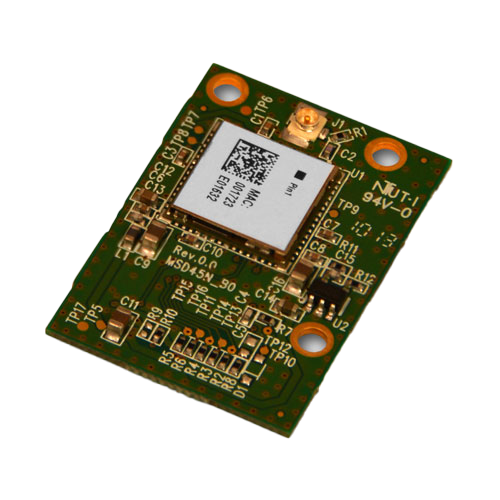
Overview
The Ezurio 45 series PCB-based MSD45N SDIO module combines low-power 802.11a/b/g/n WiFi with a complete software feature set, which is proven on mobile computers and other business-critical mobile devices that operate in harsh environments. No other Wi-Fi radio module can match the range, robust security, seamless mobility, and easy administration of the MSD45N module. Each MSD45N module delivers:
- Hardware: Minimized power consumption and broad operating temperature range
- Software: Enterprise-level security, fast and reliable roaming, and enterprise administration
- Certifications: Regulatory and Wi-Fi Alliance certifications. The MSD45 module is backed by a full set of support services including system integration support, regulatory process assistance, and technical support from product and Wi-Fi experts.
Buy Now
Specifications
| Part Number | Price @ 1K | Antenna Options | Antenna Type | Chipset (Wireless) | Dimension (Height - mm) | Dimension (Length - mm) | Dimension (Width - mm) | Frequency Range (Max) | Frequency Range (Min) | Frequency Range 2 (Max) | Frequency Range 2 (Min) | Logical Interfaces | OS/Software | Product Type | System Architecture | Technology | Wi-Fi Interfaces |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
MSD45N EOL Buy Options | N/A | External | QCA AR6003 | 3.38 mm | 32 mm | 22 mm | 2495 MHz | 2400 MHz | 5825 MHz | 5150 MHz | SDIO | Linux, Android | Embedded Module | Hosted | 802.11abgn | 1x1 SISO (Single Input, Single Output) | |
SSD45N EOL Buy Options | N/A | External | QCA AR6003 | 1.3 mm | 11 mm | 11 mm | 2495 MHz | 2400 MHz | 5825 MHz | 5150 MHz | SDIO | Linux, Android | Embedded Module | Hosted | 802.11abgn | 1-bit or 4-bit Secure Digital I/O | |
WH-MSD45N EOL Buy Options | N/A | U.FL Connector (x1) | External | QCA AR6003 | 2495 MHz | 2400 MHz | 5825 MHz | 5150 MHz | SDIO | Linux, Android | Embedded Module | Hosted | 802.11abgn | ||||
WH-SSD45N EOL Buy Options | N/A | External | QCA AR6003 | 2495 MHz | 2400 MHz | 5825 MHz | 5150 MHz | SDIO | Linux, Android | Embedded Module | Hosted | 802.11abgn |
Documentation
Browse Application Notes, Certifications, Documentation and Software in our Support & Documentation Center.
What is the ITU code for Wi-Fi with WiFi/BT combo module?
Mode | ITU-Code |
2.4-2.4835GHz | - |
802.11b_Nss1,(1Mbps)_1TX | 12M2G1D |
802.11g_Nss1,(6Mbps)_1TX | 16M7D1D |
802.11n HT20_Nss1,(MCS0)_1TX | 17M9D1D |
802.11n HT40_Nss1,(MCS0)_1TX | 36M6D1D |
5.15-5.25GHz | - |
802.11a_Nss1,(6Mbps)_1TX | 16M4D1D |
802.11ac VHT20_Nss1,(MCS0)_1TX | 17M6D1D |
802.11ac VHT40_Nss1,(MCS0)_1TX | 36M2D1D |
802.11ac VHT80_Nss1,(MCS0)_1TX | 75M7D1D |
5.25-5.35GHz | - |
802.11a_Nss1,(6Mbps)_1TX | 16M4D1D |
802.11ac VHT20_Nss1,(MCS0)_1TX | 17M6D1D |
802.11ac VHT40_Nss1,(MCS0)_1TX | 36M2D1D |
802.11ac VHT80_Nss1,(MCS0)_1TX | 75M7D1D |
5.47-5.725GHz | - |
802.11a_Nss1,(6Mbps)_1TX | 16M4D1D |
802.11ac VHT20_Nss1,(MCS0)_1TX | 17M7D1D |
802.11ac VHT40_Nss1,(MCS0)_1TX | 36M2D1D |
802.11ac VHT80_Nss1,(MCS0)_1TX | 75M8D1D |
5.725-5.85GHz | - |
802.11a_Nss1,(6Mbps)_1TX | 16M4D1D |
802.11ac VHT20_Nss1,(MCS0)_1TX | 17M7D1D |
802.11ac VHT40_Nss1,(MCS0)_1TX | 36M2D1D |
802.11ac VHT80_Nss1,(MCS0)_1TX | 75M7D1D |
What is the ITU code for BT with WiFi/BT combo module?
Mode | ITU-Code |
2.4-2.4835GHz | - |
BT-BR(1Mbps) | 889KF1D |
BT-EDR(3Mbps) | 1M22G1D |
BT-LE(1Mbps) | 1M05F1D |
For SSD45N/MSD45N in Linux platform, if during the regulation test, need to adjust 3dB in 2.4G, how to set this number during the driver initialization so that the TX power will match what they test in regulation test?
SMU is the safest way to set it.
# smu_cli set tx-max-bg 6
# smu_cli get tx-max-bg
Reg Domain: WW
BG Antenna Adj: 3 dB
A Antenna Adj: 0 dB
Remember the value is in ½ db increments so you need to use 6 to get 3 dBm.
Also fw_setenv is able to set it as well.
rfPowerAtten2=6
# fw_printenv
...
usbnet_devaddr=de:ad:be:ef:00:01
md5_at91bs=75a5a900d8df5657ebc89796756eed70
md5_u-boot=cc8187cf4471832e51580a284df37f86
md5_kernel-a=300d5b9d93abaec368fb700933a95bdb
md5_rootfs-a=62e98ead848d552ab6199b6ed543dd4d
bootargs=console=ttyS0,115200 loglevel=4 rw noinitrd mem=64M rootfstype=ubifs root=ubi0:rootfs ubi.mtd=6
bootcmd=nand read 0x22000000 0x000e0000 0x00500000; bootm
rfPowerAtten2=6
What is the adjacent channel rejection for the MSD45/SSD45?
Adjacent Channel Rejection for 2.4 GHz Operation
Symbol
Parameter
Conditions
Min
Typ
Max
Unit
radj
Adjacent Channel Rejection
dB
CCK
2 Mbps
-
43
-
CCK
11 Mbps
-
37
-
OFDM
6 Mbps
-
37
-
OFDM
54 Mbps
-
21
-
HT20
MCS0
-
36
-
HT20
MCS7
-
20
-
HT40
MCS0
-
27
-
HT40
MCS7
-
7
-
Adjacent Channel Rejection for 5 GHz Operation
Symbol
Parameter
Conditions
Min
Typ
Max
Unit
Radj
Adjacent Channel Rejection
dB
OFDM
6 Mbps
-
26
-
OFDM
54 Mbps
-
12
-
HT20
MCS0
-
25
-
HT20
MCS7
-
7
-
HT40
MCS0
-
25
-
HT40
MCS7
-
8
-
Where can I find the SDK for the Enterprise Wi-Fi Radios?
Where can I find the SDK for the Enterprise Wi-Fi Radios? If there is no SDK available for download in the product's Software Downloads section then the SDK will be in the release .zip folder.
What is the step to load SD module in windows?
1) The SD host controller driver (their driver, not ours) detects that a device is on the SDIO bus and signals the SD bus driver (a Microsoft driver) 2) The SD bus driver enumerates the card to determine what device it is and what client driver needs to be loaded. The bus driver does this at a low clock frequency because it doesn?t yet know what bus speed the client device can support. Note that the host controller driver is the one that actually performs all accesses to the card as it is the one that manages the actual SDIO controller hardware on the host platform. The bus driver is accessing the card via the host controller driver. 3) The SD bus driver determines that our driver is the ?client driver? registered for the card by reading the vendor/product IDs from the card and looking up that information in the registry. Our driver is registered for that combination of VID/PID. 4) The bus driver loads the client driver, which in this case is our driver. 5) The client driver continues initialization, which includes accessing the card itself by making calls to the SD bus driver which passes those calls on to the host controller driver which implements the actual card access via the host controller itself in the host CPU. It?s important to note that the client driver (us) only requests that a card access be made; it is the host controller driver that implements the access via the host controller on the host CPU. 6) Very early in the initialization sequence the client driver (us) makes a call to the bus driver to configure the bus speed, bus width etc. The speed is the lower of what the card supports and what the host controller supports on that slot. From that point on, all accesses are occurring at a much higher bus speed. 7) The card continues initialization, which includes downloading the firmware and then enabling interrupts. From this point on, interrupts have to be working for the card to function properly.
For EAP tunnel authentication, what is the outer ID set in the packet?
By default, it will show annoSUMMIT as outer ID to protect the ID not showing in public. If really need to show the real ID in outer ID, then need to add semicolon (;) at the end of ID configuration to make it happen.
Does Ezurio Linux package support uClibc in 45 and 50 series?
No, Laird Linux package doesn't support uClibc in 45 and 50 series.
What is the meaning of autoProfile parameter when it is enabled?
Auto profile is to roam among multiple profiles you add into the auto profile list. You can add this by LCM or by registry as below. Auto Profile Registry Setting You can enable Auto Profile from the registry. Key autoProfile Path HKLM\Comm\SDCCF10G1\Parms\Configs\GlobalConfig Note: The HKLM\Comm\SDCCF10G1\Parms\Configs\... path is the same for all radios. Type DWORD Config01 is (by default) the default profile and cannot be used for auto profile. It must be set to 0. For example, if you want to automatically connect to Config02, Config05, and Config10, that would equal 10000100101 Convert that number to decimal which is 1061. The number 1061 would be entered as the value for the autoProfile key.
How to disable roaming in CE/WM platform?
Roaming cannot be disabled. You may set the roam trigger to the lowest RSSI value in the list which will cause the client to remain connected without scanning to roam until this very low RSSI is measured. However, beacon lost and some other situations may also trigger roam scan. On loss of association the client disregards the roam trigger, delta, and period and immediately begins scanning to re-associate as quickly as is possible. Roam Trigger The signal strength (RSSI) (in dBm) at which the radio scans for an access point with a better signal strength. When scanning for a different access point, the radio looks for one with a RSSI at the indicated roam delta dBm level or stronger. Key Roam Trigger Path HKLM\Comm\SDCCF10G1\Parms\Configs\GlobalConfig\RoamTrigger Note: The HKLM\Comm\SDCCF10G1\Parms\Configs\... path is the same for all radios. Value -50 (0x32) -55 (0x37) -60 (0x3c) -65 (0x41) -70 (0x46) -75 (0x4b) -80 (0x50) -85 (0x55) or Custom Default -70 Type DWORD
What's the relationship with UAPSD and WMEenabled in CE/WM platform? Should the 2 parameter use together?
WMM APSD stands for Wi-Fi Multimedia (WMM) Automatic Power Save Delivery. It is basically a feature mode that allows your mobile devices to save more battery while connected to your wifi network. So to use APSD, WMEenabled must be set. WMM Use of Wi-Fi Multimedia Extensions, also known as WMM. Key WMM Path HKLM\Comm\SDCCF10G1\Parms\Configs\GlobalConfig\WME Note: The HKLM\Comm\SDCCF10G1\Parms\Configs\... path is the same for all radios. Value (0) On (1) Off
Does Ezurio SDK support check certificate valid date?
Yes, we support certificate valid date checking, but need to enable bit 2 in suppInfo. unsignedlongsuppInfo - Meaning: Turn on or off other protocols. - Value: bit 0 is Summit FIPS on/off; bit 1 is reserved; bit 2 is CA cert date-check enable; bit 3 is pre 2014 WPA1 operation
What?s meaning of CA cert date-check?
We will check if the CA cert is out of date. If yes, have error code during the authentication process.
How to check full driver version in CE/WM platform?
The value that is in the CF10G_STATUS driverVersion field from SDK is not the complete, full driver version. It contains the A value in the upper 16 bits, the B value in the next 8 bits and the C value in the lowest 8 bits. In addition, there are some flags that are OR?ed in to the lower 16 bits. Overall, it is nearly useless as a driver version field but due to backwards combability issues so can?t be changed at this point. The driver writes its full version to the registry at boot as below. This is where the LCM gets the driver version,. [HKLM\Comm\SDCCF10G1\Parms] ?DriverFullVersion?
Who is responsible for providing the Bluetooth QDID for a host system?
The responsibility for providing the QDID for a host system is with the provider of the stack that is used on that system. If for instance the host system uses a module that requires the Bluetooth stack to run on that system (e.g. Lairds Sterling-LWB in a Linux platform) the QDID must be provided by the stack vendor who's stack is running on that Linux platform. Challenges might occur when an open-source, community based stack is used. If a module with integrated stack us used (e.g. Lairds BL652) the QDID is provided by the module vendor.
How can I control / switch between different WiFi modes on Ezurio WiFi modules in a Linux system? E.g. Access Point, Ad-hoc, Client, Wi-Fi direct/P2P when available?
All this can be controlled through standard Linux commands/programs like ?iw?, ?hostapd?, ?wpa_supplicant?, ?wpa_cli?, etc.
Do we recommend conformal coating your modules?
We highly do not recommend conformal coating the radio module. If you plan on encapsulating the radio module in a potting compound or conformal coating, you must assure that the compound in liquid or solid form does not enter under the shield where there are sensitive RF components. Some of the capacitive and inductance values are as low (pF and nH) and could be sensitive to contacting materials such as potting compounds. There are potting compounds and conformal coatings which have very good dielectric constants and are suitable for 2.4 GHz potting applications, however, when you apply any of these, they were not accounted for in the circuit design and might reduce performance of the device (or all together cause it not to function). You should run tests on their particular potting compound and evaluate radio's performance and range. Also, it's worth mentioning that applying any compound, conformal coating or potting directly to the module WILL void the warranty. If your application requires 100% sealing of the radio module, there is a way to do this very successfully without impacting the module performance. Simply place the module on your PCB. Place a plastic cover over the module (like a hat), make the cover large enough to cover the whole module. Apply glue around the bottom perimeter of the cover where it sits on the PCB. This allows the module to function in free air-space while there is a complete seal around it. This information is only for reference and we recommend you should conduct your own testing with your prototype of your end application to find the best suitable fit for your design.
How many reflows do you recommend for your modules?
We only recommend reflowing our modules once as it can damage the module and void the warranty.
Does Ezurio provide 3D files for modules?
Ezurio provides 3D files (STEP) files for most but not all of it's modules. Based on the nature of the information in the files, in most cases Laird requires a login to access these files as well as layout files and software/firmware downloads. As such, for most modules, the 3D files are found under the Software Downloads tab of the product page. The page offers a credentials request link for customers who need credentials. In most cases, the credentials are provided via return email within about 10 minutes. Please contact support if you have any additional questions or have any issues accessing our downloads.
What are the available CAD file formats?
Ezurio provides layout files PADS and PADS ASCII formats. The ASCII files will import to Altium (and Protel varients) as well as Cadence (Orcad and Allegro) CAD packages. As far as we know, there is no way to import to Eagle CAD. Please be sure to use the .asc file for PCB and the .txt file for the schematic when importing to Altium. Ezurio uses ORCAD for schematics (Gerbers).
What's the recommended process to clean modules?
The recommended cleanser is "hydrocarbon cleaning oil", which can be used to clean the RF shield and PCB. We do not recommend the use of alcohol as it doesn't work as well and could leave residue on the boards.
How do you keep the tray icon off permanently in CE/WM platform?
Setting the following registry to 0 can achieve this: HKLM\Comm\SDCCF10G1\Parms\Configs\GlobalConfig DWORD: trayIcon - 0 = Hide Icon - Non-0 = Show Icon
What build should be used for EN 301 893 1.8.1 and EN 301 893 1.7.1 testing?
For the 30AG, we recommend the 3.5.0.9 cab build or later for both test cases. For the 40NBT, use 3.4.13.36 cab build or later. As for the 45N, cab build from 3.5.1.6 can support both test cases.
Following WPA / WPA2 authenticated failure, scu_tray will pop up a message indicating authentication failure. How do I enable/disable this feature?
You can modify this feature by creating a new registry called ?NotifyAttempts? under ?hklm/software/Laird/ScuTray?, this allows you to disable / enable the pop-up message for WPA / WPA2 authentication and even set the number of attempts before notification. -DWORD: NotifyAttempts -Values: 0 (disabled); NOT 0 (the number of attempts before notification)
Are the roam settings used to switch between profiles within the auto profile list?
Yes, here is an example. 1. The auto profile list contains SSID_1 and SSID_2 2. Device is connected to SSID_1 3. RSSI drops below roam trigger, the radio scans for other APs and finds SSID_2 is a better candidate 4. The radio disconnects from SSID_1 and connects to SSID_2
How do I troubleshoot the status information in LCM / SCU?
For the 10, 15, 30, and 40 series, the status of the LCM / SCU can be in one of two states, "non-associated? and ?associated". Once the radio has associated with an AP, it will move from "non-associated? to ?associated". If WPA / WPA2 authenticates failure, the status will switch between "non-associated? and ?associated". If authentication occurs without an IP the radio cannot be identified from the status field -- you will need to check in the IP field. For the 45 and 50 series, the status in LCM / SCU can be in one of three states, "Not Associated", "Associated", and "Connected?. Associated with no IP is a valid state for our radios to attempt to reconnect with an invalid PSK. Once the radio has associated with an AP, it will move from "not associated? to ?associated". Only after the radio authenticates and has an IP will it move to the "Connnected" state. In the case of WPA or WPA2 authenticated failure or authentication without an IP the radios will remain in an "associated" state.
How do I set the 45 or 50 series to adhoc mode for a Linux platform?
You can use the following command to make adhoc mode work: sdc_cli profile adhoc add sdc_cli profile adhoc set ssid adhoc sdc_cli profile adhoc set mode adhoc sdc_cli profile adhoc activate sdc_cli status
Before LCM detects a Wi-Fi radio, how do I hard code the radio module it would use?
The radio chipset value is written by the driver when it loads, and indicates which radio is actually installed. LCM uses this value to determine some parameters that vary between radio types. If you want to hard code the Wi-Fi radio before the driver loads, you can do so with this registry: [HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE/Comm/SDCCF10G1/Parms/Configs/GlobalConfig] "RadioChipSet"=dword:00000006 The values for that registry key are in the sdc_sdk.h as follows: typedef enum _RADIOCHIPSET { RADIOCHIPSET_NONE = 0, RADIOCHIPSET_SDC10 = 1, //BCM4318 RADIOCHIPSET_SDC15 = 2, //BCM4322, RADIOCHIPSET_SDC30 = 3, //AR6002, RADIOCHIPSET_SDC40L = 4, //BCM4319, RADIOCHIPSET_SDC40NBT = 5, //BCM4329, RADIOCHIPSET_SDC45 = 6, //AR6003, RADIOCHIPSET_SDC50 = 7, //AR6004, } RADIOCHIPSET;
On the WEC2013 platform with Ezurio modules, should I use C or C sharp for the SDK?
Either C or C sharp can be used.
Does NDIS5 or NDIS6 run in Ezurio's WEC7 release?
NDIS5 runs Laird's WEC7 release.
How do I set the 45 or 50 series to AP mode on a Linux platform?
You can use this command in sdc_cli: "sdc_cli iface set hostapd wl on"
Can CE5 and CE6 support SHA-2?
No, the patch that supports SHA-2 is in the Windows Embedded Compact 7 Monthly Update (April 2016). Prior to that, the OS itself doesn't support it.
What is the difference between eap-mschapv2 and mschapv2 in EAP_TTLS?
With EAP-MS-CHAPv2, the data sent in tunnel will be encapsulated as EAP-MESSAGE AVP (attribute-value pair). In the case of MS-CHAPv2, there is no such extra encapsulation it is just the MS-CHAPv2 message.
What is the difference between WEP ON and WEP AUTO in the weptype setting for the Linux platform of the MSD45N?
WEP ON is for legacy Wi-Fi WEP with no WPA/WPA2 authentication. WEP AUTO is configured for a profile where you want to use 802.1x authentication with WEP encryption. Rather than setting WEP with a static key, WEP AUTO allows the WEP keys to be set dynamically following a successful EAP authentication.
Which EAP types Ezurio supports in CCKM?
CCKM is supported with all EAP types Laird supports?LEAP, EAP-FAST, PEAP-MSCHAPv2, PEAP-GTC, PEAP-TLS, EAP-TLS and EAP-TTLS. ACS supports all of the EAP types except EAP-TTLS. However, supporting CCKM is not dependent on using ACS as the RADIUS server. Laird can do CCKM with any RADIUS server since CCKM support is in the wireless infrastructure.
In what case need to set auth_type to AUTH_NETWORK_EAP in Linux platform with MSD45N?
The auth type of Network EAP is an 802.11 auth type that Cisco defined that basically indicates that open 802.11 authentication and association will be followed by EAP authentication. The possible 802.11 auth types Laird support are open (0x0), shared (0x1) or Network EAP (0x80). With Cisco autonomous access points, it is possible to configure an SSID where only an 802.11 auth type of Network EAP is allowed, but this configuration is discouraged by Cisco and they indicate that if Network EAP is configured on the infrastructure, Open authentication with EAP should also be configured on that same network. Network EAP is rarely used by anyone at this point, and Cisco always recommends that it never be the only 802.11 auth type configured on the infrastructure. Either Open or Network EAP can be used with LEAP or any enterprise EAP authentication type. The only time Network EAP must be used is if that is the only 802.11 auth type that is configured on the infrastructure, but it would be rare that anyone would configure the network in that way.
What EAP types does the WB45 support?
The WB45 supports the following EAP types: LEAP EAP-FAST PEAP-MSCHAPv1 PEAP-MSCHAPv2 PEAP-GTC EAP-TLS EAP-TTLS PEAP-TLS
How do I remove the BT or WiFi configuration/information in LCM?
In Config page, Status page, and Diags pages, by default both BT and WiFi configuration/information are shown in LCM. Either WiFi or BT configuration/information can be removed by the editing the following registries. [HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Summit\SCU] "Config"=dword:00000003 "Status"=dword:00000003 "Diags"=dword:00000003 1 = Show Wi-Fi only 2 = Show Bluetooth only 3 = Show Wi-Fi and Bluetooth.
How do I update the server certificate in the MSD45N/WB45N for Linux?
For the WB45N, the server certificate should be located under path ?/etc/ssl?. Use a USB storage drive or wget to upload the file to WB45N and copy this file to ?/etc/ssl? folder. You will need to reboot the system to take effect. For the MSD45N, this certificate can be changed by customers during their integration. By default, it?s located in ?/etc/ssl?.
As the PMKcaching, two options in the setting, standard or opmk. What is the definition of these two options?
Standard: indicates PMK Caching: This means that the 802.1x authentication can be skipped on an access point that a client has already authenticated to once before. Only the 4-way handshake needs to happen. This is useful for a client that needs to reconnect to an access point that it roamed away from previously, due to signal loss etc. However, if a client has not roamed to a particular access point during its current working session, it must then authenticate to that specific access point using 802.1x. PMK Caching is the method defined in the 802.11x (WPA/WPA2) specification. Opportunistic Key Caching: With this method, a client device can skip the 802.1x authentication with an access point after a full authentication,and only needs to perform the 4 way handshake when roaming to access points that are centrally managed by the same WLC in an LWAPP or other controller-based infrastructure. This means that the client doesn't need to authenticate with access points that it wants to roam to, as long as the client has authenticated successfully to at least one of the access points in the same zone as the access point that handled the previous successful authentication. In this case, the PMK identifier has been cached at a central location, like the WLC (or wireless switch.) With OKC, the client must support this method for it to be used, even if the infrastructure has been configured with OKC enabled.
What regulatory domains are supported in the MSD45N linux platform and the WB45N?
The default mode, REG_WW, will enable 802.11d. The following specific regulatory domains are supported: REG_FCC, REG_ETSI REG_TELEC REG_KCC, REG_CA, REG_FR, REG_GB, REG_AU, REG_NZ, REG_CN. The following regulatory domains are planned to be available in the near future. REG_BR (Brazil) REG_RU (Russia)
KCC domain
The attached document is the list current channels for the KCC domain as of 2015. In document, red means DFS required.
Current consumption for 40NBT and MSD45N
Current consumption for Wi-Fi radios at low power state(D3) 40NBT : 7.7 mA 45N : 200 uA note : this should be included in HIG (not only this but we should fill in all the TBD in HIG)
What connector types do your Wi-Fi radios support?
A list of our radios and supported connector types can be found here: WiFi + Bluetooth Modules
DFS channels in KCC
The following channels require DFS in Korea KCC/KC domain. Channel Frequency MHz 52 5260 56 5280 60 5300 64 5320 100 5500 104 5520 108 5540 112 5560 116 5580 120 5600 124 5620
How do I hide Wi-Fi or BT sections in LCM?
The following three registry keys should be set to show Wi-Fi or BT interface only. [HKLM\SOFTWARE\Summit\SCU] DWORD: Status (= 3 by default) [HKLM\SOFTWARE\Summit\SCU] DWORD: Config (= 3 by default) [HKLM\SOFTWARE\Summit\SCU] DWORD: Diag (= 3 by default) value: 1 - Show Wi-Fi Only 2 - Show Bluetooth Only 3 - Show Both If you want to show Bluetooth only in LCM, you should set all the above three registry keys to 1.
What is the difference between sdcgina.exe and sdc_gina.exe?
sdcgina.exe vs sdc_gina.exe : sdcgina.exe spawns all of the components we need (e.g. supplicant, scutray). sdc_gina.exe is a UI application that, for example, pops up when the credentials must be input.
Does Ezurio recommend ways to suspend/resume for Wi-Fi radios?
Method 1: Radio driver is asked by power manager to go to low power state Suspend/resume without cutting power to radio Method 2: Radio driver is asked by power manager to go to low power state Cut power to radio Suspend/ Resume Reapply power to radio Eject/insert radio Note 1: Method 1 is the simplest way to deal with suspend/resume, but the OEM needs to consider the current consumption of the radio at a low power state. For example, current consumption for the 40NBT is 7.7mA and for the 45N it is 200uA. Note 2 : In general, method 1 is more recommended because method 2 may cause a delay to make the radio reconnect after resume.
What are the reasons for the null packets in an RF trace?
There are two reasons to send out null packets with p bit enabled. 1. Its RSSI has crossed over the Roam Trigger and the client radio is supposed to start scanning for a new AP. 2. The client radio is running one of our power-save modes (Fast or Max) and is going to sleep for a brief (e.g. 20 ms) period and is telling the AP so it will buffer traffic for it while it sleeps. After a radio has slept for some period of time (defined as the interval between DTIM periods) it is supposed to wake up and indicate to the AP that it is awake by sending a null packet with the P-bit turned off. The radio should only wake if it has traffic to send or it sees from the DTIM in the AP?s beacons that the AP has traffic to send to it.
What kind of certificate format do we support in Ezurio Linux platform?
For user certs, we support PKCS#12 (.pfx/.p12) or PEM (.pem). In both cases, the cert needs to contain both the user certificate and the user encryption key. For CA certs we support both the PEM (.pem) and DER (.der) format.
In EAP-TLS, there is a setting of username. What is the purpose of it? Will it be used during the authentication? Does it need to be the same as in CA?
EAP-TLS is a tunnel authentication. outer identity: this is the User-Name in the RADIUS packet and visible to all intermediate parties inner identity: this is the actual user identification. It is only visible to the user himself and the Identity Provider The user cert is issued to a user identified by the username, so the username has to be configured so we know which user cert we should be using for the authentication. By default, the username is also used during authentication as the outer identity which gets sent in the identity response packet.
mandatory/optional input for EAP type
mandatory/optional input for EAP type EAP credentials Mandatory input Optional input LEAP User name, user password EAP FAST User name, user password PAC file, FAC password PEAP MSCHAP User name, user password CA cert PEAP GTC User name, user password CA cert EAP TLS User name, user cert CA cert EAP TTLS User name, user password CA cert PEAP TLS User name, user cert CA cert Note 1: this settings should be read in user perspective but not for actual implementation. For example, when a user does not input PAC file, it will use auto PAC provisioning. If a user inputs it, it will do a manual PAC provisioning. Note 2: user password is not used for TLS but only user cert is used instead.
Become an Ezurio Customer to Gain Exclusive Access to Our Design Experts
- Antenna Scans
- Antenna selection and placement
- Custom antenna design
- Worldwide EMC testing / certifications
- Embedded RF hardware / firmware design
- Cloud architecture and integration
- Mobile application development
- Product & Industrial Design
Distributors
| Distributor | Phone Number | Region | Website |
|---|---|---|---|
| Arrow Electronics | 1-855-326-4757 +44 2039 365486 |
APAC, North America, South America, EMEA | Website |
| Braemac Australia, New Zealand, South East Asia | +61 2 9550 6600 +64 9 477 2148 |
APAC | Website |
| DigiKey | 1-800-344-4539 |
North America, South America, APAC, EMEA | Website |
| EBV Elektronik | EMEA | Website | |
| Farlink Technology China, Hong Kong | +86 13266922199 |
APAC | Website |
| Farnell | 1-800-936-198 +44 3447 11 11 22 |
EMEA | Website |
| Future Electronics | 1-800-675-1619 1-514-428-8470 |
North America, South America, APAC, EMEA | Website |
| Glyn | +49-6126-590-0 |
EMEA | Website |
| Hy-Line Germany Only | +49 89 614 503 0 |
EMEA | Website |
| Jetronic China, Hong Kong and Taiwan | 852-27636806 |
APAC | Website |
| M2M Germany | +49-6081-587386-0 |
EMEA | Website |
| Martinsson | +46 8 7440300 |
EMEA | Website |
| McCoy South East Asia | +65 6515 2988 |
APAC | Website |
| Mouser Electronics | 1-800-346-6873 +44 1494 427500 |
North America, South America, APAC, EMEA | Website |
| RS | +852-2421-9898 +44 3457-201201 |
North America, South America, APAC, EMEA | Website |
| Ryoyo Japan | +81-3-3543-7711 |
APAC | Website |
| Solsta UK Only | +44 (0) 1527 830800 |
EMEA | Website |
| Supreme Components International India, South East Asia | +65 6848-1178 |
APAC | Website |
| Symmetry Electronics | 1-866-506-8829 |
North America | Website |
| Tekdis Australia and New Zealand | +61 3 8669 1210 |
APAC | Website |
| Telsys | +972 3 7657666 |
EMEA | Website |
| WPG | +44 1628 958460 |
EMEA | Website |






/filters:background_color(white)/2024-11/NANOBLADE1.png)
/filters:background_color(white)/2024-12/EMF2471.png)
/filters:background_color(white)/2024-12/ANT-DS-NanoBlue-Main-Image.png)
/filters:background_color(white)/2024-12/MSD45N.png)
/filters:background_color(white)/s3fs-public/2018-10/ssd45n-small.jpg)