Embedded Python for Wireless Devices
Canvas Firmware incorporates platform middlewareoffering APIs to RTOS functions (low level drivers, bootloader, filesystem, peripheral bus, timers, radio/networking stacks, etc.) and Scripting Engine support. This enables most applications to be developed entirely in a scripting language while providing access to powerful embedded hardware features through C-based modules as needed. This architecture abstracts most of the chipset, SDK and RTOS details from the upper layers of the software stack allowing developers to focus on writing applications to a consistent API in high-level scripting languages like Python.
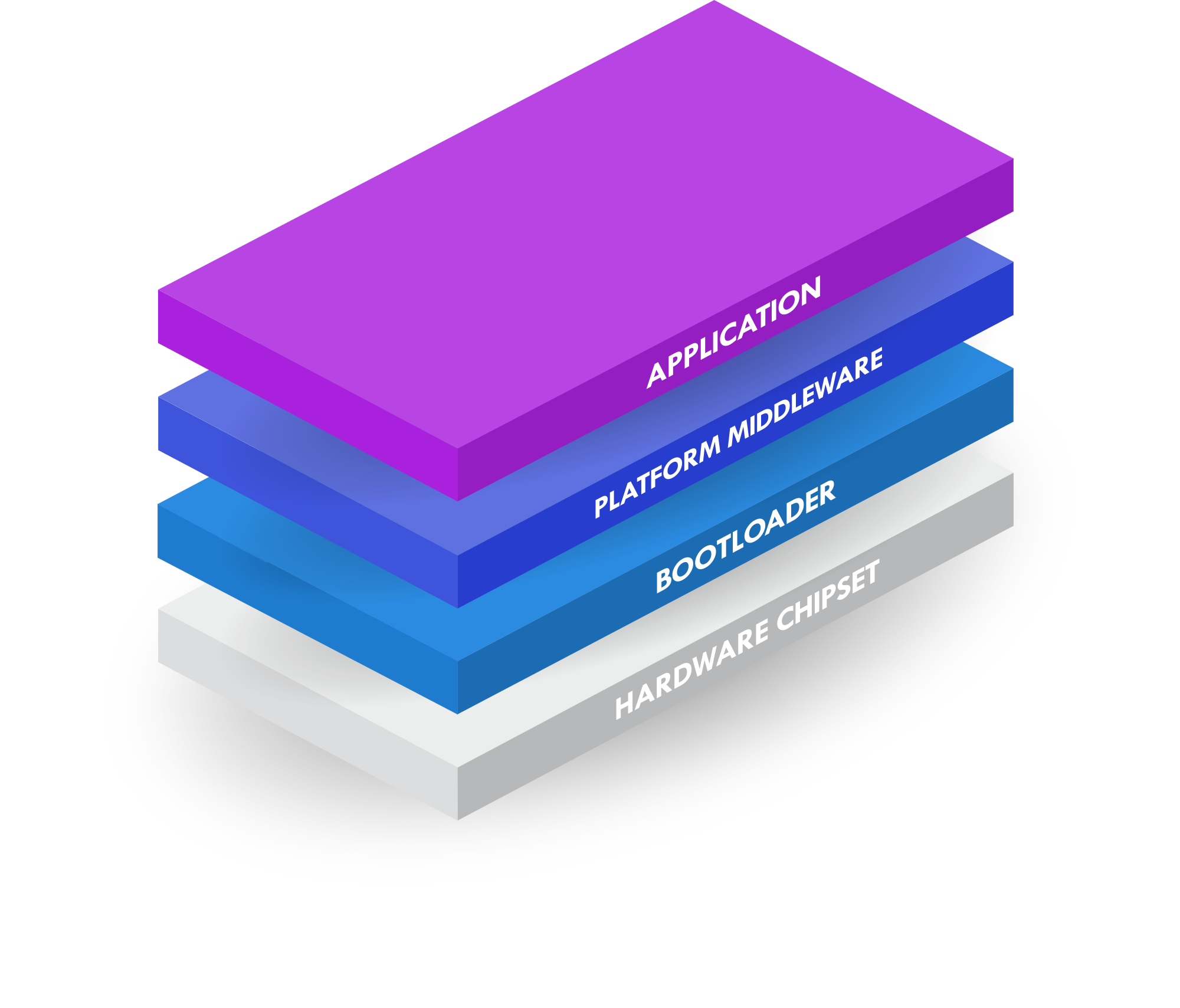
This document focuses on how developers can write their applications in Python using the tools provided by the Canvas Software Suite.
Hardware Configuration Options
Hostless/Standalone Operation
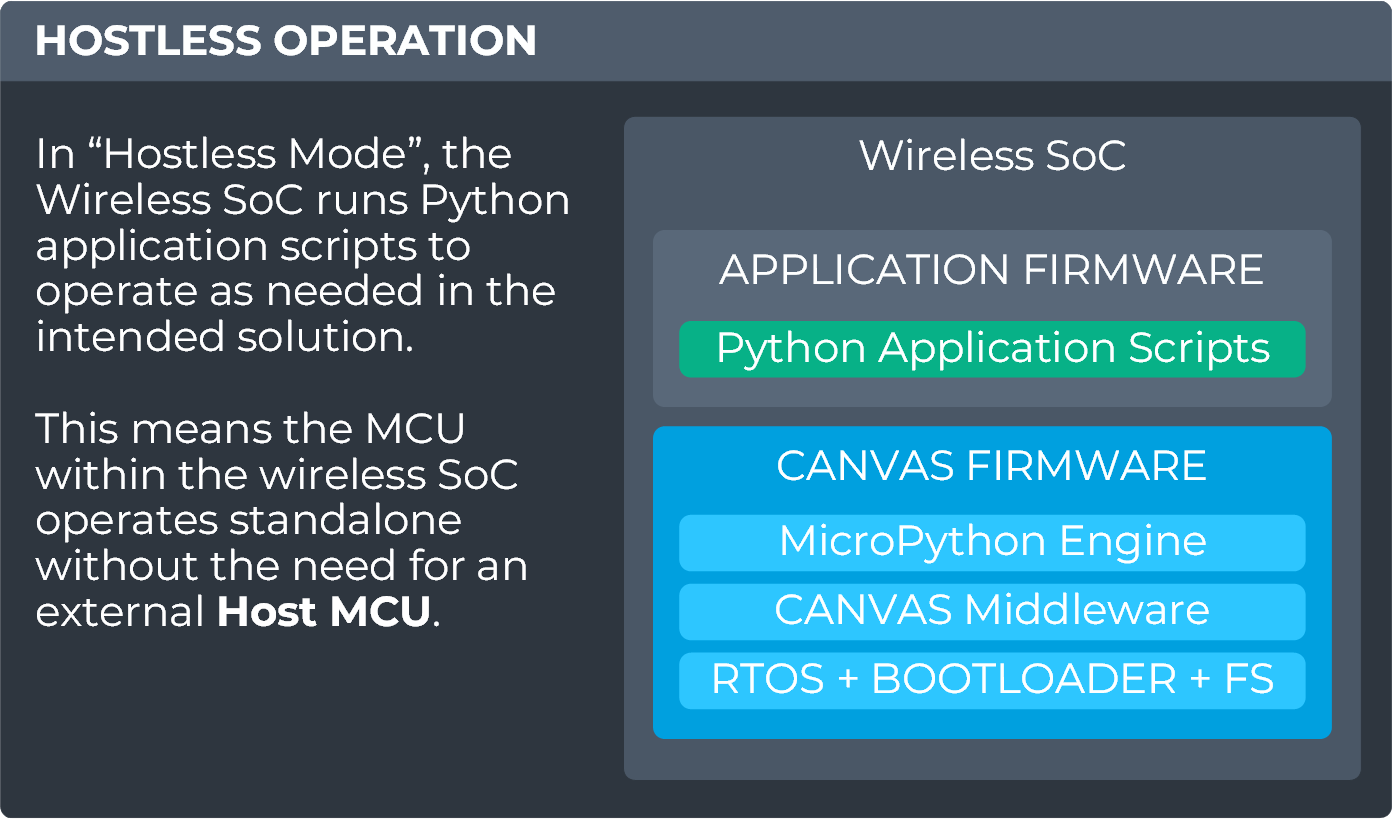
Devices supporting Canvas Firmware include an embedded MicroPython engine capable of operating radios (e.g., Ultrawideband, Bluetooth Low Energy) and peripheral bus interfaces through on-device Python APIs to ease integration with sensors and other hardware needed by your application. Integrating Canvas-enabled wireless radio modules into your product design has never been simpler now that you can develop your embedded software applications using Python!
Hosted Operation
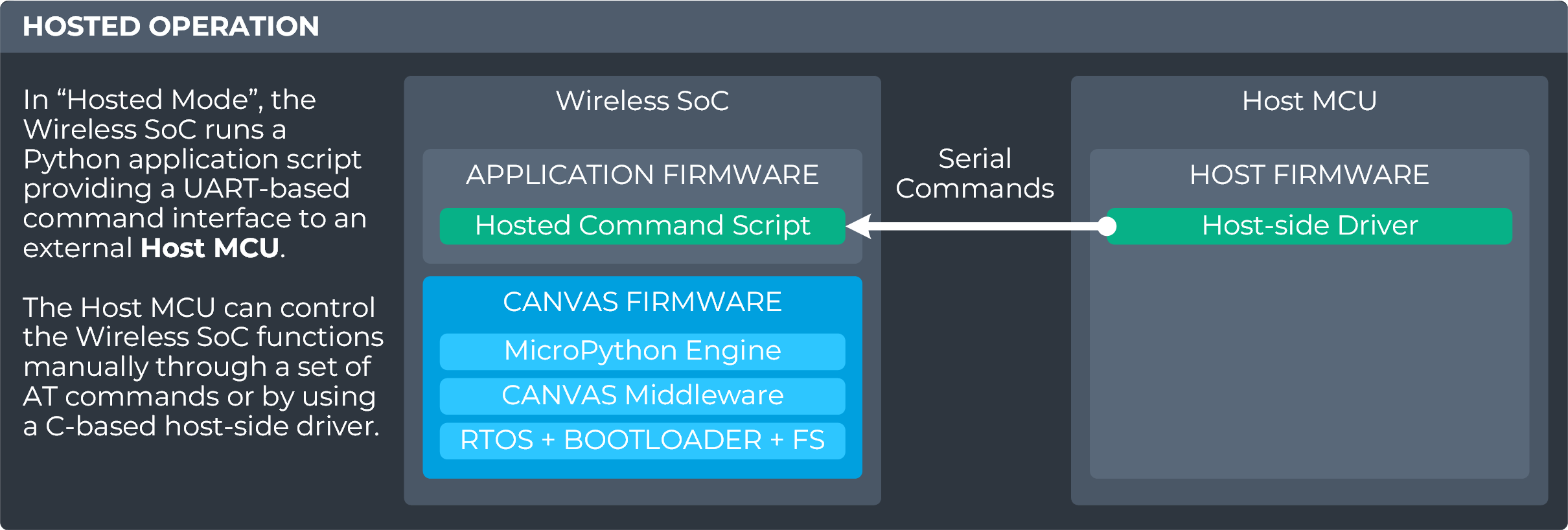
Need to operate a Canvas-enabled module from an external host MCU? No problem! Canvas Firmware also offers AT command scripting and host-side driver code to access radio functionality from an external host. This is implemented this via on-module Python scripts providing handlers for either AT commands or radio-side implementation of the host driver. Choose an AT Command Set Python script (text transport) or Host-side driver Python script (binary transport) depending on your preferred interface to the module.
Xbit VS Code Extension
To simplify authoring and editing Pythons scripts for applications on Canvas-enabled hardware, we’ve developed the Xbit VS Code Extension (orXbit VSC for short). Xbit VSC is available right from inside the VS Code Extensions menu via the Extensions Marketplace. Click the Extensions menu and search for ‘xbit’.
The Xbit tools for VS Code Marketplace Page provides details on how to use the extension to load and edit Python files on supported DVK boards and other products.
Sample Applications
To get started with Python on your Canvas Firmware supported device, you can try running one of the following sample Python applications to get familiar with how embedded Python can provide access to the embedded hardware.
Each sample below will contain a code section that can be copied/pasted into a file named main.py on your board using Xbit VSC. After saving to your board, press the Reset button within Xbit VSC or physical RESET button on the board to start running the script.
Hello World
This simple Python script provides a very basic example for displaying a string to the serial terminal. In this case, a simple greeting and the version of Canvas Firmware currently running on your board.
main.py:
import os
print('\n\nHello from Canvas Firmware v' + os.uname().release + '\n')A Simple Timer
This sample shows how to setup a simple timer and increment a counter to display a message.
main.py:
import canvas
# Create a callback function to be called by the timer
def timer_callback(event):
# Check if the counter has reached 50
if(event['counter'] == 50):
timer.stop()
print('Counter is', event['counter'], ', Timer stopped')
else: # otherwise print the counter and increment it
print('Counter is', event['counter'], 'and timer is running')
event['counter'] = event['counter'] + 1
# Create a dictionary to hold the timer data
timer_data = {'counter': 1}
# Setup a timer to tick every 50 milliseconds
timer = canvas.Timer(50, True, timer_callback, timer_data)
# Display a message and start the timer
print('\n\nStarting a timer to print a counter 50 times.')
timer.start()More sample applications can be found on the Canvas Python Samples page:
https://github.com/Ezurio/canvas_python_samples
Canvas Python API Documentation
To learn more about what APIs are available from within Python on Canvas-enabled devices, take a look at the detailed Canavs Python API Docs here:
/filters:background_color(white)/2024-06/BL54L10-Group.png)
/filters:background_color(white)/2024-01/BL54L15-Group.png)
/filters:background_color(white)/2024-06/BL54L15ug_SA%20and%20ST-right11.363.png)
/filters:background_color(white)/2024-03/canvas-software-suite-red.png)
/filters:background_color(white)/2024-03/Family%20-%20Sera%20NX040%20-%20Embossed%20-%20nxp-nordic.png)