Applications of IIoT Across Industries
The versatility of IIoT allows it to be applied across various industries, each benefiting uniquely from its capabilities. Manufacturing, energy, and healthcare are among the primary sectors leveraging this to enhance their operations. By utilizing smart devices and connected networks, these industries can optimize their processes, improve efficiency, and gain instantaneous insights into their operations via data visualization.
Manufacturing
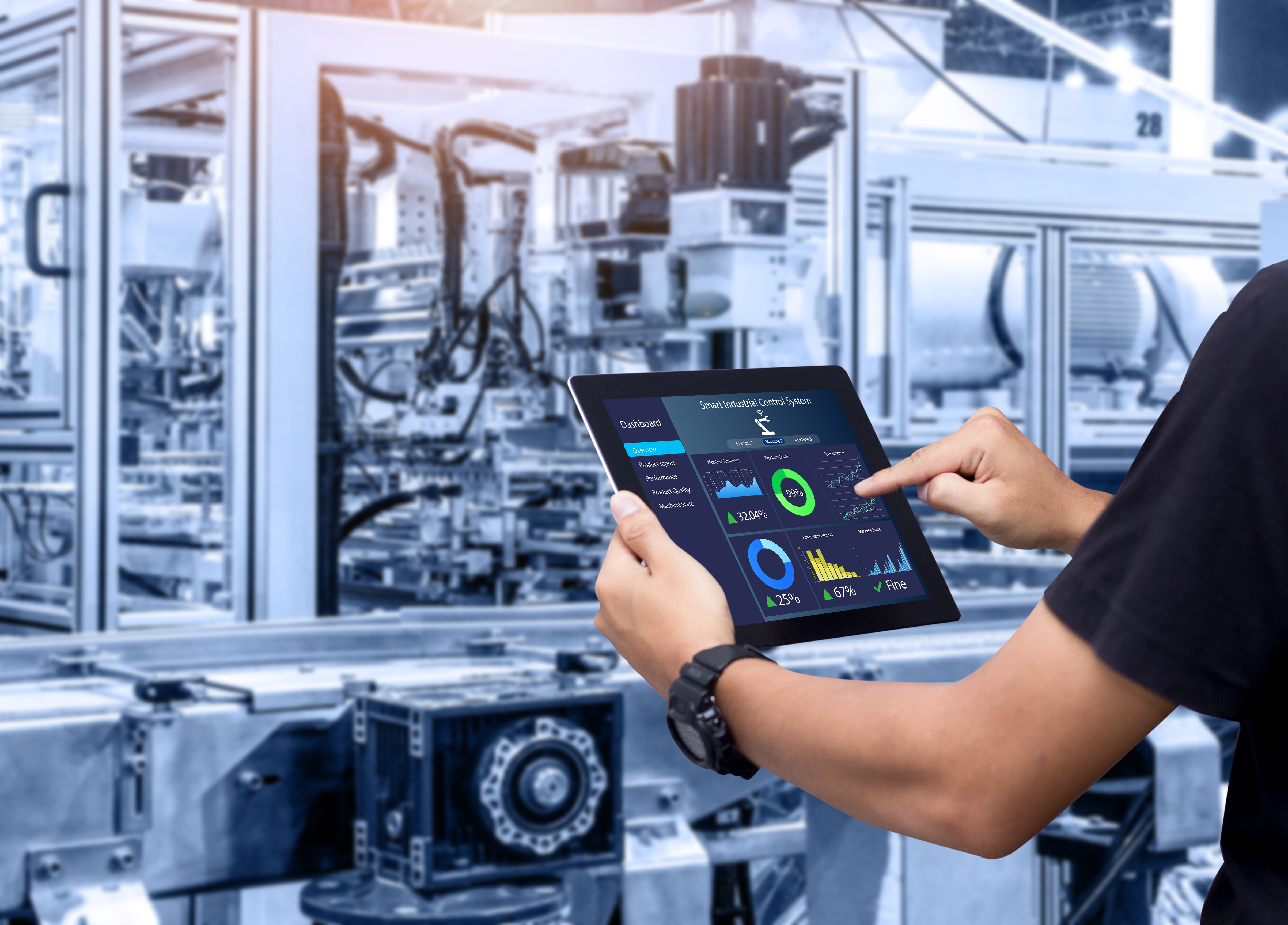
In the manufacturing industry, IIoT devices are transforming traditional production processes through predictive maintenance and continuous monitoring. By anticipating manufacturing equipment failures before they occur, IIoT helps minimize downtime and reduce maintenance costs. Manufacturing Execution Systems (MES) provide product and maintenance data to IIoT networks, enabling precise predictions and timely interventions. Furthermore, integrating these smart systems enhances safety by reducing human error and monitoring operational conditions.
Real-world examples demonstrate the impact of IIoT in manufacturing companies. Airbus’s digital manufacturing initiative, known as the factory of the future, utilizes IIoT to enhance production efficiency and asset management. Similarly, Magna Steyr employs IIoT to track assets and automatically order stock, streamlining supply chain processes.
These applications highlight how smart industry is revolutionizing the manufacturing landscape, making operations more efficient and responsive to market demands.
Energy Management
In energy management, IIoT technologies enable continuous data collection to optimize energy production and consumption. Smart grids, powered by IIoT, can dynamically adjust energy distribution based on demand and environmental conditions, ensuring efficient and reliable operations.
This capability is particularly valuable in the oil and gas industry, where precise control over energy resources is crucial for operational efficiency and cost management.
Healthcare
Healthcare is another sector where IIoT devices are making significant strides. By connecting smart medical devices, this improves patient diagnostics and treatment accuracy. Remote monitoring of vital signs allows healthcare providers to track patient health up to the minute, making data-driven decisions to enhance patient care.
These advancements not only improve the quality of care but also streamline healthcare operations, reducing the burden on medical staff and facilities.