In the last several years, applications for Wi-Fi modules in the realm of the IoT (Internet of Things) have broadened dramatically. From everyday household items to complex industrial systems, Wi-Fi technology is integral in facilitating seamless communication between devices. This blog post explores how Wi-Fi modules are utilized across various sectors, including smart home appliances, healthcare, and retail, enhancing a product’s functionality and providing users with a more interconnected experience. We delve into the technical aspects, potential challenges, and the future prospects of Wi-Fi technology in IoT applications.
What is a Wi-Fi Module?
A Wi-Fi module is a self-contained PCB board that enables wireless communication and data connectivity to a Wi-Fi network. These modules typically consist of a high-performance microcontroller, a Wi-Fi transceiver, and onboard memory that stores not just firmware, but also things like certificates, credentials, and other necessary files. The module is designed to be integrated into a host electronic device or system, providing them with the capability to connect to and communicate over a Wi-Fi network without the need for complex hardware or software development.
Wi-Fi modules are designed for flexibility, available in various forms such as compact surface-mount modules suitable for space-constrained devices, and larger modules that include external antennas for extended range requirements. This versatility makes them ideal for a wide range of applications, from consumer electronics to industrial embedded systems.
One of the key features of a Wi-Fi module is its ability to provide seamless wireless connectivity for IoT (Internet of Things) devices. IoT devices, such as smart home appliances, industrial sensors, and wearable technology, often require a wireless connection to the internet to send and receive data. Wi-Fi modules enable these devices to leverage the ubiquity and reliability of Wi-Fi networks, making it possible for users to access and control their devices remotely. This functionality has contributed to the proliferation of smart devices in various aspects of modern life, from home automation to healthcare monitoring and industrial automation.
Another important application of Wi-Fi modules is in the development of embedded systems and wireless communication products. By incorporating a Wi-Fi module into a design, engineers and developers can quickly add wireless connectivity to their products without having to build the Wi-Fi functionality from scratch. Developers can leverage pre-certified modules to avoid the lengthy and costly process of regulatory approval in their end device, significantly reducing development time and complexity, allowing for faster time-to-market and more efficient utilization of resources. With the widespread adoption of Wi-Fi in consumer and industrial applications, Wi-Fi modules have become essential building blocks for creating innovative and connected products across various industries.
Often, a Wi-Fi module will also feature Bluetooth on the same device. Wi-Fi + Bluetooth combination modules (such as our Sona™ line of Wi-Fi 6/6E + Bluetooth 5 modules) further simplify integration by providing both Wi-Fi and Bluetooth connectivity in a single module. This is a further value-add for hardware manufacturers, as Bluetooth and Wi-Fi are two of the most commonly used wireless protocols and are available on nearly every personal device (such as smartphones and tablets). This makes an OEM’s device further connectable to the existing ecosystem of products in the hands of most users.
Common Applications of Wi-Fi Modules
Wi-Fi modules have become crucial components in a wide range of applications due to their ability to enable wireless connectivity and communication. Here are some common applications where Wi-Fi modules are utilized:
IoT Devices
Wi-Fi modules play a significant role in the Internet of Things (IoT) ecosystem. They enable smart devices such as thermostats, lights, cameras, and speakers to connect to a home or building network, thereby allowing users to control and monitor these devices remotely through smartphones, control panels, or other connected devices.
For example, products like smart thermostats use Wi-Fi modules to connect to the internet, leveraging standards like IEEE 802.11ax (Wi-Fi 6/6E) to provide sufficient bandwidth, range, and data rates to handle multiple device connections and even stream high-definition video (smart cameras).
Industrial Automation
In industrial environments, such as manufacturing and logistics, Wi-Fi modules need to be robust and reliable to create wireless networks that connect various sensors, machines, and devices. This connectivity facilitates real-time data monitoring, remote diagnostics, and control, leading to increased efficiency, productivity, and cost-effectiveness.
For instance, industrial manufacturing plants use Wi-Fi 6 to connect various robots and automated guided vehicles (AGVs) on the assembly line to the greater network. The ability of Wi-Fi 6 to handle high density of devices environments ensures that AGVs and robotic arms can receive and transmit information with minimal delays. This synchronization is crucial for real-time data processes where timing and coordination directly impact production efficiency and quality.
Healthcare & Connected Hospitals
Wi-Fi modules are employed in medical devices and wearables, enabling healthcare professionals to collect and analyze patient data remotely. These modules also facilitate wireless communication between medical devices, providing seamless connectivity to hospital networks and systems, helping in patient monitoring, and improving the overall quality of healthcare services.
Healthcare devices are required to comply with strict security protocols to protect sensitive patient data. Wi-Fi modules equipped with Wi-Fi Protected Access 3 (WPA3) encryption are commonly used to ensure data transmitted by diagnostic equipment, patient monitors, and medical records remain secure. Some of the most advanced Wi-Fi modules or System-on-Modules (SOMs) also support onboard FIPS acceleration, which complies with stringent encryption requirements imposed by the US Federal Government in places like government hospitals.
Retail and Hospitality
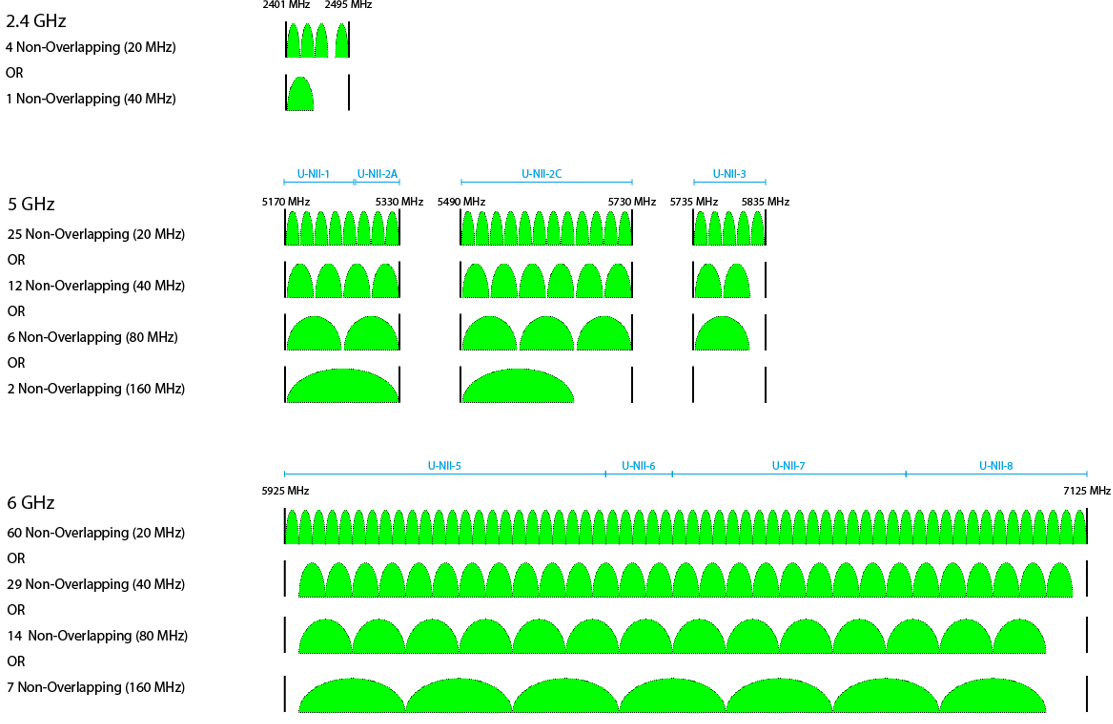
The retail and hospitality sectors utilize Wi-Fi modules to not only provide wireless internet access to customers, but also support backend services like inventory tracking and customer management systems. Wi-Fi modules since Wi-Fi 4 generally support dual-band connectivity (2.4 GHz and 5 GHz) to accommodate a high density of users with minimal interference. Wi-Fi modules are integrated into routers and access points, enabling reliable and high-speed internet connectivity for guests in hotels, restaurants, cafes, and shopping centers.
In addition to the above applications, Wi-Fi modules are extensively used in consumer electronics, automotive, agriculture, and many other industries. These modules have revolutionized the way we interact with technology, allowing for seamless wireless connectivity and the ability to integrate devices into the larger digital ecosystem. Wi-Fi is generally the most popular Wireless Local Area Network (WLAN) technology, and it’s crucial to all of these environments and applications.
How To Select a Wi-Fi Module
Choosing the right Wi-Fi module is key for seamless wireless connectivity and communication. Let's explore the key considerations in selecting a Wi-Fi module for your specific IoT application.
Understanding Wi-Fi Protocols
The Wi-Fi module you choose not only affects the security and efficiency of your IoT application, but also determines its compatibility and future scalability. Modules should support standard protocols like TCP/IP for networking and HTTP for web services. Additionally, lightweight IoT applications can leverage protocols like MQTT or CoAP over Wi-Fi, which are designed for IoT with low bandwidth design for effective machine-to-machine (M2M) communication.
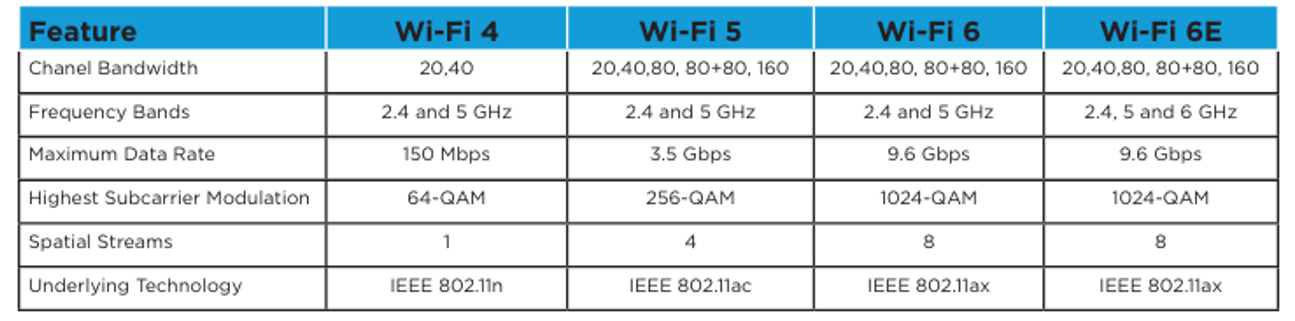
Wi-Fi modules support a wide range of standards from 802.11b/g/n to 802.11ax, accommodating various application needs. The choice of protocol impacts your module’s data rate, range, and energy efficiency.
- 802.11be (Wi-Fi 7) was just released in January 2024 by the Wi-Fi Alliance. This advancement promises to boost the speed and stability of wireless connections, however, it is not yet recommended for design as support is scarce.
- 802.11ax (Wi-Fi 6) is highly recommended for applications that demand high data throughput and efficiency, particularly useful in environments with many connected devices. It allows OEMs to optimize for both ends of the performance scale, from low bandwidth and low power consumption up to high bandwidth and throughput, and everywhere in between.
- 802.11ac (Wi-Fi 5) offers improved speed and bandwidth for sense areas.
- 802.11n (Wi-Fi 4) provides a cost-effective solution with a good balance of range and speed for less demanding applications.