Sentrius IG60-BL654 and IG60-BL654-LTE Wireless IoT Gateway
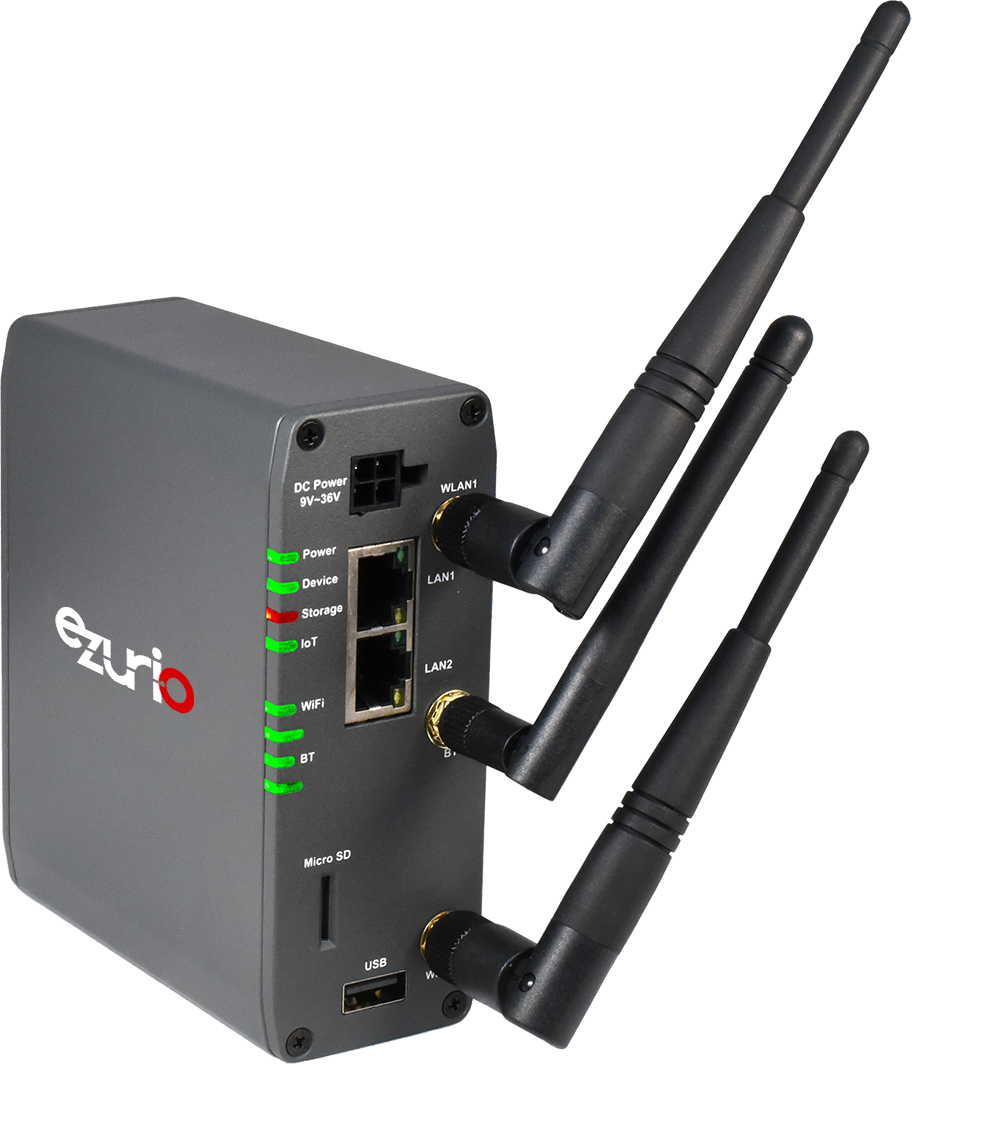

Overview
New! IG60-BL654-LTE adds LTE Cat-1 Modem!
The Sentrius™ IG60-BL654 brings all of Ezurio’s industrial wireless and IoT capabilities into one unique solution. The IG60-BL654 replaces the previous model's serial port with an integrated BL654 module, bringing advanced Bluetooth 5 features for next-gen IoT Bluetooth applications. IG60-BL654-LTE model features additional LTE Cat-1 functionality (requires active SIM card with supported mobile carrier).
Based on Ezurio's 60-series and BL654, capture data from Bluetooth 5 sensors, add cloud-managed edge intelligence, and send to the cloud with 802.11ac Wi-Fi.
We provide them with Laird Linux, a rugged, open environment for your application, provided with our Linux build, hardware root of trust, and development tools. Based on our powerful 60 Series SOM.
- Best-in-Class Wireless Performance - Full Bluetooth 5 and 802.11ac Wave 2 with 2x2 MIMO
- Multiple Ways to Connect - Wi-Fi, Bluetooth 5, Ethernet, USB
- Chain of Trust - signed and secured at every layer to protect your device
- Industry Leading Support - Global Tier 2 and FAE support for your application
Buy Now
Power Supplies Sold Separately
Don’t forget to also order a power adapter! The IG60 does NOT come with one!
| REGION | PART NUMBER |
|---|---|
| US AC Adapter | 223-00007 |
| Europe AC Adapter | 223-00008 |
| UK AC Adapter | 223-00009 |
| DC Adapter | 131-00225 |
Prove it Works! Request a Whiteboard Session with our team.
Developing and implementing wireless IoT solutions is complex and there are a lot of moving parts. We will help you map it out so you know exactly what you need.
What’s involved:
- Map the business model
- Define the technology
- Tackle tough questions like security, provisioning, and updates at scale
- Select the right products and applications to meet the technical requirements at the right price points
Talk to our team about getting your application connected to the cloud.
Ezurio is an NXP Gold Partner
Ezurio is honored to be approved as an NXP Gold Partner! We look forward to working with the NXP team to deliver the solutions our customers need in an ever changing wireless future. Please follow the link for more information.

Specifications
| Part Number | Price @ 1K | Additional Description | Antenna Type | Chipset (Wireless) | Frequency Range (Max) | Frequency Range (Min) | Frequency Range 2 (Max) | Frequency Range 2 (Min) | Logical Interfaces | OS/Software | Product Type | Software | System Architecture | Technology |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
131-00225Buy Options | N/A | DC Cable (Global), 20AWG, UL2464, 41 Strands, Black | DC Cable | |||||||||||
223-00007Buy Options | N/A | AC Adapter (US), 12V-4A, US, 4-pin 7.5mm x 9.2mm Plug | AC Adapter | |||||||||||
223-00008Buy Options | N/A | AC Adapter (Europe), 12V-4A, EU, 4-pin 7.5mm x 9.2mm Plug | AC Adapter | |||||||||||
223-00009Buy Options | N/A | AC Adapter (UK), 12V-4A, UK, 4-pin 7.5mm x 9.2mm Plug | AC Adapter | |||||||||||
455-00076 Active Buy Options | N/A | Sentrius™ IG60-BL654 Gateway with Laird Linux | External | NXP (Marvell) 88W8997, Nordic nRF52840 | 2483 MHz | 2400 MHz | 5825 MHz | 5150 MHz | USB, Ethernet, Micro SD | Laird Linux | IoT Gateway | Pre-Compiled images (or from source). Includes our BSP, Eclipse IDE support, and SDK | Hostless | 802.11ac, Bluetooth 5.1, Dual Mode (Classic + BLE), 802.15.4 / Thread / Zigbee |
455-00088 NRND Buy Options | N/A | Sentrius™ IG60-BL654-LTE Gateway with Laird Linux | External | NXP (Marvell) 88W8997, Nordic nRF52840 | 2483 MHz | 2400 MHz | 5825 MHz | 5150 MHz | USB, Ethernet, Micro SD | Laird Linux, smartBASIC | IoT Gateway | Pre-Compiled images (or from source). Includes our BSP, Eclipse IDE support, and SDK | Hostless | 802.11ac, Bluetooth 5.1, Dual Mode (Classic + BLE), 802.15.4 / Thread / Zigbee |
455-00081 EOL Buy Options | N/A | Sentrius™ IG60-BL654 Gateway with AWS Greengrass | External | NXP (Marvell) 88W8997, Nordic nRF52840 | 2483 MHz | 2400 MHz | 5825 MHz | 5150 MHz | USB, Ethernet, Micro SD | AWS IoT Greengrass | IoT Gateway | Integrated AWS Greengrass. Continuous over-the-air software updates from Laird for 3 years. Security built-in. | Hostless | 802.11ac, Bluetooth 5.1, Dual Mode (Classic + BLE), 802.15.4 / Thread / Zigbee |
455-00089 EOL Buy Options | N/A | Sentrius™ IG60-BL654-LTE Gateway with AWS Greengrass | External | NXP (Marvell) 88W8997, Nordic nRF52840 | 2483 MHz | 2400 MHz | 5825 MHz | 5150 MHz | USB, Ethernet, Micro SD | AWS IoT Greengrass, smartBASIC | IoT Gateway | Integrated AWS Greengrass. Continuous over-the-air software updates from Laird for 3 years. Security built-in. | Hostless | 802.11ac, Bluetooth 5.1, Dual Mode (Classic + BLE), 802.15.4 / Thread / Zigbee |
Documentation
Browse Certifications, Documentation, Legacy Materials, Product Briefs and Software in our Support & Documentation Center.
How do I configure my network connection?
NMCLI should be utilized to configure network interfaces.
How to connect to the IG60 serial console.
You can use the USB of IG60 for a serial interface. This is particularly useful when connection to the gateway can be lost, such as configuring network settings.
The following hardware is required:
1x Serial Null Modem Cable - DB-9 (F) to DB-9 (F)

2x USB to Serial RS232 Adapter Cables

To connect:
- Connect the three cables together.
- Insert one USB end to the IG60 and the other to your workstation.
- On the workstation open a terminal emulator.
- Enter the COM (serial interface) port that coincides with the serial interface to the IG60.
- Configure the connection Baud Rate 115200.
- Start the connection, the root password is "summit"
What are the difference between AWM-lite and AWM (Adaptive World Mode) ?
AWM, if active, sets the regulatory domain and country of the 60 series radio to the current location with the help of beacons it receives from surrounding access points.
To be FCC compliant, it's mandatory that the routine to determine the location must run every 30 minutes. This is a draw-back for softAPs created on the 60 series radio as connections will be interrupted every 30 minutes. Some clients may affected more heavily than others.
However, running the AWM routine regularly is not mandatory for the other regulatory domains for which the 60 series is certified. For those, it is enough that the location is determined upon the first run of the routine; it does not have to be repeated after that. That is what AWM-lite does.
For radios only deployed in ISED, ETSI, MIC, and KC regulatory domains, AWM-lite can be used. This also enables the seamless use of the 60 series radio as a softAP in conjunction with AWM(-lite).
It is also good practice to consult the application note app_note_60_summit_awm, which is located in the documents library of the 60 series radio software releases.
How do I enable the LTE modem inside an IG60-BL654-LTE ?
The LTE modem inside an IG60-BL654-LTE can be enable with the following command:
echo 0 > /sys/devices/platform/gpio/lte_on/value
A succesfull action will be indicated by two USB interfaces appearing:
# ip addr show
1: lo:
link/loopback 00:00:00:00:00:00 brd 00:00:00:00:00:00
inet 127.0.0.1/8 scope host lo
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
inet6 ::1/128 scope host
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
2: eth0:
link/ether fa:87:d7:c4:c1:e3 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
3: eth1:
link/ether 36:42:a6:34:a7:4e brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
4: wlan0:
link/ether c0:ee:40:44:e1:b4 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
5: usb0:
link/ether fa:96:11:12:13:14 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
6: usb1:
link/ether fa:96:11:12:13:16 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
Only usb0 is used by the LTE modem. usb1 can be ignored.
How to set MAC addresses of ETH Phys on 60-SOM and IG60 from release 10.140.0.12 onward?
From release 10.140.0.12 there is an easy way to set the MAC addresse for the two Ethernet phys on the 60-SOM and the IG60.
The command is called "mac". Please see example below:
# mac
Eth0:
Eth1:
# mac --help
usage: write: mac [-f] [xx:xx:xx:xx:xx:xx]
read: mac
# mac -f 11:22:33:44:55:66
Eth0: 11:22:33:44:55:67
Eth1: 11:22:33:44:55:66
# mac
Eth0: 11:22:33:44:55:67
Eth1: 11:22:33:44:55:66
How can I add my files to a Ezurio Linux build?
To add files to a Laird Linux build, enable "BR2_ROOTFS_OVERLAY" in your config and provide it with an absolute path to the directory you would like to overlay. Files in this directory will be inserted relative to "/". For example, if you would like to add files to "/etc" and the path to the overlay directory is "/buildroot/overlay", create a directory "/buildroot/overlay/etc/<files>
Should I use Adaptive World Mode when hosting an AP?
Adaptive World Mode should not be used when hosting an AP. The channel hopping algorithm can cause disconnect issues in some cases. The best option is to set the regulatory domain in firmware manually, but at the minimum the "adaptive_ww" service should be disabled.
How can I implement an HCI interface for the IG60-BL654?
An HCI interface can be implemented in lieu of using smartBASIC to communicate with / program the BL654 in Laird's IG60.
To achieve this, build the hci_uart example for BL654_DVK.
Bluetooth: HCI UART — Zephyr Project Documentation
Direct the output to a folder, for example:
west build -b bl654_dvk samples/bluetooth/hci_uart --pristine -d my_firmware
Download Ubutil—
Linux:
UBUtil Firmware Upgrade Generation Utility v1.0 – Linux / MAC | Ezurio
Windows:
UBUtil Firmware Upgrade Generation Utility v1.0 – Windows | Ezurio
Follow these instructions to create a .UBU:
Firmware Programming Guide (ezurio.com)
TLDR:
Copy the zephyr.hex from the "my_firmware" directory in Zephyr.
./UBUtil --create-key hci_uart.pem
./UBUtil --application-key-file hci_uart.pem --a0-version 1 --a0-compressed --a0-target 0 --a0-startaddress 0x1000 --a0-filetype 1 --a0-filename zephyr.hex --a0-keytype 1 --append-pub-key --output zephyr.hex --ubu-output hci_uart.ubu --ubu-platform 5ECB654F --ubu-flash-size 2097152 --ubu-sector-size 4096 --ubu-base-address 0 --ubu-align-length 4
Copy the .ubu to the IG60.
With the file on the gateway execute the following command:
- btpa_firmware_loader.py /dev/ttyS2 115200 hci_uart.ubu BL654
Reboot the system, then check /sys/class/bluetooth for hci0. If this sysfs node is present you've successfully created the HCI interface.
How do I set up a Wi-Fi Bridge connection?
Laird has added custom packages to Laird Linux. These can be found in "menuconfig", under the "Ezurio" / "Packages" section.
To enable a Wi-Fi bridge, select the package "BR2_PACKAGE_LRD_WIFI_BRIDGE" and then set the destination interface. For example, set the destination interface to "Ethernet" if you would like to bridge the Wi-Fi to a wired connection.
Installing and configuring REPO the easy way!
The repo tool is often available to be installed using a package manager. In the case you're facing challenges with this method, or would like to directly add the repo files to your path, the following commands can be used:
sudo wget https://storage.googleapis.com/git-repo-downloads/repo -O /usr/local/bin/repo
sudo chmod a+rx /usr/local/bin/repo
When you run the repo init command for the first time you will be asked to configure your name and email. You can also set these values with the following commands:
git config --global user.email "you@example.com"
git config --global user.name "Your Name"
git config --global color.ui trueHow to establish SSH connection with 60SOM and IG60 on builds without Network Manager entries for Ethernet?
With newer builds there are no default connections for Ethernet eth0 and eth1 anymore.
That prevents the device from getting an IP address to SSH in at.
In order to be able to establish an SSH connection again, it is possible to log in to the device through the serial debug console and define an Ethernet connection with this simple command:
# nmcli con add type ethernet con-name eth-connection ifname eth1
# nmcli con showNAME UUID TYPE DEVICE
eth-connection a6183425-8fd1-4e06-9ff5-7a8d0bb5b346 ethernet eth1
Routers providing IP addresses through DHCP will now issue an IP address to the 60SOM or IG60 again. If no DHCP is available, IP addresses can be added manually:
# nmcli con mod "eth-connection" ipv4.addresses "aaa.bbb.ccc.ddd"
IG60 How to set static IP in Ezurio Linux
Use Network Manager to set an IP address as static in Laird Linux. In the example below the IP address of ETH0 will be set to 192.168.2.150.
nmcli con add type ethernet con-name "static-ip" ifname eth0 ipv4.method manual ipv4.addresses 192.168.2.150/24
nmcli connection show
nmcli dev status
Does IG60 support Greengrass V2?
Yes, but it requires integrating Canvas Device Manager and EdgeIQ. This currently is only supported for high volume customers. Please contact your local Laird sales representative if need be.
How do I exit Bluetooth DTM direct test mode on the BL654 module in the IG60 Ezurio Linux
DTM functionality is integrated into our SmartBASIC firmware preloaded on the BL654 in the IG60 Laird Linux. Activation of DTM is done by AT+DTM command as described in this application note. Instead of using our UwTerminalX program you can use e.g., microcom to connect to the BL654 and communicate (microcom -s 115200 -p /dev/sttyS2, exit microcom with ctrl-x). After that DTM commands can be exercised which in fact are binary commands sent at 19200 baud instead of 115200 used for SmartBASIC interactive mode. However, most commands are composed of non-ascii bytes and hence it is not possible to enter these into microcom or other terminal programs. The below sequence shows how to send the exit-DTM-mode command from the Linux console as an example:
Set the serial port parameters to 19200/8N1:
stty -F /dev/ttyS2 19200 cs8 -parenb -cstopb
Echo a two-byte command (0x3f, 0xfe bytes) into the serial port device:
echo -ne "\x3f\xfe" > /dev/ttyS2
The -n switch will suppress the newline at string end and -e will allow for escape’ing of hex numbers. That way it will send the required bytes 0x3f and 0xff directly and raw into the serial port device.
Other DTM commands could be sent in the same way by replacing \x3f... with different hex numbers.
How do I disable the changing of the MAC address after each reboot for the IG60 and 60-SOM DVK running off an SD card with Ezurio Linux
You need to boot into Linux and after Login log in issue the command
fw_setenv ethaddr <desired MAC address> for example: fw_setenv ethaddr AABBCCDDEEFF and reboot You can read out the address previously set with: fw_printenv ethaddr
Is there an external IO pin on the IG60 Ezurio Linux I can use for my purposes?
Yes, there is one pin (4) on the power supply connector that can either be configured as an input or output.
The same pin can be connected to the AD converter of the IG60s host processor by software.
Consult Lairds application note "Configuring external I/O pin of the IG60 Laird Linux variant as input or output" to configure pin4 and this tutorial to use the AD converter on the host processor:
https://lairdcp.github.io/guides/60-som-dvk-docs/1.0/ad-converter-tutor…
How can I update the smartBASIC app on the BL654 in my IG60-BL654 Ezurio Linux?
Please see our IG60-BL654 online guide on Working with SmartBASIC on the IG60-BL654 Laird Linux Gateway.
How do I find out which clients are connected to the soft AP I created using my Ezurio Wifi module with Linux
Once you have created the soft AP on your Linux system and have successfully connected clients to the soft AP you can issue the command:
# iw wlan0 station dumpThis will get a list of connected clients.
Note: the interface name (here: wlan0) might be different in your system.
How can I talk to the BL654 BLE module inside the IG60 Gateway?
With access to the IG60 Laird Linux console you can start the terminal program "microcom" to issue AT commands to the integrated BL654 BLE module.
The BLE modulel istens on /dev/ttyS2.
# microcom /dev/ttyS2
To exit microcom use ctrl-x.
How do I set up an open hotspot using Network Manager?
You can use the Network Manager command line interface to create an open hotspot using this command:
nmcli con add con-name open_hotspot ifname wlan0 type wifi ssid yourSSID mode ap wifi.band bg wifi.channel 6 ipv4.method shared
Can I update the firmware of the BL654 module inside my IG60-BL654 Ezurio Linux gateway?
Yes. There is a python script on the IG60-BL654 LL developer SD card image called
btpa_firmware_loader.py
This can be used to upload a new firmware to the BL654 inside IG60-BL654 LL.
How to Exit a smartBASIC $autorun$ Application on the IG60-BL654 Gateway
There exist pre-defined GPIOs in the IG60 to control the BL654 module, which can be found under /sys/devices/platform/gpio:
- bt_nautorun: If set to 0 (low) autorun is active and and $autorun$ application will start after power up/reset and if set to 1 (high) autorun will be disabled.
- card_nreset: Setting to 0 (low) asserts BL654 reset and 1 (high) releases reset.
To exit an $autorun$ application nAUTORUN needs to be set high followed by a module reset.
echo 1 > /sys/devices/platform/gpio/bt_nautorun/value (disables autorun) echo 0 > /sys/devices/platform/gpio/card_nreset/value (assert reset) echo 1 > /sys/devices/platform/gpio/card_nreset/value (release reset) echo 0 > /sys/devices/platform/gpio/bt_nautorun/value (re-enable autorun)
You should now be able to connect to the BL654 through e.g. microcom with access to the smartBASIC interactive mode:
microcom -s 115200 /dev/ttyS2
You can now use e.g. AT&F* to clear the flash file system before loading a new smartBASIC app to the module with the above Python script. (Note: CTRL-x will exit microcom).
Note: You can always check the current state of the above GPIOs with
cat /sys/devices/platform/gpio/.../value
See also the IG60-BL654 Online Guide on SmartBASIC with the IG60.
What is IP rating
IP stands for Ingress Protection. Its a standard we use to check the sealability of a product once it is installed.
It is composed as IP## , where first digit is for dust/solid objects and the 2nd digit, is for liquids.
Here is the meaning for each numerical code:
| First Digit | Description |
|---|---|
| 0 | No protection |
| 1 | Ingress of solid object diameter 50 mm is protected |
| 2 | Ingress of solid object diameter 12.5 mm is protected |
| 3 | Ingress of solid object diameter 2.5 mm is totally protected |
| 4 | Ingress of solid object diameter 1.0 mm is totally protected |
| 5 | Protected against harmful dust |
| 6 | Totally protected against dust |
| 2nd Digit | Description |
|---|---|
| 0 | No protection no protection against liquid object No test |
| 1 | Protection against water drop vertically |
| 2 | Protection against water drop 15° Tilt from its normal position |
| 3 | Protection against water spray 60° from the vertical direction |
| 4 | Protection from water splash from all direction |
| 5 | Protection from water jets from all direction |
| 6 | Protection from strong water jets from all direction |
| 7 | Protection from water dip 1 m depth water for 30 min |
| 8 | Protection from water sink should be decided between customer and manufacturer |
Can I XCompile a smartBASIC script without a module attached to UWTerminalX?
There exist three solutions:
Using the offline XCompiler
- Copy the relvant version of XCompiler (found in the firmware zip file for your relevant firmware version) to the folder that contains your smartBASIC application.
- Say, your XCompiler is called xcomp_bl652_1234_5678.exe and your smartBASIC app is called jenniferRocks.sb. Then open a command prompt window in that folder and issue the command xcomp_bl652_1234_5678.exe jenniferRocks.sb and if there are no errors you will see a file called jenniferRocks.uwc being created which is what gets downloaded to the module by UwTerminal.
- In the file name xcomp_bl652_1234_5678.exe The ?bl652? comes from the AT I 0 response and the ?1234_5678? comes from the AT I 13 response
Using the online XCompiler
- Lairds online XCompiler is available at http://uwterminalx.no-ip.org/
- You can upload a SmartBASIC source code file and when successfully compiled, the browser will automatically download the compiled .uwc file.
- Note that compiling with the online XCompiler is limted to a single source code file (#include statements are not supported)
Using the Online XCompiler Tool
- The Online XCompiler Tool is a frontend for our online XCompiler and supports multiple source code files through #include statements. You can select a source code file and the tool automatically compiles it and stores the .uwc locally.
Become an Ezurio Customer to Gain Exclusive Access to Our Design Experts
- Antenna Scans
- Antenna selection and placement
- Custom antenna design
- Worldwide EMC testing / certifications
- Embedded RF hardware / firmware design
- Cloud architecture and integration
- Mobile application development
- Product & Industrial Design
Distributors
| Distributor | Phone Number | Region | Website |
|---|---|---|---|
| Arrow Electronics | 1-855-326-4757 +44 2039 365486 |
APAC, North America, South America, EMEA | Website |
| Braemac Australia, New Zealand, South East Asia | +61 2 9550 6600 +64 9 477 2148 |
APAC | Website |
| DigiKey | 1-800-344-4539 |
North America, South America, APAC, EMEA | Website |
| EBV Elektronik | EMEA | Website | |
| Farlink Technology China, Hong Kong | +86 13266922199 |
APAC | Website |
| Farnell | 1-800-936-198 +44 3447 11 11 22 |
EMEA | Website |
| Future Electronics | 1-800-675-1619 1-514-428-8470 |
North America, South America, APAC, EMEA | Website |
| Glyn | +49-6126-590-0 |
EMEA | Website |
| Hy-Line Germany Only | +49 89 614 503 0 |
EMEA | Website |
| Jetronic China, Hong Kong and Taiwan | 852-27636806 |
APAC | Website |
| M2M Germany | +49-6081-587386-0 |
EMEA | Website |
| Martinsson | +46 8 7440300 |
EMEA | Website |
| McCoy South East Asia | +65 6515 2988 |
APAC | Website |
| Mouser Electronics | 1-800-346-6873 +44 1494 427500 |
North America, South America, APAC, EMEA | Website |
| RS | +852-2421-9898 +44 3457-201201 |
North America, South America, APAC, EMEA | Website |
| Ryoyo Japan | +81-3-3543-7711 |
APAC | Website |
| Solsta UK Only | +44 (0) 1527 830800 |
EMEA | Website |
| Supreme Components International India, South East Asia | +65 6848-1178 |
APAC | Website |
| Symmetry Electronics | 1-866-506-8829 |
North America | Website |
| Tekdis Australia and New Zealand | +61 3 8669 1210 |
APAC | Website |
| Telsys | +972 3 7657666 |
EMEA | Website |
| WPG | +44 1628 958460 |
EMEA | Website |





/filters:background_color(white)/2024-09/223-00027.png)
/filters:background_color(white)/2024-09/223-00008.png)
/filters:background_color(white)/2024-09/223-00009.png)
/filters:background_color(white)/2024-10/IG60-BL654 Angle - Large.png)
/filters:background_color(white)/2024-10/IG60-BL654-LTE-Front-Angle-large1.png)