be visible to other users prior to publication)
- If you have multiple End Products to list then you can select ‘Import Multiple Products’, firstly downloading and completing the template, then by ‘Upload Product List’. This will populate Qualification Workspace with all your products.
- Specify the Design:
- Do you include any existing Design(s) in your Product? Answer Yes, I do.
- Enter the single DN or QDID used in your, (for Option 1 only one DN or QDID can be referenced)
- Once the DN or QDID is selected it will appear on the left-hand side, indicating the layers covered by the design.
- Select ‘I’m finished entering DN’s
- What do you want to do next? Answer, ‘Use this Design without Modification’
- Save and go to Product Qualification Fee
- Product Qualification Fee:
- It’s important to make sure a Prepaid Product Qualification fee is available as it is required at this stage to complete the Qualification Process.
- Prepaid Product Qualification Fee’s will appear in the available list so select one for the listing.
- If one is not available select ‘Pay Product Qualification Fee’, payment can be done immediately via credit card, or you can pay via Invoice. Payment via credit will release the number immediately, if paying via invoice the number will not be released until the invoice is paid.
- Once you have selected the Prepaid Qualification Fee, select ‘Save and go to Submission’
- Submission:
- Some automatic checks occur to ensure all submission requirements are complete.
- To complete the listing any errors must be corrected
- Once you have confirmed all design information is correct, tick all of the three check boxes and add your name to the signature page.
- Now select ‘Complete the Submission’.
- You will be asked a final time to confirm you want to proceed with the submission, select ‘Complete the Submission’.
- Qualification Workspace will confirm the submission has been submitted. The Bluetooth SIG will email confirmation once the submission has been accepted, (normally this takes 1 working day).
- Download Product and Design Details:
- You can now download a copy of the confirmed listing from the design listing page and save a copy in your Compliance Folder
For further information, please refer to the following webpage:
https://www.bluetooth.com/develop-with-bluetooth/qualification-listing/
Example Design Combinations
The following gives an example of a design possible under option 1:
Ezurio End Product design using Silicon Labs Component based design
| Design Name | Owner | Declaration ID | QD ID | Link to listing on the SIG website |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lyra 24P / Lyra 24S | Ezurio | D063149 | 221359 | https://qualification.bluetooth.com/ListingDetails/192322 |
Qualify More Products
If you develop further products based on the same design in the future, it is possible to add them free of charge. The new product must not modify the existing design i.e add ICS functionality, otherwise a new design listing will be required.
To add more products to your design, select ‘Manage Submitted Products’ in the Getting Started page, Actions, Qualify More Products. The tool will take you through the updating process.
Ordering Information
Lyra 24S series modules operate in the 2.4 GHz ISM frequency band (BLE range: 2402-2480MHz).
The maximum RF TX power allowed by different regional regulatory authorities may differ from the maximum output power a module can produce. End-product manufacturers must then verify that the module is configured to meet the regulatory limits for each region in accordance with the local rules and the formal certification test reports.
See section Maximum Regulatory Certified RF TX Power per Country.
Lyra 24S modules are pre-programmed with Lyra 24S BGAPI UART/OTA DFU bootloader. Lyra 24S AT firmware can be loaded by the customer (via SWD interface or via boot loader (UART or OTA)).
| Part | Description |
|---|---|
| 453-00170C | Module, SIP, LYRA 24S, Integrated Antenna (Silicon Labs EFR32BG24) – Cut/Tape |
| 453-00170R | Module, SIP, LYRA 24S, Integrated Antenna (Silicon Labs EFR32BG24) – Tape/Reel |
| 453-00170-K1 | Development Kit, SIP, LYRA 24S, Integrated Antenna |
Legacy - Revision History
| Version | Date | Notes | Contributors | Approver |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.0 | 24 May 2023 | Initial Release | Robert Gosewehr, Raj Khatri, Dave Drogowski | Jonathan Kaye |
| 1.1 | 26 Jun 2023 | Added content for section 13.2 Maximum Regulatory Certified RF TX Power per Country | Raj Khatri | Jonathan Kaye |
| 1.2 | 31 Aug 2023 | Removed mention of Matter support. | Dave Drogowski | Jonathan Kaye |
| 1.3 | 15 Sept 2023 | Updated Bluetooth SIG Qualification. Updated to Bluetooth 5.4 | Dave Drogowski | Jonathan Kaye |
| 1.4 | 27 Mar 2024 | Changed Laird Connectivity to Ezurio | Raj Khatri | Jonathan Kaye |
| 1.5 | 30 Oct 2024 | Updated Bluetooth SIG Qualification. | Dave Drogowski | Jonathan Kaye |
| 2.0 | 11 Mar 2025 | Ezurio rebranding | Sue White | Dave Drogowski |
/filters:background_color(white)/2024-03/Lyra%2024%20-%20Collection1.png)